Last First Period Date Chemistry 2 a, b, c Biological, chemical, and
advertisement
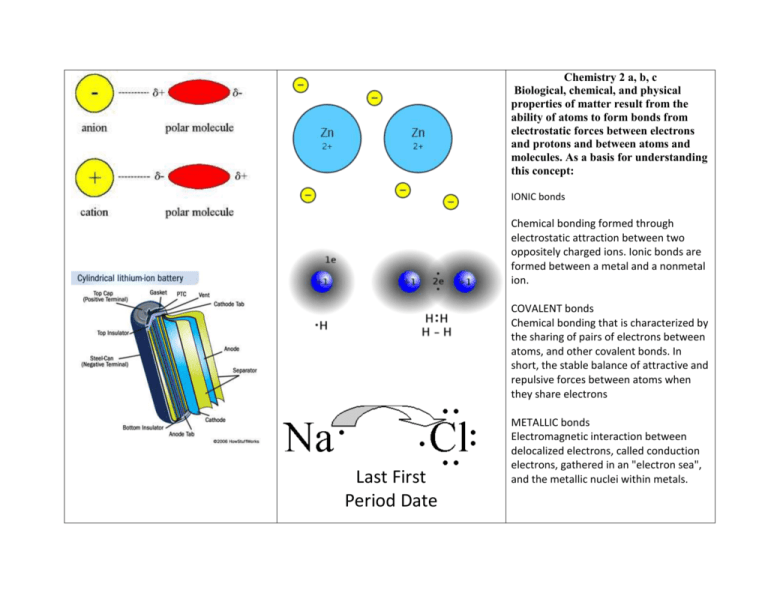
Chemistry 2 a, b, c Biological, chemical, and physical properties of matter result from the ability of atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. As a basis for understanding this concept: IONIC bonds Chemical bonding formed through electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions. Ionic bonds are formed between a metal and a nonmetal ion. COVALENT bonds Chemical bonding that is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms, and other covalent bonds. In short, the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons Last First Period Date METALLIC bonds Electromagnetic interaction between delocalized electrons, called conduction electrons, gathered in an "electron sea", and the metallic nuclei within metals. CH 2. a. Students know atoms combine to form molecules by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchanging electrons to form ionic bonds. CH 2. b. Students know chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as H2, CH4, NH3, H2CCH2, N2, Cl2, and many large biological molecules are covalent. What is the difference between an ionic and a molecular compound? 2 H2(g) + O2(g) → 2 H2O(l) + 572 kJ (286 kJ/mol) Ionic compounds are between metals and nonmetals. Molecular (covalent) compounds are between only non-metals. (Metallic compounds are between metals and other metals) An ionic compound is a pure substance that is formed from a metal and a nonmetal. It has a fairly high melting point and is a conductor of electricity when in a molten or aqueous state. A molecular compound, on the other hand, is a pure substance that is formed from nonmetals. It has a fairly low melting point, and cannot conduct electricity regardless of state. Another important difference between the two is that an ionic compound is a crystalline solid at standard temperature and pressure (STP), whereas a molecular compound can be in a solid, gas or liquid state at STP. CH 2. c. Students know salt crystals, such as NaCl, are repeating patterns of positive and negative ions held together by electrostatic attraction. Chloride and sodium ions, the two major components of salt, are needed by all known living creatures in small quantities. Salt is CH4 + O2 → CO + H2 + H2O involved in regulating the water content (fluid balance) of the body. However, too 2 NH4Cl + 2 CaO → CaCl2 + Ca(OH)2 + 2 much salt increases the risk of health NH3 problems, including high blood pressure. H2CCH2 This compound is the simplest form of an alkene (a hydrocarbon that contains a carbon carbon double bond) called ethene or ethylene 6 Li + N2 → 2 Li3N 3 Mg + N2 → Mg3N2 Cl2 + H2O HCl + HClO