Study guide - chapter 10
advertisement

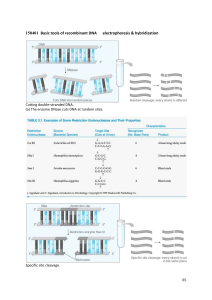
NSB 230 – MICROBIOLOGY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. CHAPTER 10 – STUDY GUIDE Define bioengineering. Define biotechnology. Briefly describe the practical properties of DNA. What is a restriction endonuclease? What is a palindrome? How is it involved in restriction endonucleases action? What is a restriction fragment? What does restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) refers to? What are sticky ends? Briefly describe how restriction endonucleases and ligases are used to “cut and paste” DNA pieces. What is the function of reverse transcriptase? What is cDNA? Describe gel electrophoresis. What is it used for? Describe nucleic acid hybridization. What is a gene probe? Briefly describe the Southern blot method. What is it used for? Briefly describe fluorescent in situ hybridization. What is it used for? What is the purpose of DNA sequencing? Name examples of sequencing methods. Name and briefly describe the different “-omics” fields in biology. What is the purpose of polymerase chain reaction (PCR)? Why does it need primers? Why is it PCR useful? 19. Define recombinant DNA technology. What is it used for? 20. What is a vector? What is a cloning host? 21. Describe the three important attributes of a good vector. Why are plasmids and bacteriophages classified as good vectors? 22. List desirable features in a microbial cloning host. 23. Name some examples of biochemical products of recombinant DNA technology. 24. What is a genetically modified organism (GMO)? Why are GMOs useful? 25. What is the purpose of gene therapy? Briefly describe the two methods of gene therapy. 26. What is the purpose of gene silencing techniques? How does an anti-sense RNA block gene expression in prokaryotes? And in eukaryotes? 27. What is the purpose of DNA fingerprinting? What methods can be used for DNA fingerprinting? 28. What is a short tandem repeat (STR)? How is it useful in DNA fingerprinting? 29. Why is mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) useful in DNA fingerprinting? 30. What are single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)? How are they used in DNA fingerprinting? 31. What is the purpose of microarray analysis? What is it used for?