study notes - layers of the earth
advertisement

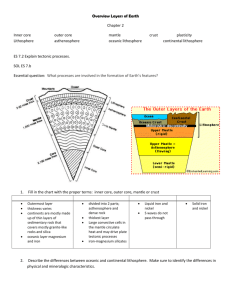
Name: ______________________________________ Period: ____ Key Points on the Earth’s Layers: 1. The Earth has four main layers: the inner core, the outer core, the mantle, and the crust. 2. The crust of the Earth is also referred to as the lithosphere. A. The crust is made up of rock. B. The Earth’s crust underneath the oceans in about three times thinner than the crust that makes up the continents. 3. The top portion of the mantle is also referred to as the asthenosphere. A. The entire mantle, including the asthenosphere, is made of molten (melted) rock. 4. The inner and outer core is made up of iron, a type of metal. A. The outer core is liquid iron and the inner core is solid iron. 5. As we move toward the Earth’s core, the temperature increases. Key Points on the Earth’s Lithosphere: 6. The Earth’s crust is also referred to as the lithosphere. 7. The lithosphere is very rigid. It will not bend but will instead crack. 8. The lithosphere is less dense than the asthenosphere. A. You can remember this because less dense substances will float on top of denser substances. Since the lithosphere is on top of the asthenosphere it must be less dense. 9. There are two types of lithosphere: A. Oceanic lithosphere is found underneath the oceans. B. Continental lithosphere makes up the continents of Earth. 10. Oceanic lithosphere is more dense than continental lithosphere because of the types of minerals that make up the rock. 11. The thickest part of the lithosphere is found in mountain ranges. A. The tallest mountain on Earth is Mt. Everest. This is also the location on Earth where the lithosphere is the thickest. Key Points on the Earth’s Asthenosphere 1. The top portion of the mantle is also referred to as the asthenosphere. Name: ______________________________________ Period: ____ 2. The asthenosphere is liquid rock, but it is very viscous (it flows very slowly). A. It is sometimes called “plastic” which means it can be bent and shaped while hot and will hold its shape when it hardens. 3. The asthenosphere is very hot. It has a much higher temperature than the lithosphere. 4. The asthenosphere is a liquid and convection currents form in it just like they do in a pot of boiling macaroni. 5. Convection Current Within the Earth: A. Molten rock in the asthenosphere is cooled as it comes into contact with the lithosphere. B. This cool molten rock is more dense than the hotter molten rock below and sinks toward the core. C. As the cool molten rock gets closer to core it is heated up again. D. This hotter molten rock is less dense and rises toward the surface of the Earth. E. As it reaches the top of the mantle, it cools and gets more dense, sinking toward the core again 1) Remember, this top portion of the mantle where the molten rock is cooler is called the asthenosphere. F. This happens over and over again forming a convection current. Key Points on Convergent Boundaries: 1. Boundaries are the spots were two plates meet 2. Convergent Boundaries: where two tectonic plates are moving toward one another A. The word converge means come together. 3. There are three different types of convergent boundaries. The types are based on the two types of lithosphere colliding. A. Oceanic – oceanic convergent boundary = two plates with oceanic lithosphere are colliding. B. Oceanic – continental convergent boundary = a plate with oceanic lithosphere is colliding with a plate with continental lithosphere. C. Continental – continental convergent boundary = two plates with continental lithosphere are colliding. 4. Underwater convergent boundaries form trenches. A. Oceanic – oceanic and oceanic – continental convergent boundaries B. A trench is like a deep ditch in the seafloor. Name: ______________________________________ Period: ____ C. The deepest trench in the world is the Mariana Trench. It is 6.85 MILES below the ocean’s surface at its deepest part. 5. Convergent boundaries on land form mountain ranges. A. Continental – continental convergent boundaries. B. Large mountain ranges like the Himalaya Range in Nepal and the European Alps between Italy and Germany were formed by continental-continental convergent boundaries. Convergent Key Points on Subduction: 1. Boundaries are the spots were two plates meet 2. Convergent Boundaries: where two tectonic plates are moving toward one another 3. Subduction occurs at some convergent boundaries = one plate moves under the other plate. D. Subduction only occurs with oceanic – oceanic and oceanic – continental convergent boundaries. E. Trenches form where subduction occurs. A trench is like a deep ditch in the seafloor. 4. The density of the two plates determines which plate sinks and which rises. a. The plate that is more dense will sink and the plate that is less dense will rise. b. The plate that moves under the other eventually melts into molten rock in the asthenosphere. c. The density of a material can be described with a number. It will usually have 𝐠 units of 𝐜𝐦𝟑 . These units mean each cubic centimeter of the material weighs a certain number of grams. 𝐠 i. Oceanic lithosphere has a density of 2.9 𝐜𝐦𝟑 𝐠 ii. Continental lithosphere has a density of 2.7 𝐜𝐦𝟑