Grade 9 and 10 Literary Terms
advertisement

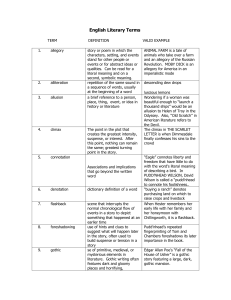
Grade 9 Literary Terms Analogy - a comparison between two things, typically on the basis of their structure and for the purpose of explanation or clarification. Denotation - the literal or primary meaning of a word, in contrast to the feelings or ideas that the word suggests. Connotation - an idea or feeling that a word invokes in addition to its literal or primary meaning. Mood - evokes certain feelings or vibes in readers through words and descriptions. Repetition - the action of repeating something that has already been said or written. Symbolism - the use of symbols to represent ideas or qualities. Grade 10 Literary Terms Character Development - The process of creating a character's background, physicality, appearance, and personality. Irony - the expression of one's meaning by using language that normally signifies the opposite, typically for humorous or emphatic effect. Satire - the use of humor, irony, exaggeration, or ridicule to expose and criticize people's stupidity or vices, particularly in the context of contemporary politics and other topical issues. Sarcasm - the use of irony to mock or convey contempt. Syntax - the arrangement of words and phrases to create wellformed sentences in a language. Voice - the distinctive style or manner of expression of an author or narrator. Poetry Terms Rhyme - The occurrence of the same or similar sounds at the end of two or more words. Meter/rhythm - The arrangement of a line of poetry by the number of syllables and the rhythm of accented (or stressed) syllables. Alliteration - The repetition of initial sounds. I.e. Seven steaks sizzled Stanza - Two or more lines of poetry that together form one of the divisions of a poem. The stanzas of a poem are usually of the same length and follow the same pattern of meter and rhyme. Poet vs. Speaker - The speaker of a poem is not always the poet. A poem is a crafted performance, a portrayal, or a dramatization similar to a play. The speaker is a created character. Free verse - Poetry composed of either rhymed or unrhymed lines that have no set meter Form - The structural components of a poem e.g. stanza pattern, metre, syllable count etc Lyric - A poem, such as a sonnet or an ode, that expresses the thoughts and feelings of the poet. A lyric poem may resemble a song in form or style. Assonance - the repetition of the sound of a vowel or diphthong in nonrhyming stressed syllables near enough to each other for the echo to be discernible (e.g., penitence, reticence ). Consonance - the recurrence of similar sounds, especially consonants, in close proximity Rhyme Scheme - the ordered pattern of rhymes at the ends of the lines of a poem or verse. Ballad - a poem or song narrating a story in short stanzas. Sonnet - a poem of fourteen lines using any of a number of formal rhyme schemes, in English typically having ten syllables per line. Metonymy - a figure of speech that consists of the use of the name of one object or concept for that of another to which it is related The given lines are from Shakespeare’s “Julies Caesar” Act I. “Friends, Romans, countrymen, lend me your ears.” Soliloquy - an act of speaking one's thoughts aloud when by oneself or regardless of any hearers, especially by a character in a play.