Overview Layers of Earth - pams
advertisement
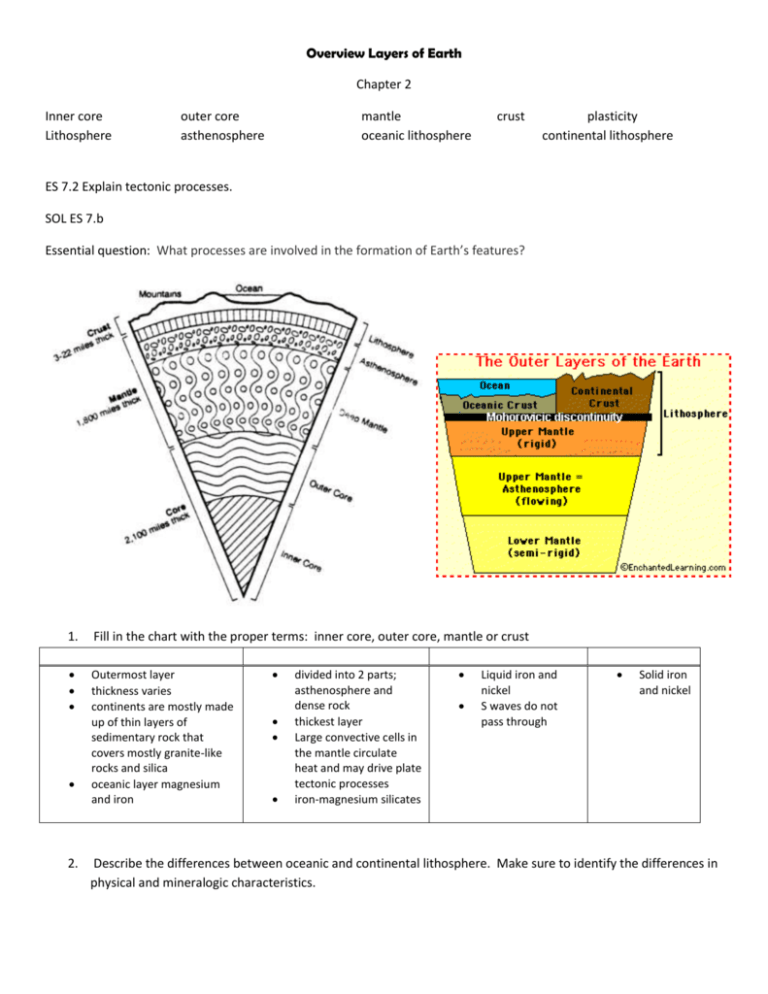
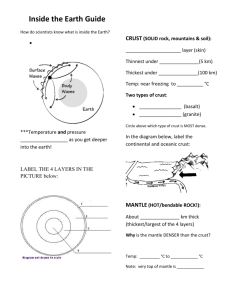
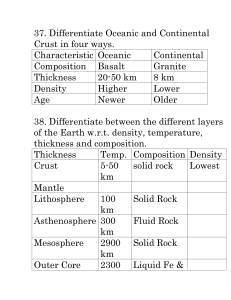
Overview Layers of Earth Chapter 2 Inner core Lithosphere outer core asthenosphere mantle oceanic lithosphere crust plasticity continental lithosphere ES 7.2 Explain tectonic processes. SOL ES 7.b Essential question: What processes are involved in the formation of Earth’s features? 1. Fill in the chart with the proper terms: inner core, outer core, mantle or crust Outermost layer thickness varies continents are mostly made up of thin layers of sedimentary rock that covers mostly granite-like rocks and silica oceanic layer magnesium and iron 2. divided into 2 parts; asthenosphere and dense rock thickest layer Large convective cells in the mantle circulate heat and may drive plate tectonic processes iron-magnesium silicates Liquid iron and nickel S waves do not pass through Solid iron and nickel Describe the differences between oceanic and continental lithosphere. Make sure to identify the differences in physical and mineralogic characteristics. 3. The composition of some meteorites supports the inference that the Earth's core is composed of a. aluminum and calcium b. iron and nickel c. silicon and oxygen d. magnesium and potassium 4. Which statement best describes the continental and oceanic crusts? a. The continental crust is thicker and less dense than the oceanic crust. b. The continental crust is thicker and more dense than the oceanic crust. c. The continental crust is thinner and less dense than the oceanic crust. d. The continental crust is thinner and more dense than the oceanic crust. 5. 6.Use the diagram below to answer the following question. a. What is the name of the upper plastic-like region of the mantle? b. Which layer is the lithosphere found in? 7. Place these terms mantle, lithosphere and asthenosphere in order in the chart to show how the layers are actually arranged. Surface Mantle