Name Plate Tectonics Internet Web Quest Use the Internet to look up
advertisement

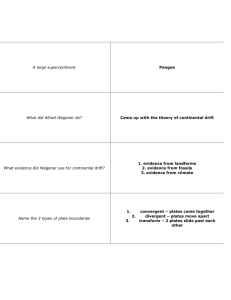
Name ____________________________ Plate Tectonics Internet Web Quest Use the Internet to look up the following information. 1. The idea of continental drift has been around for hundreds of years. Define continental drift. Continental drift was a theory that explained how continents shift position on Earth's surface. Set forth in 1912 by Alfred Wegener, a geophysicist and meteorologist, continental drift also explained why look-alike animal and plant fossils, and similar rock formations, are found on different continents. www.livescience.com/37529-continental-drift.html 2. While people have noted for the past 400 years or more that the continents look like they fit together and may have “drifted” to their current locations, Alfred Wegener more fully supported the idea in the early 1900’s. Research and name at least two pieces of evidence that support the idea of continental drift. Rock, fossil, and climatic evidence. www.livescience.com/37529-continental-drift.html 3. What is the name of Wegener’s supercontinent and about how long ago did it begin to break apart? Pangaea About 200 million years ago, the supercontinent began to break up. http://www.livescience.com/38218-facts-about-pangaea.html 4. While Wegener provided many pieces of evidence for continental drift, he died before scientists accepted his idea. He was never able to explain how the continents could have moved that far apart. That was not discovered until the mid-1900s in an idea called sea floor spreading. Define sea floor spreading and explain how it could be responsible for continental drift. Seafloor spreading is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics. http://www.mlhi.org/science/period6/Sea.htm 5. We didn’t know exactly what the ocean floor looked like until the development of sonar. Define sonar and explain how it was used to map the ocean floor. Sonar, which stands for SOund Navigation And Ranging, works by measuring the time it takes for sound to travel to a reflecting surface and back. Check out the following webpage for an explanation of how it works. http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/earthguide/diagrams/sonar/sonar.html 6. Sonar revealed a 40,000 mile long chain of underwater mountain ranges called mid-ocean ridges. Name three of the longer mid-ocean ridges found around the world (see http://imagesmediawiki-sites.thefullwiki.org/09/1/2/9/15028053949789413.gif). Mid-Atlantic, Central Indian, and Pacific Antarctic (any others could work here, too) 7. There are several pieces of evidence that sea floor spreading is occurring. One piece of evidence is the age of the ocean crust (see http://geology.about.com/od/platetectonicmaps/ss/World- Seafloor-Ages.htm). Describe where the youngest ocean crust is found and explain why it is found there. The youngest crust is found at the mid-ocean ridges (generally in the middle of the ocean basins). This is where magma is rising through rifts, or cracks, in Earth’s crust. When the magma cools it forms new sea floor rock. 8. What type of igneous rock forms when magma cools at mid-ocean ridges? Basalt 9. Another piece of evidence for sea floor spreading is found in the magnetic record of the rocks on the ocean floor. The sea floor rocks show alternating bands of normal and reverse polarity with a mirror image of the pattern on the other side of the mid-ocean ridge (see http://www.pbs.org/saf/1207/features/Platetech6.htm). This pattern could only be generated if spreading was occurring at the mid-ocean ridge. Define normal and reverse polarity. Normal polarity: Time when the compass needle points to the magnetic north pole. Reversed polarity: Time when a magnetic needle points to the south pole. http://www.ge-at.iastate.edu/glossary-of-geologic-terms/ 10. A third piece of evidence for sea floor spreading is how the thickness of ocean sediment changes as you move away from the mid-ocean ridge. What happens to the thickness of ocean sediment as you move away from a mid-ocean ridge and explain why this is the case? The thickness of the ocean sediment increases as you move away from the mid-ocean ridge because the rock is getting older and the sediment has been settling for a longer time the farther away from the ridge you are. 11. In addition to mid-ocean ridges, sonar also revealed many ocean trenches around the world. These trenches, or deep depressions, are the deepest parts of the ocean basins and are formed at subduction zones. Define subduction zone and explain why it occurs. A subduction zone is where a denser tectonic plate goes under another, less dense, tectonic plate. This occurs at a convergent boundary. http://www.geo.cornell.edu/hawaii/220/PRI/images/subduction2.jpg 12. Continental drift and sea floor spreading eventually gained enough evidence and support to become theories. These theories led to the theory of plate tectonics. Define the theory of plate tectonics. Plate tectonics is the theory that Earth's outer shell is divided into several plates that glide over the mantle, the rocky inner layer above the core. The plates act like a hard and rigid shell compared to Earth's mantle. This strong outer layer is called the lithosphere. http://www.livescience.com/37706-what-is-plate-tectonics.html 13. There are between 15 to 20 tectonic plates. These plates move in different directions and different speeds on the Earth’s surface. The tectonic plates are made up of lithosphere. Define lithosphere. Lithosphere: Rigid, rocky outer layer of the Earth, consisting of the crust and the solid outermost layer of the upper mantle. It extends to a depth of about 60 mi (100 km). http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/343783/lithosphere 14. The lithosphere moves at about the rate your fingernails grow. The lithosphere moves on a layer of the mantle called the asthenosphere. Convection currents within the asthenosphere cause the plates to move. Define asthenosphere and convection current. Asthenosphere: zone of Earth’s mantle lying beneath the lithosphere and believed to be much hotter and more fluid than the lithosphere. The asthenosphere is thought to extend from about 60 miles (100 km) to about 450 miles (700 km) below Earth’s surface. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/39770/asthenosphere 15. A tectonic plate boundary is where two tectonic plates meet. Explain how we determine where tectonic plate boundaries are? Frequent earthquakes occur at all plate boundaries. http://www2.sunysuffolk.edu/hornj/ESC102_PlatesAssgnmt_Fig1.jpg 16. About how many earthquakes occur each day? Thousands a day with around 50 of them reported by the National Earthquake Information Center (NEIC). 17. A tectonic plate boundary can be defined as convergent, divergent, or transform. Define convergent boundary and give three examples of mountains around the world formed at convergent boundaries. A convergent boundary is where two plates are colliding. Mountains formed at convergent boundaries include the Himalayas in northern India, the Andes in South America, and the Alps in Europe. The Appalachians and Rockies in the United States formed at ancient convergent boundaries. All three types of boundaries are shown in the diagram below. http://www.livescience.com/37706-what-is-plate-tectonics.html 18. If two continents collide at a convergent boundary, folded mountains will form. The Appalachian Mountains outside our window formed in this way when continents slammed together as Pangaea was beginning to form between 400 and 300 million years ago. When ocean crust collides with continental crust, however, folded mountains will not form. Explain what happens when ocean crust collides with continental crust and name at least two features that will form as a result. The ocean crust will subduct beneath the continental crust because the ocean crust made of basalt is denser than the continental crust made of granite. A trench will form at the subduction zone and volcanoes will form on the continent. 19. Ocean crust can also collide with other ocean crust. When this occurs one ocean crust will subduct beneath the other ocean crust. A trench will form and a line of volcanic islands will form above the trench. This line of volcanic islands is commonly called a volcanic arc, or volcanic island arc. What volcanic island arc is located off the coast of Alaska and what is the name of the trench next to these volcanic islands? The Aleutian Islands are the volcanic islands and the trench is called the Aleutian Trench. http://home.earthlink.net/~dengelhardt/images/zonesmedium.jpeg 20. A divergent boundary is where two tectonic plates are pulling away from each other. When this occurs, the process of rifting occurs and volcanic activity is common. Define what a rift is. Definition: form fissures, cracks, or breaks, especially through large-scale faulting; move apart. 21. Explain how the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the East Africa Rift Zone are similar. Both are found at a divergent boundary where rifting is occurring. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a site of sea floor spreading while the East Africa Rift Zone will eventually create a new ocean. The figure below explains how. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e9/Ocean-birth.svg/2000px-Oceanbirth.svg.png 22. A transform boundary is a boundary where two plates slide past each other. The San Andreas Fault in California is a famous transform boundary. How long is the San Andreas Fault and between which two tectonic plates is it found? The entire San Andreas Fault system is more than 800 miles long and extends to depths of at least 10 miles within the Earth. It is located between the Pacific and North American plates. http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/earthq3/safaultgip.html