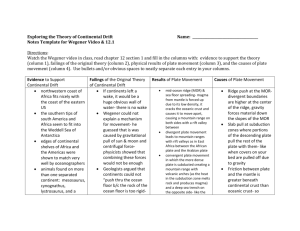
What are the SI base units for length, mass and volume? Meter
advertisement

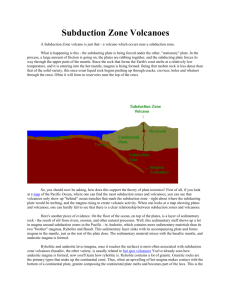
What are the SI base units for length, mass and volume? Meter, kilogram and liter. Add 3.88 + 9.2+ 4.1 Record your answer to the appropriate number of significant figures. 17.2 How many cm are in 4 meters? 400 cm How many km are in 8 miles? (.621 mi= 1km) 12.88 km but since there is only 1 sig fig in the data we only report to 1 sig fig so 10 km What is the mass of an object whose volume is 6 cm3 and density is 2 g/mL? 12 g Name two renewable and two nonrenewable resources. Renewable: water, wind, solar Nonrenewable: oil, coal, gas, wood Which two layers of the Earth make up the lithosphere? The crust and the uppermost portion of the mantle What is the energy source for each of the four spheres of Earth? Hydro, Bio and Atmosphere- Sun Geosphere- Heat from within the Earth Compare and contrast the appearance and formation of intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks. Intrusive- form underground, form from magma, have time to cool slowly so they have large crystals and a coarse grained appearance (speckled) Extrusive- from on the surface, form from lava, cool off very quickly so the crystals have little to no time to grow, giving the rock a fine grained or glassy appearance Which is an example of an element? H2O (water), SiO2 (Quartz), CH4 (methane) or Au (Gold) Gold, all of the others are compounds Where is most of Earth’s fresh water found? Trapped in glaciers What are 3 erosional features of glaciers and 3 of running water? Glaciers- U-shaped valleys, cirques, horns, erratics, moraines Running water- V-shaped valleys, waterfalls, levees, meanders, oxbow lakes, deltas, alluvial fans Compare and contrast 3 volcano types by shape, eruption and magma type. Shield- broad, and flat. Have basaltic magma, very hot and has low silica content, makes for quiet eruptions. Found at hotspots (Hawaii) and divergent plate boundaries (MOR). Cinder cone- small, steep sided volcano that has eruptions consisting mainly of steam and cinders/ash. Stratovolvano/ Composite volcano- tallest of all, steep sides, VERY DANGEROUS. Usually made of grantic/andesitic magma. Magma is cooler and has A LOT of silica, this makes the lava sticky and causes explosive eruptions with dangerous pyroclastic flows. These are found at subduction zones, like the Andes mountains. Which seismic waves travel the fastest? Primary waves travel the fastest and arrive at a seismograph station first. Of the scales used to measure EQ intensity, which measure by amount of damage done? Modified Mercalli scale measures by visual damage. Richter measures ground shaking and moment magnitude measures amount of energy released. When does plate subduction occur? Plate subduction occurs at any CONVERGENT plate boundary that involves an oceanic plate. Oceanic plates are the only ones dense enough to be subducted. *No subduction occurs at a continentalcontinental convergent boundary* Summarize the features found at all plate boundaries. *See notes* Explain seafloor spreading. Divergent boundary in the ocean allows for magma to seep upward from the mantle. The magma hardens and cools. As it cools, the rock expands and pushes older seafloor away from the MOR. This, combined with the movement of the plates pushes old seafloor towards continental plates or another oceanic plate. Once the ocean plate converges with another plate, the more dense one gets subducted. It melts back into the mantle and will eventually seep out of the MOR again. If two half lives have passed, what percentage of PARENT isotope remains? 25% Compare and contrast absolute and relative dating? Both can be used to determine the age of a rock or other sample. Relative dating can only give a time range (this rock formed between 145-120 mya) or a series of events without any specific date (this happened, then this, then this, but we don’t know if those things happened 10mya or 2bya.) Absolute dating uses radioactive isotopes and gives an exact, specific (absolute) age of the rock (this rock is 14 million years old) What makes a good index fossil? Must be widely distributed, easily identifiable and have only existed for a short time period. (Examples: trilobite, goniatite, ceratites) What was Earth’s early atmosphere like? Where did the oxygen come from? Like our stellar neighbors, our early atmosphere had high levels of carbon dioxide and no oxygen. This carbon dioxide was added to the atmosphere when the gases escaped the Earth during volcanic eruptions. Later, photosynthesizing organisms (like cyanobacteria and stromatolites) evolved. As they underwent the process of photosynthesis they used up much of the carbon dioxide and replaced it with oxygen. During which geologic ERA did the dinosaurs live and what killed them? Mesozoic era, a giant meteorite How do low and average mass stars end their life? They turn into white dwarfs which we theorize will eventually cool into black dwarfs. When are the solstices and equinoxes in the Northern Hemisphere? Summer solstice- 6/21, winter solstice- 12/21, vernal equinox- 3/22 and autumnal equinox- 9/22 *The opposite is true in the southern hemisphere* What is responsible for heating Earth’s atmosphere? The Sun only indirectly heats the atmosphere. Sunlight comes as visible light (NOT HEAT), but when that visible light strikes the earth most of it is absorbed and then re-radiated as heat (infrared light) So the sun heats the earth and the earth heats the atmosphere.