Unit 3 Guide: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception
advertisement

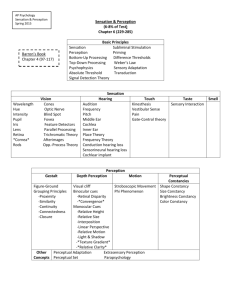
Unit 3 Guide: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception: Unit Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. Explain the difference between sensation and perception. Explain the difference between bottom-up and top-down processing. Name and define the two types of thresholds. Describe Signal Detection Theory and why it is used. Evaluate the scientific basis behind subliminal messages and ESP. Describe different types of ESP. Describe and give examples of sensory adaptation (light, dark, etc). Differentiate between selective attention, cocktail party effect, inattentional blindness, and change blindess. Describe the nature and characteristics of light (wavelength, intensity). Describe the path that light takes as it makes its way through the eye. Locate eye parts on a diagram, and identify their functions (including the process of accommodation). List the three types of cells that are present in the retina. Explain the difference between rods and cones. Describe the two major theories of color vision. Describe feature detectors and where visual information is processed in the brain. Describe the nature and characteristics of sound (wavelength, amplitude). Identify the path that sound takes as it makes its way through the ear, and locate eye parts on a diagram. Differentiate between pitch (hearing) theories. Describe how we locate sounds. Describe the major causes of deafness. Identify the “smell” center of your brain; Identify where smell is processed in the brain. Describe how your sense of smell is affected by gender and age. Identify the chemical senses. Locate the receptor cells for taste. Define your major body senses: vestibular and kinesthetic. Identify the sensations that skin receptors give rise to. Describe the phenomenon of paradoxical heat. Differentiate between the Gate-Control Theory and Biopsychosocial Theory of pain. Recognize and explain the perceptual organizational principles (figure-ground; proximity; similarity; closure; continuity). Define perceptual constancy and distinguish between size, shape, color, and brightness constancy. Explain the two types of cues that we use to determine depth perception. Describe how the visual cliff has added to our understanding of depth perception. Describe the major monocular cues of depth perception including: interposition, linear perspective, aerial perspective, elevation (relative height), texture gradient, shadowing, and relative motion, relative size. Describe the major binocular depth cues including stereoscopic vision, retinal disparity, and convergence. Explain the difference between monaural and binaural sound cues. Describe the major ways in which we perceive movement including: stroboscopic motion, the phi phenomenon, and the autokinetic illusion. Explain what causes visual illusions. Vocabulary 1. Transduction/Receptor Cells 2. Psychophysics 3. Thresholds: Absolute, Difference 4. Weber’s Law 5. Signal Detection Theory 6. Processing: Top-Down, Bottom-Up 7. Attention: Selective Attention, Inattentional Blindness, Change Blindness 8. Sensory Adaptation 9. Eye Parts: Cornea, Pupil, Iris, Lens, Retina, Fovea, Blind Spot, Optic Nerve, Optic Chasm* 10. Eye Cells: Rods/Cones, Bipolar Cells, Ganglion Cells* 11. Feature Detectors 12. Color Theories: Trichromatic (Young-Helmholtz), Opponent-Process 13. Ear Parts: Ear Canal, Tympanic Membrane, Ossicles, Oval Window, Cochlea, Basilar Membrane, Organ of Corti, Auditory Nerve, Hair Cells* 14. Theories of Hearing: Place, Frequency, Volley 15. Hearing Disorders: Sensorineural, Conduction 16. Olfactory Bulb 17. Pheromones 18. Body Senses: Kinesthesis(Kinesthetic), Vestibular 19. Pain Theories: Gate-Control, Biopsychosocial 20. Gestalt Principles of Organization: Proximity, Similarity, Closure, Continuity, Figure- Ground* 21. Perceptual Constancies: Size, Shape, Color, Brightness* 22. Monocular Depth Cues: Retinal Disparity, Convergence 23. Binocular Depth Cues: Interposition, Linear Perspective, Aerial Perspective, Elevation (Relative Height), Texture Gradient, Shadowing, Relative Size, Relative Motion 24. Monaural v. Binaural Cues 25. Perception of Motion: Autokinetic Illusion, Stroboscopic Motion, Phi Phenomenon 26. Perceptual Adaptation, Perceptual Set Names 1. Richard Axel 2. Georg von Bekésy 3. Linda Buck 4. Gustav Fechner 5. Eleanor Gibson 6. Ewald Hering 7. David Hubel 8. Harry McGurk 9. Ronald Melack 10. James Randi 11. Herman von Helmholtz 12. Richard Walk 13. Patrick Wall 14. Ernst Weber 15. Torsten Wiesel 16. Thomas Young