Photosynthesis in a nutshell
advertisement

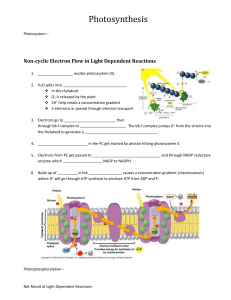
Photosynthesis in a nutshell Redox reactions = chemical reactions that transfer electrons from one molecule to another. Oxidation = lose electrons; reduction=gain electrons Follow the atoms to demonstrate the law of conservation of matter. Energy has been used to rearrange atoms and molecules to produce the high energy sugar molecule. Photosynthesis consists of 3 main ‘parts’: The first two occur in the thylakoid membrane, and are light dependent. Photosystem II, which uses water as a source or electrons. Known of as the water splitting reaction (photolysis). Ultimately produces ATP for the Calvin cycle. This is noncyclic photophosphorylation: formation of ATP by non-cyclic electron flow Photosystem I, uses electron transport molecules to reduce NADP+ (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) to NADPH. This high energy molecule goes into the Calvin cycle. The Calvin Cycle (light independent and occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast) which fixes CO2 ultimately into G3P. It uses a total of 3 molecules of CO2 (per round) 9 ATP and 6 NADPH. It produces 6 G3P molecules. 1 is exported and 5 are recycled to reform ribulose biphosphate. Photosystem II: Location: Thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast Chlorophyll a is the primary pigment involved directly in light reactions. Chlorophyll b is an important accessory pigment Light harvesting complex and reaction center at P680 Water molecule is split to yield O2, electrons and H+ (protons) The electrons are passed down an electron transport chain through plastoquinone (which is reduced), and through the cytochrome complex As the electrons move through the electron transport chain, their energy is used to pump protons from the stroma across the thylakoid membrane into the thylakoid lumen. This contributes to the proton differential across the membrane which is used to make ATP Plastocyanin carries the electron to photosystem I The electrons are replaced by splitting the water molecule Meanwhile the buildup of protons are used in a proton pump across the thylakoid membrane, where ATP synthase generates ATP – a high energy molecule that then goes to ‘fuel’ the Calvin cycle So…PSII passes the electrons ultimately used to reduce NADP+ to NADPH in PSI, and it uses energy generated in the electron transport chain to synthesize ATP for the Calvin cycle Photosystem I: Location: Thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast Chlorophyll a is the primary pigment involved directly in light reactions. Chlorophyll b is an important accessory pigment Light harvesting complex and reaction center at P700 Plastocyanin carries the electron to the P700 center (same electrons generated in the water splitting of PSII) Light is again used to excite the electron Ferredoxin is reduced (gains the electron), and carries it to NADP+ - reducing it to NADPH. This high energy molecule goes to ‘fuel’ the Calvin cycle too. So….results of PSII and PSI are ATP and NADPH for the light independent reactions of the Calvin cycle Calvin Cycle: Occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast Also known of as Carbon fixation: fixing CO2 into organic molecules, specifically sugar (G3P or Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate) Faciiltated by the large enzyme Rubisco In sum: 3 CO2 + 6 NADPH + 9 ATP→ (G3P) Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (1 will be ‘shipped out’, 5 will be recycled) Step I – Rubisco catalyzes the carboxylation of ribulose 1,5 biphosphate (RuBP) by carbon dioxide. This produces 3-phosphoglycerate (3phosphoglyceric acid, or 3PGA) 3PGA is phosphorylated into 1-3-bisphosphoglycerate 1-3BPGA (also glycerate-1,3-bisphosphate) using ATP. 1,3 BPGA is reduced into G3P by NADPH (which is oxidized into NADP+) 1 G3P exits, and 5 are recycled The 5 are used to regenerate RuBP (Ribulose biphosphate), which uses 3 more ATPs. Ultimately 3 CO2, 6 NADPH, and 9ATP are used for ‘one cycle’.