AssignmtSheet.Geography Basics
advertisement

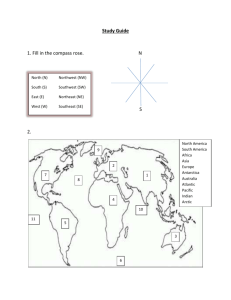
G E O G R AP H Y B AS I C S MAP: WORLD (Big Picture) CLASS NOTES: Meaning of “political, economic, military, social, cultural” THE POLITICAL WORLD TEXT—World Studies: Foundations of Geography Investigate the Political World, p.2 1. Who draws the borders between countries? 2. Which is the only continent that is also a country? 3. Contrast (i.e., tell the difference): ocean, sea, bay, gulf [Look these up in the text & on your own.] National Geographic Student Atlas The Political World, pp.30-31 4. How many countries are there in the world today? 5. “Boundaries are dynamic”—meaning? 6. Physically, which is the biggest country? 7. What is at the A) North Pole? B) South Pole? THE PHYSICAL WORLD National Geographic Student Atlas Define: axis (p.5) 8. WHY do Earth’s seasons change? (p.5) The Physical World, pp.14-15 9. How much of the Earth’s surface is covered by water? 10. A) Which is the only continent without a population? Could you tell me what kind of dirt is on this continent? B) Define: permafrost 11. What type of map is shown on pp.14-15? 12. Overall: Contrast (tell the difference between) political maps and physical maps. MAP PROJECTIONS TEXT—World Studies: Foundations of Geography GLOBES & MAPS, pp.16-17 Globes & Their Weaknesses; Maps & Mapping Define: distortion, projection; cartographer [look it up] 13. What are the problems with globes? 14. A) What is the problem with flat maps? B) Explain the orange peel analogy (comparison). GETTING IT ALL ON THE MAP, pp.18-19 15. Which map projection is still most commonly used by navigators at sea? 16. A) What is the problem with the Mercator Projection? B) How are Greenland & South America an example of this problem? 17. Today, which map projection do many geographers think is best? WHY? (MORE) READING A MAP TEXT—World Studies: Foundations of Geography The Global Grid: text, pp.10-12 18. Define: geography, culture [go to p.91], latitude, longitude, hemisphere, parallel, meridian, equator, prime meridian, global grid, absolute location 19. What is the purpose of latitude and longitude? 20. How are latitude and longitude measured? 21. A) What is 0 degrees of latitude? B) What is 0 degrees of longitude? What city does it run through? 22. What divides the Northern & Southern Hemispheres physically 23. What divides the Eastern & Western Hemispheres physically? 24. Which hemisphere is historically known as the A) “Old World, B) “New World” [Look this up outside the text.] 25. What would you use to find the exact location of any point on Earth? Reading Maps, p.20-21 26. Identify the basic parts that most maps have. Note how each part is useful. National Geographic Student Atlas Reading Maps, pp.8-9 27. How are latitude and longitude measured? 28. Can two places on Earth have the same geographic address? WHY? 29. See the map of the southern U.S.: How many miles is it from point A to point B? [END]