Molecular Modeling Lab
advertisement

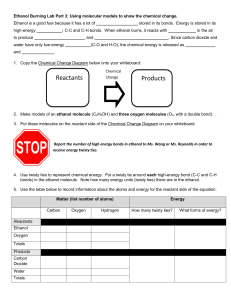
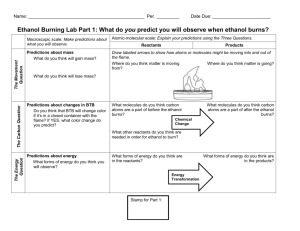
Modeling Lab – Simple Biological Molecules Background Information – read carefully In biology the four (4) most important elements found in living things are: C – carbon which can make up to 4 bonds with other atoms H – hydrogen which can make one bond with another atom O – oxygen which can make up to 2 bonds with other atoms N – nitrogen which can make up to 3 bonds with other atoms P – phosphorus which can make up to 3 bonds with other atoms S – sulfur which can make up to 2 bonds with other atoms Of these six (6) elements, carbon is the dominant player because it can: bond with up to 4 other elements, bond to other carbons to make chains, rings and branched structures, and support single, double or triple bonds. Carbon in found in almost every molecule in living things. These carbon rich molecules come in a variety of shapes and these shapes with their “hot spots” i.e. functional groups, are what enable life processes (chemical reactions) and life’s structures to exist. So shape matters!!! The huge molecules in living things are collections of smaller building blocks are that coupled together in very specific ways to create very specific shapes. It is the specific shape and the functional groups in the molecules that make life possible. Today you will use molecular modeling kits to build a variety of these simpler molecules and important functional groups. Lab Objectives: build basic structures of simple molecules. identify the five (5) major functional groups in biomolecules visualize the three dimensional structure of these molecules and sketch them. Part I – A Quick Review 1. Complete the table before starting Element Hydrogen Oxygen Model color Nitrogen Carbon Chemical symbol Number of single bonds possible 2. Draw the structural formulas for each of the following simple compounds: Molecule Formula Shape Check Methane CH4 Water H2 O Carbon dioxide CO2 Ammonia NH3 3. Now build each of these molecules using your model kit. For double bonds use the long, thin, flexible connectors. When you have finished the four molecules, have your teacher initial the table above. Part II – Functional Groups 1. There are five major functional groups in the molecules of living things. a. hydroxyl group – a hydrogen and an oxygen atom are connected by a single covalent bond b. carbonyl group – a carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen atom c. carboxyl group – a carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen atom and to a hydroxyl group d. amino group – a nitrogen atom attached to tweo hydrogen atoms by single covalent bonds e. phosphate group - a phosphorus atom double bonded to one oxygen atom and singly bonded to three other oxygen atoms 2. Build the structural models for each of the following functional groups and then make a sketch in the last column: Functional Group Formula Shape (Notes) Check Hydroxyl group -OH Carbonyl group C=O Carboxyl group -COOH Amino group -NH2 Phosphate group -PO4 Part III – Building Simple Biomolecules Name Carbon Dioxide CO2 1. Using your molecular model kit, build each of the simple molecules in the table below. Formula Description shape Functional groups present O=C=O One of the main products of cellular respiration and one of the main reactants of photosynthesis Water H2O O / \ H H One of the main products of cellular respiration and one of the main reactants of photosynthesis Ammonia NH3 N / | \ H H H Main source of nitrogen for living things. Bacteria capture nitrogen from the air through a chemical reaction that produces ammonia Phosphoric Acid H3PO4 Ethanol C2H6O O || H-O-P-O-H | O-H H H H—C—C—O—H H H Impacts bone density; found in sodas yeasts carry out ethanol fermentation , breaking down sugar in the absence of oxygen to make ethanol. this reaction causes bread dough to rise and beer to ferment Check Acetic Acid C2H5O2 H O H—C—C—O—H H H The sourness of vinegar comes from the acetic acid it contains Urea CN2H4O O H—N—C—N—H H H When proteins are digested and burned for energy, ammonia (toxic) is created. Ammonia is converted to less toxic urea in the liver Questions (to be answered after completing the lab.) What types of functional groups are found in ethanol, acetic acid? How are acetic acid and ethanol alike? Different? What are the functional groups in urea?