Elements and Compounds
advertisement

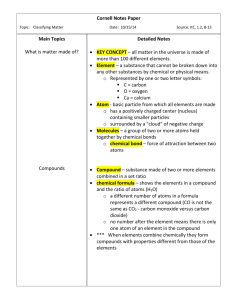
Name: _________________________________ Elements, Compounds & Mixtures Worksheet Part 1: Read the following information on elements, compounds and mixtures. Fill in the blanks where necessary. Elements: A pure substance containing only one kind of ____________. An element is always uniform all the way through (homogeneous). An element _____________ be separated into simpler materials (except during nuclear reactions). Over 100 existing elements are listed and classified on the ____________________. Compounds: A pure substance containing two or more kinds of _______________. The atoms are _________________ combined in some way. Often times (but not always) they come together to form groups of atoms called molecules. A compound is always homogeneous (uniform). Compounds ___________________ be separated by physical means. Separating a compound requires a chemical reaction. The properties of a compound are usually different than the properties of the elements it contains. Mixtures: Two or more ________________ or _________________ NOT chemically combined. No reaction between substances. Mixtures can be uniform (called ________________________) and are known as solutions. Mixtures can also be non-uniform (called ________________________). Mixtures can be separated into their components by chemical or physical means. The properties of a mixture are similar to the properties of its components. Part 2: Classify each of the following as elements (E), compounds (C) or Mixtures (M). Write the letter X if it is none of these. ___Diamond (C) ___Sugar (C6H12O6) ___Milk ___Air ___Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4) ___Gasoline ___Krypton (K) ___Bismuth (Bi) ___Uranium (U) ___Water (H2O) ___Alcohol (CH3OH) ___Pail of Garbage ___Ammonia (NH3) ___Salt (NaCl) ___Energy ___Wood ___Bronze ___Ink ___Dry Ice (CO2) ___Baking Soda (NaHCO3) ___Titanium (Ti) ___Iron (Fe) ___Electricity ___Popcorn ___A dog ___Gold (Au) ___Pizza ___Concrete Part 3: Match each diagram with its correct description. Diagrams will be used once. A B C D E ___1. Pure Element – only one type of atom present. ___2. Mixture of two elements – two types of uncombined atoms present. ___3. Pure compound – only one type of compound present. ___4. Mixture of two compounds – two types of compounds present. ___5. Mixture of a compound and an element. Chemical Changes 1. What is a chemical property? 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Chemical properties are observed only when a substance undergoes a chemical change. 3. What happens during a chemical reaction? 4. In chemical reactions, the substances present at the start of the reaction are called , and the substances produced are called 5. Circle the letter of the term that best completes the sentence. A change in the composition of matter occurs during a chemical reaction. a. sometimes b. rarely c. always d. never 6. Which representation of a chemical reaction is correct? a. products → reactants b. reactants → products . Recognizing Chemical Changes 7. List four possible clues to a chemical change. 8. Is the following statement true or false? If you observe a clue for chemical change, you can be certain that a chemical change has taken place. 9. Define a precipitate. Conservation of Mass 10. During a chemical reaction, the mass of the products is always equal to the mass of the . 11. The law of conservation of mass states that in any physical change or chemical reaction, mass is neither nor . 12. Look at Figure 2.16. How do you know that mass was conserved? A camper burned a piece of paper to start a campfire. Answer these questions about burning the paper. a. Is burning paper a physical change or a chemical change? How do you know? b. If you said the change was chemical, what are the reactants? What are the products? c. The ash produced by the burning paper has much less mass than the mass of the original paper. Was mass conserved during this change? Explain your answer. For Questions 1–12, complete each statement by writing the correct word or words. Properties of Matter 1. For a specific substance, every sample has the same 2. Solid, properties. , and gas are all states of matter. 3. A change of state is an example of a(n) physical change. Mixtures 4. Depending on the distribution of components, mixtures are either heterogeneous or . 5. Mixtures can be separated by differences in the their components. of Elements and Compounds 6. can be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. 7. If the composition of a material is not fixed, the material is a(n) 8. 9. The different elements. . represent compounds, and represent elements. can be used to easily compare properties of Chemical Reactions 10. When a change occurs, the composition of matter changes. 11. A chemical change might have occurred if energy transfers, color changes, a gas forms, or a(n) forms. 12. In a chemical reaction, the mass of the reactants products. the mass of the