AP Biology Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam will cover Chapters
advertisement

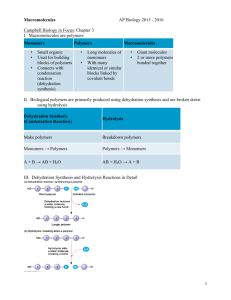
AP Biology Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam will cover Chapters 5, 6, and 7 Chapter 5 The Molecules of Life • Carbohydrates • Lipids (fats) • Proteins • Nucleic Acids Macromolecules are: • Carbohydrates • Proteins • Nucleic Acids • Proteins, for example can contain thousands of atoms • Can have a mass of over 100,000 daltons • Now that’s • MACRO! POLYMERS (poly=many, meris=many parts) • This is because they are ‘chain like’ and have many parts to them buildings blocks that make up polymers are called: MONOMERS • How do monomers connect to form polymers? • Two molecules become covalently bonded to each other through a loss of a water molecule • This is called: condensation reaction • Specifically: dehydration reaction Enzymes facilitate the dehydration • Enzymes in general speed up chemical reactions in cells (for example, enzymes also break the bonds in DNA during cell division When polymers get broken back down into monomers, we call this process • HYDROLYSIS (to break using water) • This is because in order to break them down, we need to add water (H2O) Carbohydrates (various forms Disaccharides Polysaccharides – polymers composed of many sugar building blocks Cellular respiration: Cells extract energy in a series of reactions made possible by glucose Disaccharide consists of two monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkage. Glycosidic linkage: simply – the dehydration reaction formed by the molecules forming a covalent bond. Polysaccharides – macromolecules (a few hundred to a few thousand monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages. Serve as structures and building material for cells and organisms Glycogen – A polymer of glucose Animals (including humans and other vertebrates) store glycogen in liver and muscle cells Hydrolysis in these cells release glucose when the demand for sugar increases Glycogen is stored; but not for long In humans, glycogen is depleted in about a day unless it is replenished. Gives the animal much needed fuel when none other is available. How would this be a concern for people on a low-carb diet Lipids Fats are not polymers Assembled by dehydration reaction 3 fatty acid molecules each join to a glycerol by an ester linkage = a fat = triacylglycerol Phospholipids Steroids Amino Acids Chapter 6 Organelles of the cells and their functions Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Peroxisomes Cytoskeleton Motor proteins Microtubules Cell walls of plants Pectin Wood Middle lamella Extracellular Matrix-Animal Cells Collagen ECM-Fibroconectin/Integrin Cell Walls – Plasmodesmata Chapter 7 Cellular Membranes Fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins The cell membrane sandwich model Membrane proteins Facilitated Diffusion: Passive Transport Aided By Proteins Kidney cells have a lot of water channel proteins (aquaporins) – they allow water to pass through the membrane Ion channels : function as gated channels Open and close in response to a stimulus All cells have voltages across their plasma membranes Voltage is “electrical potential energy” Cytoplasm = negative charge Voltage across a membrane = membrane potential Membrane potential = acts like a battery Two forces/actions drive ions across a membrane: Chemical Electrical Electrochemical gradient Electrogenic pump: a transport protein that generates voltage across a membrane In animal cells = sodium-potassium pump In plant cells = proton pump These store energy that can be tapped for celllular work Proton gradients in the cell is ATP during cellular respiration Cotransport – involves a single ATP powered pump that transports a specific solute and indirectly drives the active transport of several other solutes in a mechanism LABS Cells: leaves, flowers, ID of organelles Polymers