Structures of Life the Big Ideas
advertisement
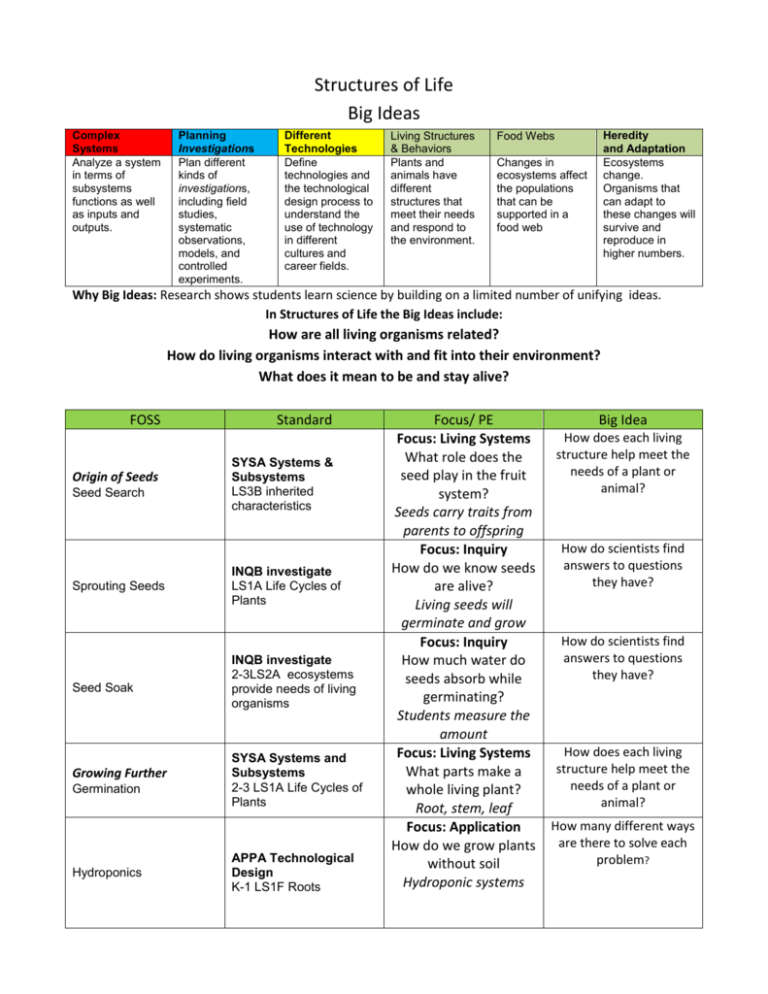
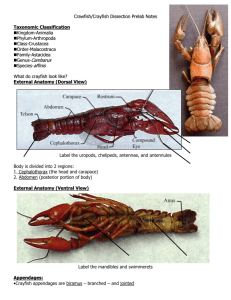
Structures of Life Big Ideas Complex Systems Analyze a system in terms of subsystems functions as well as inputs and outputs. Planning Investigations Plan different kinds of investigations, including field studies, systematic observations, models, and controlled experiments. Different Technologies Define technologies and the technological design process to understand the use of technology in different cultures and career fields. Living Structures & Behaviors Plants and animals have different structures that meet their needs and respond to the environment. Heredity and Adaptation Ecosystems change. Organisms that can adapt to these changes will survive and reproduce in higher numbers. Food Webs Changes in ecosystems affect the populations that can be supported in a food web Why Big Ideas: Research shows students learn science by building on a limited number of unifying ideas. In Structures of Life the Big Ideas include: How are all living organisms related? How do living organisms interact with and fit into their environment? What does it mean to be and stay alive? FOSS Origin of Seeds Seed Search Sprouting Seeds Seed Soak Growing Further Germination Hydroponics Standard SYSA Systems & Subsystems LS3B inherited characteristics INQB investigate LS1A Life Cycles of Plants INQB investigate 2-3LS2A ecosystems provide needs of living organisms SYSA Systems and Subsystems 2-3 LS1A Life Cycles of Plants APPA Technological Design K-1 LS1F Roots Focus/ PE Focus: Living Systems What role does the seed play in the fruit system? Seeds carry traits from parents to offspring Focus: Inquiry How do we know seeds are alive? Living seeds will germinate and grow Focus: Inquiry How much water do seeds absorb while germinating? Students measure the amount Focus: Living Systems What parts make a whole living plant? Root, stem, leaf Focus: Application How do we grow plants without soil Hydroponic systems Big Idea How does each living structure help meet the needs of a plant or animal? How do scientists find answers to questions they have? How do scientists find answers to questions they have? How does each living structure help meet the needs of a plant or animal? How many different ways are there to solve each problem? FOSS Life Cycle of the Bean Standard INQ Investigations 2-3 LS1A Life Cycles of Plants Meet the Crayfish SYSA Systems & Subsystems 4-5 LS1B Structures have Functions Crayfish Habitat 2-3 LS2A Habitat 2-3 LS2B Habitats change Crayfish at Home INQB Investigate 4-5 LS1C Response to Environment INQB Investigate Crayfish Territory Land Snails Land Snails at Home 4-5 LS1B Behaviors have Functions APPA Technological Design 2-3 LS2A Habitat Crayfish & Snails INQB Investigate 4-5 LS1B Structures have Functions Snail Pull INQB Investigate 2-3 PS1B Force 2-3 PS1C Size of Force 2-3 PS1D Comparing Force Choose your own Investigation INQB Investigate Focus/ PE Focus: Life Cycles What happens during a plants life cycle? Germination, growth, reproduction Focus: Living Structures How do crayfish parts keep it alive? Parts are linked to living functions Focus: Ecosystems How can we model a crayfish habitat? Water, food, shelter Focus: Living Behaviors How do behaviors help animals survive? Water, food, shelter Focus: Inquiry How do scientists learn about crayfish? Observing & recording about crayfish in the field and lab? Focus: Ecosystems What does a snail need to stay alive? Food, water, shelter Focus: Living Structures How can different living structures provide the same need? Parts are linked to living functions INQB Investigate How do we measure the strength of a snail? experiment INQB Investigate Students plan investigations Big Idea Do all plants and animals have a life cycle? How does each living structure help meet the needs of a plant or animal? What happens to plants and animals when their environment changes? How does each living behavior help meet the needs of a plant or animal? Parts are linked to living functions Where do snails get the things they need to stay alive? How does each living structure help meet the needs of a plant or animal? How do scientists find answers to questions they have? How do scientists find answers to questions they have?