The States of Matter
advertisement

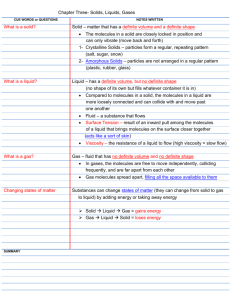
The States of Matter There are four main states of matter: solids, liquids, gases and plasma. 1) Solids – have definite shapes and definite volumes and are not compressible to any extent. There are two main categories of solids, crystalline solids and amorphous solids. Molecules are held close together in an orderly fashion with little freedom of motion. 2) Liquids – have no definite shape but have a definite volume, and they are not easily compressible. Molecules are close together, but are not held so rigidly in position and can move past one another. 3) Gases – a gas has no definite shape, it takes the shape of the container that holds it. Gases are easily compressible. Molecules are separated by distances that are large compared with the size of the molecules. 4) Plasma - This state of matter makes up 99% of the visible universe. Each of these states is also known as a phase. Phase describes a physical state of matter. The key word is physical, because things only move from one phase to another by physical means. We speak of physical changes if energy is added (like increasing the temperature or increasing pressure) or if energy is taken away (like freezing something or decreasing pressure). These kinds of forces change states of matter. Phase changes Melt (or Fusion) – a substance fuses or melts when it turns from a solid state into a liquid state. Vaporization (or Evaporation) – a substance vaporizes when it turns from a liquid state into a gaseous state. Sublimation – a substance sublimes when it turns from a solid state into a gaseous state. Condensation – a substance condenses when it turns from a gaseous state into a liquid state or when it turns from a gaseous state into a solid state. Solidification – a substance solidifies when it turns from a liquid state into a solid state. Task 1. Draw a line between the matching terms in columns A and B. A -B 1. SOLID temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid 2. CRYSTAL the change from a gas to a liquid 3. LIQUID solid with an orderly arrangement of particles 4. SUBLIMATION liquid to gas at the surface of liquid 5. VAPORIZATION change from solid state to gas 6. MELTING POINT state of matter that has definite shape and definite volume 7. CONDENSATION state of matter that has no definite shape and has a definite volume Task 2. a) Find the synonyms for the given phrases. phase of matter . . . . . . . . . ., rise of temperature . . . . . . . . . ., drop of temperature . . . . . . . . . . b) Label the changes from one state to another one. Use both noun and verb forms. Gaseous state 4 6 2 Liquid state 5 3 1 Solid state Phase Changes Noun Verb 1 _______________________ _______________________ 2 _______________________ _______________________ 3 _______________________ _______________________ 4 _______________________ _______________________ 5 _______________________ _______________________ 6 _______________________ _______________________ Task 3. Answer the following questions according to the text. 1. Specify all known states (phases) in which matter exists. 2. There are physical and chemical changes of matter. Which ones are necessary if we want to change the phase of a thing? 3. How would you describe physical changes of matter? 4. How can we add energy to matter? 5. How can we take away energy from matter? 6. Do the physical changes influence the chemical properties of an element or a compound? 7. What happens if a solid reaches the temperature of its melting point? Task 4. Describe the picture. Does it illustrate physical or chemical changes of matter?