Using Mathematics and Computational Thinking
advertisement
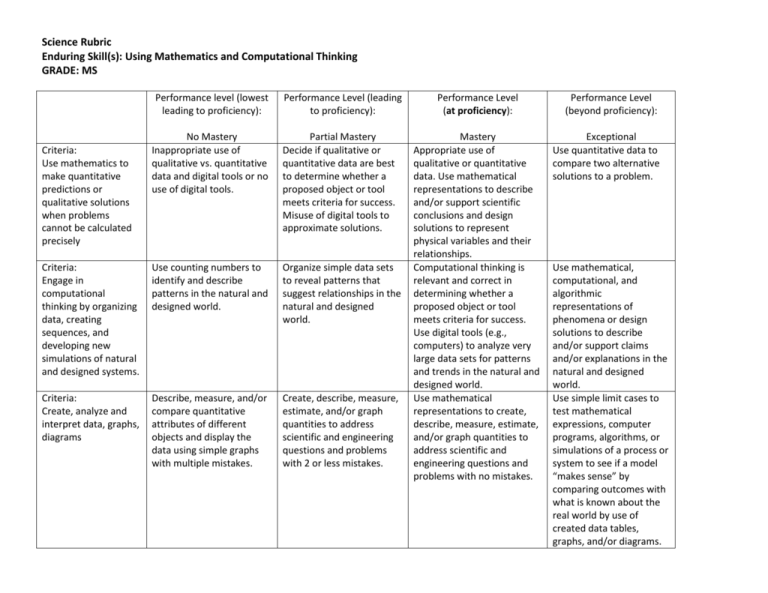
Science Rubric Enduring Skill(s): Using Mathematics and Computational Thinking GRADE: MS Performance level (lowest leading to proficiency): Performance Level (leading to proficiency): No Mastery Inappropriate use of qualitative vs. quantitative data and digital tools or no use of digital tools. Partial Mastery Decide if qualitative or quantitative data are best to determine whether a proposed object or tool meets criteria for success. Misuse of digital tools to approximate solutions. Criteria: Engage in computational thinking by organizing data, creating sequences, and developing new simulations of natural and designed systems. Use counting numbers to identify and describe patterns in the natural and designed world. Organize simple data sets to reveal patterns that suggest relationships in the natural and designed world. Criteria: Create, analyze and interpret data, graphs, diagrams Describe, measure, and/or compare quantitative attributes of different objects and display the data using simple graphs with multiple mistakes. Create, describe, measure, estimate, and/or graph quantities to address scientific and engineering questions and problems with 2 or less mistakes. Criteria: Use mathematics to make quantitative predictions or qualitative solutions when problems cannot be calculated precisely Performance Level (at proficiency): Mastery Appropriate use of qualitative or quantitative data. Use mathematical representations to describe and/or support scientific conclusions and design solutions to represent physical variables and their relationships. Computational thinking is relevant and correct in determining whether a proposed object or tool meets criteria for success. Use digital tools (e.g., computers) to analyze very large data sets for patterns and trends in the natural and designed world. Use mathematical representations to create, describe, measure, estimate, and/or graph quantities to address scientific and engineering questions and problems with no mistakes. Performance Level (beyond proficiency): Exceptional Use quantitative data to compare two alternative solutions to a problem. Use mathematical, computational, and algorithmic representations of phenomena or design solutions to describe and/or support claims and/or explanations in the natural and designed world. Use simple limit cases to test mathematical expressions, computer programs, algorithms, or simulations of a process or system to see if a model “makes sense” by comparing outcomes with what is known about the real world by use of created data tables, graphs, and/or diagrams.










