ch. 4 study guide
advertisement

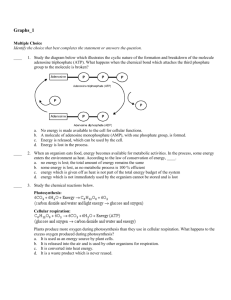
Name _______________________________________Chapter 4 Section 1 Study Guide ( Pages99-103) 1. Diagram and explain the central dogma of biology. 2. What is a gene? 3. It takes about 20,000 genes to make a human, but a typical human cell produces only about 2000 different proteins. Why doesn’t a human cell produce 20,000 different proteins? 4. What is “the genome”? 5. Do all cells in your body have the same genome? Explain. 6. If DNA in a plant is identical to the DNA in a human, (they both have phosphate groups, 5-carbon deoxyribose sugars, and nitrogenous bases), then what makes a plant different from a human? 7. What does the abbreviation “bp” stand for? 8. How many bp make up the haploid human genome? 9. If there are 3,000,000,000 base pairs in the human genome and there are about 20,000 genes in the human genome, then, on average, how many base pairs are in one gene? 10. What false assumption did we make in the previous calculation? 11. T or F All DNA codes for protein. 12. What are the monomers that make up DNA? 13. How many different nucleotides make up DNA? 14. What makes one DNA nucleotide different from another? 15. Draw a double-stranded DNA molecule. Be sure to show the antiparallel nature of the double- stranded molecule. Show proper pairing of base-pairs (A,T,G,C). Label a phosphodiester bond and hydrogen bonds. Circle one nucleotide. Draw a box around one base pair. 16. Draw the four nitrogen bases. Which two are purines? Which two are pyrimidines? i 17. T or F A nucleotide and a nitrogenous base are the same thing. Explain! 18. If we know the amount of adenosine deoxynucleotide in a DNA molecule, what else do we also know is true for that DNA molecule? 19. Why is it important that a DNA double-helix has a constant width and a uniform shape along its entire length? 20. Diagram and explain how a DNA molecule replicates. 21. How is DNA replication different from transcription? How is it similar? 22. The DNA molecule shown in figure 4.5 on page 102 is most likely from what typed of organism? Prokaryote or Eukaryote? 23. Make sure you can answer the four review questions at the end of section 4.1