Health Related Fitness Quiz Study Guide
advertisement

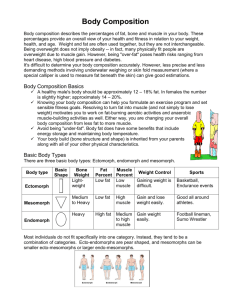
JUNIOR AND SENIOR HEALTH-RELATED FITNESS STUDY GUIDE Physical Fitness - The ability of your body systems to work together efficiently which means you are able to do daily activities with the least amount of effort. A fit person is able to carry out the typical activities of living, such as work or school, and still have enough energy to enjoy leisure activities. Health – Early definitions of health focused on illness. Health was nothing more than the absence of disease. As medical experts received better training, they began to focus on the prevention of illness and disease. Its definition has been expanded to include the prevention of illness or disease. Wellness – A state of being that enables you to reach your fullest potential. It includes your social, emotional, physical and spiritual health. Physical Fitness is made up of eleven parts; five parts are health related and six parts are skill related. Health-related fitness – Helps you stay healthy Skill-related fitness – Helps you perform well in sports and activities HEALTH-RELATED PARTS OF FITNESS 1. Cardiovascular fitness: The ability to exercise your entire body for long periods of time. Cardiovascular fitness requires a strong heart, healthy lungs, and clear blood vessels to supply the cells in your body with the oxygen they need. 2. Strength: The amount of force your muscles can produce or exert. Strength is often measured by how much weight you can lift. People with good strength are able to perform daily tasks efficiently. 3. Muscular Endurance: The ability to use your muscles many times without tiring. People with good muscular endurance are likely to have better posture and fewer back problems. They are also better able to resist fatigue. 4. Flexibility: The ability to use your joints fully through a wide range of motion. You are flexible when your muscles are long enough and your joints are free enough to allow movement. People with good flexibility have fewer sore or injured muscles. 5. % Body Fat: The percentage of weight that is made up of fat when compared to other body tissue, such as bone and muscle. People who are in a healthy range of body fatness are more likely to avoid illness and even have lower death rates than those outside the healthy range. Note: The extreme ranges are the most dangerous; too little body fat, like too much, can cause health problems. Healthy body fat ranges are listed below: Gender Female Male Under 30 Years of Age 17-24% 14-20% Over 30 Years of Age 20-27% 17-23% UNDERSTANDING BODY COMPOSITION Weight: Total body weight includes bones, muscle, fat, water, etc. BMI (Body Mass Index): Correlates physical stature and body weight with mortality ratios i.e. diabetes, cardio-pulmonary disease, cancer, etc. BMI is recognized as a valid assessment tool in identifying obese individuals BMR: Basal Metabolic Rate measures the energy expended by the body to maintain normal functions such as respiration and circulation. Impedance: The impedance value reflects how hard a mild electrical signal has to work to travel through the body. Lean mass (containing water and electrolytes) conducts the current, while fat mass acts as a resistor to the current. Fat Mass: Actual fat mass in the body. FFM: Fat Free Mass is comprised of muscle, bone, tissue, water, and all other fat free mass in the body. A healthy ratio for Fat Free Mass to Fat Mass is approximately 5:1 for females, and 7:1 for males. Generally speaking, males carry more muscle than females, therefore they will report a higher FFM. TBW: Total Body Water reflects the amount of water in the body. To monitor hydration level, use the following formula: TBW/Weight x 100 = Hydration. Women should be approximately 50-60% hydrated Males should be approximately 60-70% hydrated *Note: B/C hydration levels fluctuate, testing should occur at the same time of day whenever possible.