Graphs_1
advertisement
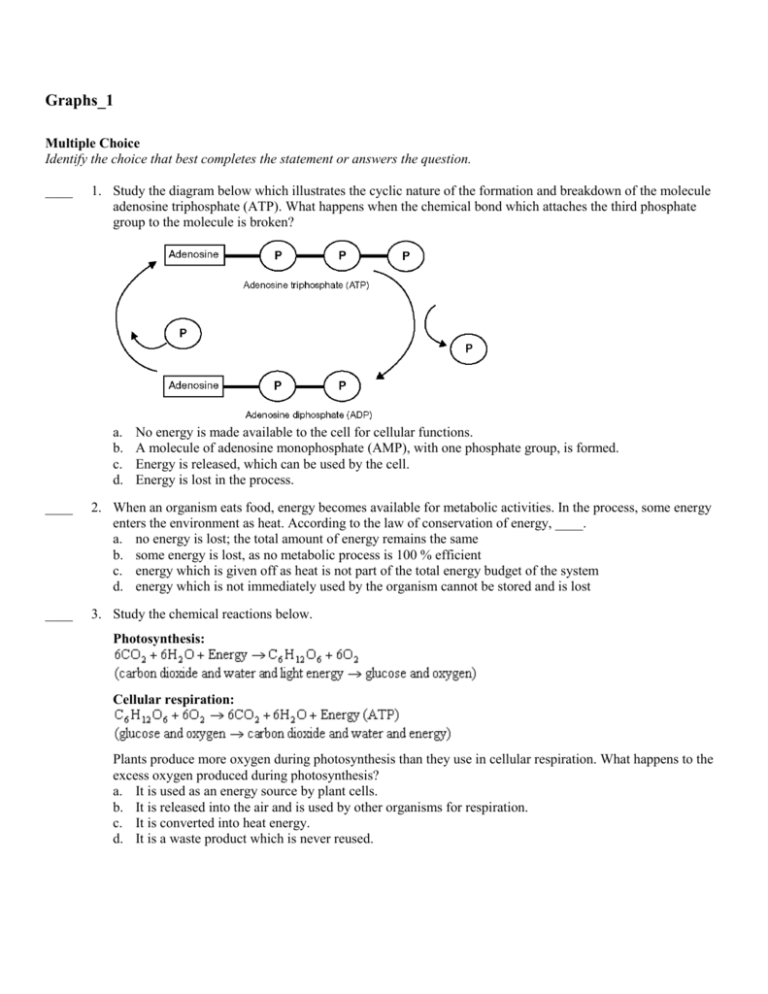
Graphs_1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Study the diagram below which illustrates the cyclic nature of the formation and breakdown of the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). What happens when the chemical bond which attaches the third phosphate group to the molecule is broken? a. b. c. d. No energy is made available to the cell for cellular functions. A molecule of adenosine monophosphate (AMP), with one phosphate group, is formed. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. Energy is lost in the process. ____ 2. When an organism eats food, energy becomes available for metabolic activities. In the process, some energy enters the environment as heat. According to the law of conservation of energy, ____. a. no energy is lost; the total amount of energy remains the same b. some energy is lost, as no metabolic process is 100 % efficient c. energy which is given off as heat is not part of the total energy budget of the system d. energy which is not immediately used by the organism cannot be stored and is lost ____ 3. Study the chemical reactions below. Photosynthesis: Cellular respiration: Plants produce more oxygen during photosynthesis than they use in cellular respiration. What happens to the excess oxygen produced during photosynthesis? a. It is used as an energy source by plant cells. b. It is released into the air and is used by other organisms for respiration. c. It is converted into heat energy. d. It is a waste product which is never reused. ____ 4. Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is an adenosine molecule with three phosphate groups attached. When it breaks down to form adenosine diphosphate, or ADP, the chemical bond between the second and third phosphate groups is broken. Which of these processes results in a release of energy? a. b. c. d. forming an ADP molecule from the breakdown of an ATP molecule forming an ATP molecule by adding a phosphate group to an ADP molecule Energy is not released in any part of this cycle. Both processes result in a release of energy. ____ 5. Four major groups of organic compounds are particularly important to living things. Most life processes rely on molecules from one or more of these groups. To which group do RNA molecules belong? a. nucleic acids c. lipids b. carbohydrates d. proteins ____ 6. Which of the following statements about enzymes is true? a. Enzymes speed the reactions which occur during food digestion. b. Enzymes always slow the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. c. Enzymes change the amount of product created during a chemical reaction. d. Only a small number of the body's metabolic processes involve enzymes. ____ 7. Nitrogen is found in a variety of forms in living things and in the environment. Molecules include N2, a diatomic molecule, and NH3, ammonia. Other forms include NO3-, or nitrate, and -NH2, an amino group. Which of these forms is produced by nitrogen fixation? a. ammonia c. nitrate b. amino group d. diatomic nitrogen ____ 8. Cell organelles carry out specific metabolic processes. Which cell organelles manage the process by which worn out organelles¸ food particles¸ and engulfed viruses or bacteria are digested? a. ribosomes c. vacuoles b. lysosomes d. Golgi bodies ____ 9. Jackson is growing a bean plant in a pot. One day Jackson notices that the plant is wilting. He waters the bean plant and within a few minutes the plant begins to perk up. This is because the plant has taken up water by osmosis. At what structural level does osmosis occur? a. organs c. cells b. tissues d. organ systems ____ 10. Certain types of biomolecules are crucial to a variety of life processes and body structures. One of these types of molecules are carbohydrates, which are ____. a. organic compounds used by cells to store and release energy b. insoluble in water and are used by the body for energy storage and insulation c. complex biomolecules that store genetic information d. substances that increase the OH- concentration of a solution Guard cells are pairs of cells that surround stomata, which are small openings or pores in the leaf. Guard cells control the opening and closing of the stomatal pores. ____ 11. Read the information above. The guard cells determine whether or not the stomatal pores are open. When guard cells absorb water, they swell, and the pores open. When guard cells lose water, they shrink, and the pores close. When stomata are open the plant loses water through the pores in a process known as transpiration. What is the most likely effect on the plant if the guard cells stay swollen on a hot day? a. The plant will turn yellow. c. The plant will lose its leaves. b. The plant will wilt. d. The plant’s roots will grow. ____ 12. Refer to the information above. Guard cells from a tomato plant are kidney-bean shaped. Which cell type would you expect to look most similar to tomato guard cells? a. root cells from a tomato plant b. guard cells from a marigold plant c. leaf palisade cells from a tomato plant d. stem cells from a corn plant ____ 13. Ling is doing an experiment on some bean plants. She is growing two bean plants (A and B) under fluorescent lights. Plant A and plant B both receive the same amount of water and light, but plant B sits in front of a blowing fan for an hour every day. Plant A is kept far away from the fan. After two weeks Ling looks at the plants under a microscope. She notices that the stem cells in plant B have thicker cell walls than the stem cells in plant A. What can you conclude about this experiment? a. b. c. d. Cell walls are involved in water transport in plants. Cell walls contain chlorophyll. Cell walls undergo photosynthesis. Cell walls help support plants. ____ 14. Suzanne is looking at muscle tissue using a microscope. She notices that cells from a stomach muscle (A) do not look striped, while tissue from leg muscle appears to be striped (B). What is the reason that the two tissue types look different? a. b. c. d. The stomach muscle is full of dividing cells. Stomach muscle functions differently than leg muscle. The stripes in the leg muscle do not relate to its function. The two muscles have similar functions despite their appearance. ____ 15. Specific biomolecules serve various functions in the body. Identify the molecule which is broken down during respiration forming water and carbon dioxide releasing energy. a. deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) b. glucose c. nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) d. hemoglobin ____ 16. A special type of cell division, called meiosis, is used to form sex cells or gametes. Which statement is true about this type of cell division? a. The products of meiosis are two identical cells. b. DNA is not copied at all during meiosis. c. The new cells have half the DNA of the parent cell. d. Meiosis is complete after only one round of cell division. ____ 17. Which of the following correctly shows a complementary base pair of nitrogenous bases in a DNA molecule? a. adenine - guanine c. cytosine - adenine b. guanine - cytosine d. guanine - thymine ____ 18. DNA is a polymer which is made up of subunits called nucleotides. Nucleotides have three basic parts. Which of these is not a nucleotide component? a. deoxyribose sugar c. ribose sugar b. phosphate group d. nitrogenous base ____ 19. A nitrogenous base is an important component of the nucleotides making up DNA. Which of the following correctly lists the four possible nitrogenous bases in DNA? a. adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil b. leucine, proline, tyrosine, phenylalanine c. glutamine, proline, tyrosine, phenylalanine d. adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine ____ 20. RNA molecules use instructions from DNA to assemble proteins. There are three types of RNA molecules: mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA. What specific function does mRNA perform in the process of making proteins? a. It brings instructions from DNA in the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm. b. It clamps onto messenger RNA and uses its information to assemble amino acids. c. It transports amino acids to the ribosomes to be assembled into proteins. d. It creates another molecule of DNA through replication. ____ 21. In order for DNA instructions to move from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm of a cell, an RNA copy of a DNA strand must be made. This process, which takes place in the cell nucleus, is called ____. a. translation c. mutation b. DNA replication d. transcription ____ 22. The chart below shows the ten countries which had the largest oil reserves in 2002. How was this data collected to ensure a lack of bias? 2002 Rank 1 2 3 4 5 a. b. c. d. Country Saudi Arabia Iraq Iran Kuwait United Arab Emirates Greatest Oil Reserves by Country, 2002 2002 Proved Reserves 2002 Country (billions of barrels) Rank 261.7 6 Russia 115.0 7 Venezuela 99.1 8 Libya 98.9 9 Nigeria 62.8 10 China 2002 Proved Reserves (billions of barrels) 53.9 50.2 30.0 30.0 29.5 Only the largest countries in each major region were surveyed. Countries in Northern Europe were not included in the data collection process. Countries with proved oil reserves of any amount were included in the survey. Only countries in Africa and Asia were included in the data collection process. ____ 23. The chart below shows how the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in Earth’s atmosphere changed between 1935 and 1994. This data shows that ____. Global Levels of Atmospheric CO2 Global Atmospheric CO2 Year Concentration (parts per million) 1935 306.6 1949 311 1958 312 1965 318 1974 330.1 1984 344.3 1994 358.8 a. b. c. d. the burning of fossil fuels causes global warming global atmospheric CO2 increased steadily between 1935 and 1994 human activities are causing CO2 levels to rise CO2 levels will continue to rise indefinitely ____ 24. The circle graph below shows the percentages of water which are used for various activities in the United States. Which statement about the use of water in the United States is false? a. b. c. d. More water is used for agricultural purposes than for any other reason. Water use by the public and industry combined does not surpass that used in agriculture. Industrial use of water is greater than the amount used to cool power plants. Cooling power plants and agricultural use accounts for more than 75% of water use. Rita conducted an experiment which involved placing a thermometer in each of four identical beakers containing four unknown liquids, each of equal volume. All four beakers had just been removed from an oven maintained at 92 degrees Celsius (°C) where they had been for the previous one hour. They were placed on a lab table in a room that was maintained at a constant 22°C. Rita recorded the temperatures read on the four thermometers every 15 minutes (min.) for one hour. The data collected is in the following table: Liquid Temperatures in degrees Celsius (°C) Liquid A B 0 min. 92 92 15 min. 82 73 30 min. 70 51 45 min. 64 39 60 min. 50 22 C 92 77 65 56 40 D 92 77 65 56 40 ____ 25. Referring to the above data from Rita’s experiment, which liquid had the greatest temperature change during the 60 minutes? a. A c. B b. C d. D ____ 26. The table below shows how the world population has changed between 1950 and 2000. Which statement about this data is TRUE? Total Midyear World Population, 1950 - 2000 Year Population 1950 2,555,078,074 1960 3,039,332,401 1970 3,707,610,112 1980 4,456,705,217 1985 4,854,602,890 1990 5,283,755,345 1995 5,690,865,776 2000 6,080,141,683 a. b. c. d. Between 1950 and 2000¸ the overall world birth rate exceeded the death rate. World population showed a steady decline between 1950 and 2000. Between 1950 and 2000¸ the overall world death rate exceeded the birth rate. Between 1950 and 2000¸ the overall world birth and death rates were roughly equal. ____ 27. A researcher who wants to learn about the behavior of a particular gas examines the relationship between temperature and gas volume when the gas is held at a constant pressure. The graph below shows the data collected. What would the data show if the temperature were decreased to 100 Kelvin? Kelvin Temperature vs. Volume 800 700 (348, 703) Volume (mL) 600 (273, 551) 500 400 (198, 400) 300 200 100 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 Temperature (Kelvin) a. b. c. d. The volume would decrease. The volume would not change. The volume would increase rapidly¸ then decrease. The volume would increase. ____ 28. Study the chart below which gives information about Group 1A elements, the alkali metals. Which statement about the data is TRUE? Element Lithium Sodium Potassium Rubidium Cesium Francium a. b. c. d. Group 1A Elements Symbol Atomic Mass Number Number Li 3 7 Na 11 23 K 19 39 Rb 37 85 Cs 55 133 Fr 87 223 Melting Point (°C) 180.5 97.8 63.2 39.5 28.4 27.0 There is a relationship between atomic number and melting point of Group 1A elements. Group 1A elements have low boiling points. Alkali metals have high melting points. There is no pattern evident in the data. Numeric Response The graphs below show how the number of acorns produced by oak trees in a forest determines the yearly population of squirrels. Population (% of Peak) Yearly Population Cycles of Squirrels and Acorns Squirrels Acorns 1997 1998 1999 2000 Year 2001 2002 Acorns Needed to Support Squirrel Population 600 Number of Squirrels 500 400 300 200 100 10000 20000 30000 40000 50000 60000 Number of Acorns 29. Refer to the graphs above. How many squirrels could be supported by 40¸000 acorns? 30. Refer to the data above. If the acorn population increased from 10¸000 in the first year to 40¸000 in the second year, how many more squirrels could be fed in the second year than in the first? 31. Study the graphs above. The peak in squirrel population in the year 2001 was most likely caused by a peak in acorn production in what year? 32. Coral bleaching is a phenomenon that happens when part of a coral reef dies and turns white. One factor that causes coral bleaching is a change in water temperature. Coral reefs are more likely to bleach when the temperature of the surrounding water goes above 29°C. The chart below shows the fluctuation of water temperature during the month of March for different years in a coral reef. Average March Water Temperatures Degrees Celcius (°C) 30 28 26 24 1995 1997 Year 1999 In what year was bleaching most likely to occur? A meadow habitat has the following food chain: grasses—grasshoppers—birds—owls The grasses have 100% of the energy. As energy moves through the food chain, there is a 50% drop in available energy with each change in organism. 33. Refer to the information above. The amount of energy the birds will have is ____ percent. 34. Refer to the information above. What percent of energy is available to the primary consumer? The Calorie (C) is a unit used by nutritionists to measure how much energy you get from various foods. One nutritional Calorie equals about 4.184 kilojoules (kJ). 35. Refer to the information above. How much energy does 325 Calories supply for the body? Answer to the nearest whole kilojoule. 36. Refer to the data above. Some foods contain more Calories than others. One gram (g) of fat, for example, contains approximately nine Calories. How much energy is supplied to the body by 3.5 grams of fat? Answer to the nearest whole kilojoule. 37. Jin conducts an experiment to determine the pH of some common substances. The graph below shows the data she collected. Based on this data, what is the pH of detergent? Oven Cleaner pH of Common Household Substances 16 15.5 15 14.5 14 13.5 13 12.5 Detergent 12 11.5 11 10.5 10 9.5 9 8 7.5 Milk Water pH 8.5 7 Coffee 6.5 6 4 3.5 3 2.5 Lemon Juice 5 4.5 Vinegar 5.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 Common Household Substances 38. The graph below shows the relationship between the germination percentage of a certain type of seed and the amount of time the seeds are exposed to cold temperatures. What percentage of seeds will germinate after being exposed to cold temperatures for 5 months? Seed Germination Rate Following Exposure to Cold Temperatures 80 75 70 65 Percent Germination 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 1 2 3 4 5 M onths Exposed to Cold Temperatures 39. The table below shows the relationship between the melting point of Group 1A elements and atomic number. What is the melting point in degrees Celsius (ºC) of potassium (K), which has atomic number 19? Melting Point in °C of Group 1A Elements Element Melting Point (ºC) Lithium (Li) 181 Sodium (Na) 98 Potassium (K) 63 Rubidium (Rb) 40 Cesium (Cs) 28 Francium (Fr) 27 40. Michael compared soil samples which were collected from six different locations across the United States. The data table below shows the observations he made about the relative silt, sand, and clay content of each sample. What percentage of soil sample number 6 is composed of clay? Silt, Sand, and Clay Content of Soil Samples Soil Percent Percent Percent Sample Silt Sand Clay 1 2 3 4 5 6 25 10 35 65 50 10 70 30 10 20 35 20 5 60 55 15 15 70 41. Jake uses the common objects shown in the chart below to determine the hardness of five unknown minerals. Mineral number 1 can be scratched by a piece of copper¸ but a fingernail will not scratch it. What is the hardness of this mineral? Hardness of Common Objects Fingernail 2.5 Piece of copper 3.5 Iron nail 4.5 Glass 5.5 Steel file 6.5 Streak plate 7.0 Short Answer 42. The marsh plants, insects, frogs and raccoons form a community in and around a pond. The insects eat the plants, the frogs eat the insects, and the raccoons eat the frogs. When the raccoon dies it is decomposed by bacteria. Part A Explain the flow of energy in this chain. What is the original source of energy in this food chain? Is any energy lost as it moves through the food chain? Part B Explain how materials are cycled in this food chain. Explain the role of decomposers in how materials are cycled. 43. Organisms living in a community rely on each other in a variety of ways, even if they are not directly connected by a feeding relationship. Organisms known as decomposers play a crucial role in how the community functions. Part A Give two examples of decomposers which might be found in a community. Part B Explain the general role played by decomposers in the communityk. 44. Reeds and cattails are common plants in wetland ecosystems. Raccoons and herons move and hide among these plants as they hunt for fish and other organisms. Ducks eat plant matter in the water and along the bottom. Insects are food for frogs and newts. Deer feed on a variety of wetland plants. Identify consumers described here which compete for the same food sources. 45. Your body weight is determined by many factors, including your age, how much you eat, and how active you are. Explain the relationship between how much a person eats (their caloric intake), their level of activity, and their body weight. 46. In a salt marsh community, water plants and marsh plants are the primary producers. First-order consumers of these plants include bay shrimp, mud snails, and crickets. Second-order consumers include billfish and redwing blackbirds. Third-order consumers in this community are ospreys, terns, and great herons. Explain what would happen if the crickets were eliminated from this community. 47. Cellular respiration is an essential process in the human body. Explain the importance of this process to body function. What happens in cells when aerobic respiration cannot take place? 48. The diagram below shows a pyramid of energy within an ecosystem. Each level represents the energy available within that trophic level. Compare the amount of energy available at successively higher trophic levels. How does the law of conservation of energy apply to the process of energy movement through ecosystems? 49. Organisms within a community exist on different trophic levels in the passage of energy and materials. These trophic levels are often diagramed as a pyramid showing the organisms found at each level. One tree can be food for many insects. What would a pyramid that shows this relationship look like? 50. The diagram below shows the structure of the phospholipid layer of the plasma membrane. Describe the structure and function of this cellular boundary. 51. The diagram below illustrates how feedback controls blood sugar levels in the body. Using the information provided, as well as your knowledge of this process, describe how insulin and glucagon function to regulate glucose levels within the body. 52. In many countries, including the United States, children receive vaccinations between birth and about 13 years of age. When a child receives certain vaccinations, it becomes unlikely he will catch certain diseases, including things like measles, mumps, and chicken pox. Part A Predict how these vaccinations affect the general health of children in countries where children receive them. Part B How might the rate of childhood illness be different in the United States than in countries where these kinds of vaccinations are not available? Does the availability of vaccinations for certain diseases have a positive or negative effect on the health of children? 53. In a population of spiders living in a given area, size is related to survival. Larger spiders in this group are easily seen and therefore captured by predators, while smaller spiders have difficulty finding food. Define the process at work in determining the size of spiders in this population, and describe what size surviving spiders are most likely to be. 54. Some species of disease-causing bacteria which could be killed by penicillin 50 years ago, today cannot be destroyed by this drug. Explain the mechanism that allows this to happen. 55. Alonzo collects and records data about the properties of an unknown piece of metal. How might Alonzo form a hypothesis about the identity of this metal? Color Gray Luster Shiny Metal Observations Mass 34.3 g Volume 4.7 cm3 Density 7.3 g/cm3 56. Experimental data shows that there is a relationship among the pressure, volume, and temperature of a fixed amount of gas. If an experimenter wants to determine the relationship between volume and temperature only, how should he establish these three factors as variables and constants in the experiment? 57. Rachel is interested in comparing the permeability of soils in different parts of the county in which she lives. She collects soils from a variety of areas, including a forested area in which there has been no development, a new housing subdivision, beside a small stream in her neighborhood, and a playground at her school. At each site, she collects a 1000 milliliter (ml) volume of soil from a depth of 3 centimeters (cm), and records observations about its composition. Rachel identifies the soil from the forested area as the standard to which she will compare the other soils, as it contains a mixture of silt, sand, and clay. Because the soil from the housing subdivision is mostly clay, Rachel believes its permeability will be the lowest of any soils she collects. In the classroom, Rachel performs an experiment in which she pours 200 ml of water into each soil sample, then observes and records the amount of time required for the water to drain through the soil. What is the purpose of this experiment? Describe the hypothesis. 58. Carla notices that she has gained about five pounds during the last several months. To understand why this has happened, Carla decides to write down everything she eats, and at what time of day. She decides to record data each day for one week. Carla plans to analyze the data by looking for trends or patterns in her eating habits. Part A Why is it important for Carla to keep a written record of her food intake in this experiment? Part B How can Carla use this data to make decisions about food choices in the future? Essay 59. During the latter part of the 1900s, a great deal of land in rainforest regions was cleared to create farmland and supply wood. The effects of deforestation are far-reaching, ultimately affecting both biotic and abiotic factors within the rainforest region and worldwide. Part A Identify specific ways that removal of rainforest vegetation has altered the local ecosystem. Part B Describe specific impacts rainforest destruction has on environmental and other conditions worldwide. 60. Making observations and developing hypotheses are critical steps in a scientific method. Based on your knowledge of scientific investigations, compare a hypothesis to an observation. Be sure to explain and include: • a description of both a hypothesis and an observation; • an explanation of how a hypothesis and an observation differ; and • the importance of both hypotheses and observations in experimental design.









