Bacterial Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
advertisement

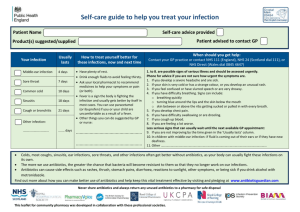
Bacterial Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Abscess Forming Infections Types of Infection Folliculitis Inflammation and infections of hair follicles Treatment 1. Cloxacillin 2. Surgery a. Carbuncle Etiological Agents Staphylococcus aureus Structure Involved Localized infection in the o Hair follicles o Axillae o Scalp o Ear canal Leads to Otitis Externa Clinical Features 1. Small 2. Erythematous a. Papules b. Pustules 3. Course of folliculitis a. Develop into Furuncle i. Deeper inflammatory nodules b. Furuncle can then extend deeper into subcutaneous fat called Carbuncle i. Bigger ii. Deeper iii. Due to multiple draining sinuses iv. Occurs at 1. Nape of neck 2. Thigh Spreading Infections Impertigo 1. The most common superficial epidermal infection 2. Due to a. Poor hygiene b. Hot and humid climate 3. Common in children Types of Infection Etiological Agents Non bullous Impertigo Streptococcus pyogenes More common Nephrotogenic strain of Begins with small Strep pyogenes type M49 vesicles o Causing nono Ruptures causing suppurative sequale superficial spread o Acute Treatment glomerulonephritis 1. Penicilin Bullous Impertigo Staphylococcus aureus phage type 71 Treatment o Produces exfoliatin 1. Cloxacillin Cellulitis A diffuse inflammation and infection of superficial skin layers Erysipelas Deeper form of cellulitis Perdisposing factors o Diabetes mellitus o Venous stasis o Alcohol abuse Treatment Cloxacillin Penicillin Structure Involved Epidermis Clinical Features 1. Serous exudates in the vesicles 2. Ruptures to produce GOLDEN-CRUSTED erosions Epidermis 1. Bullae or vesicles containing turbid fluid (serum) 2. Dangerous in infant, requires systemic antibiotics 1. Localized area of a. Mildly painful edema b. Warmth c. Swollen 2. Severe systemic infection a. Fever b. Rigors 1. Usually occurs at the face 2. Involvement of lymphatic drainage gives rise to clearly demarcated area of a. Erythema b. Induration Streptococcus pyogenes Staphylococcus aureus (polymicrobial) Epidermis Streptococcus pyogenes Staphylococcus aureus (polymicrobial) Underlying dermis Lymphatic channels Necrotizing infections Types of Infection Gas Gangrene/Clostridial Myonecrosis Etiological Agents Clostridium perfringens Clostridium septicum Structure Involved Muscles Soft tissues Predisposing factors (60-70%) o Motor vehicle accident o Penetrating injury o Crush injury Treatment Surgical debridement o Amputation might be required Penicillin Necrotizing Fascitis Streptococcus pyogenes Acute and highly toxic o Flesh-eating bugs Predisposing Factors Polymicrobial 1. Post surgery o Aerobic/facultative 2. Post trauma anaerobe 3. Strep pyogenes skin Staph aureus infection Strep spp. 4. Diabetes mellitus Enterococcus Enterobacteriacea Treatment o Anaerobic 1. Surgical exploration a. Removal of death tissues Bacteroides spp. b. Determine extend of Clostridium spp. tissue damage 2. Combination of antibiotics Widespread infection of the fascia Clinical Features Pathogenesis 1. Production of alpha toxin tissue death 2. Production of gas in the necrotic lesions 3. Cell death leads to destruction of blood supply to the affected tissues 4. Favors anaerobic condition, which in return organism will further replicate Features 1. Initial presentation appears 4-6 hours after trauma 2. Local tenderness 3. Skin appears a. Stretch b. Shining c. Later blackens 4. Foul smelling discharge 5. Crepitus 6. Systemic symptoms a. Sweating b. Tachycardia 1. Devascularization of a. Skin b. Muscle c. NOT INCLUDING BONE 2. Skin necrosis 3. Bullae formation 4. Surrounding tissue edema and inflammation 5. Gangrenous 6. Crepitus 7. Pts appears toxic with soft tissue pain Systemic Bacterial Infection with Cutaneous Involvement Types of Infection Staphylococcus Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS) Etiological Agents Staphylococcus aureus o Exfoliatin strain Structure Involved 1. Cutaneous manifestation a. Epidermis Staphylococcus aureus o TSST-I toxin (exotoxin) 1. Involved multiple organs 2. Cutaneous manifestation a. Epidermis and dermis 1. Also known as a. Infant i. Ritter’s diseases (not to be confused with Ritter’s syndromes) b. Children/adult i. Toxic epidermal necrolysis 2. May occur sporadically or in outbreak Treatment 1. Fluid replacement therapy 2. Cloxacillin Toxic Shock Syndrome Treatment 1. Fluid replacement therapy 2. Cloxacillin 1. 2. 3. 4. Clinical Features Toxin causes loss of overlying skins Toxiemia Fever Death 1. Happens in women using tampon 2. Can also occur in non-genital site in men 3. Erythematous rash 4. Skin dequamation of a. Palms b. Soles Micellaneous Skin Infections Types of Infection Etiological Agents Erysipelothrix rhusiopatheiae Erysipeloid Suspect in handlers of o Fishes o Meats Erythrasma Corynibacterium minutissimum Cat Scratch Disease Treatment 1. To shorten the course of the disease a. Tetracyclin b. Erythromycin Bartonella Henselae Cutaneous Anthrax Due to direct inoculations from o Infected animals o Contaminated animal products Treatment 1. Penicillin Bacillus anthracis Animal’s Bite Infections Treatment Pasteurella multocida Often polymicrobial o Aerobes Staph spp. Strep spp. o Anaerobes Bacteroides Anaerobic cocci 1. Thorough cleaning 2. Debridement of all damaged tissues 3. Combination antibiotics 4. Penicillin for Pasteurella multocida Clinical Features 1. Tender 2. Blue-red discoloration of the skin 3. Well demarcated 1. Often assymptomatic 2. Slowly enlarging area of dry skin which either a. Pink b. Brownish 3. Erythema spreads in moist and skin folds such as a. Axillae b. Groin c. Between toes 1. Following cat scratch 2. Nodule formation at scratched area 3. Regional lymphadenopathy a. Resolves in 1-6 months 4. Self limited 1. 2. 3. 4. Inflammed lesion with surrounding edema PAINLESS Variable skin lesions If not treated, may progress into a. Septiceamia b. Death 1. Skin loss leads to sf tissue damages 2. Exposure to animal saliva and foreign particles lead to secondary skin infection 3. Cellulitis 4. Lymphagitis 5. Localized abscess