File - Ms. Zhong`s Classes
advertisement

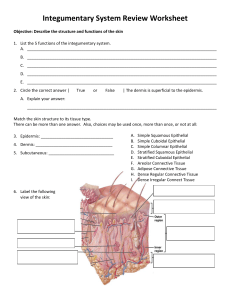
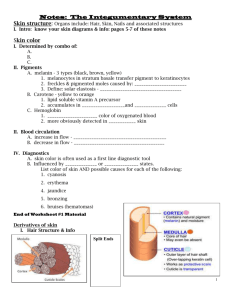
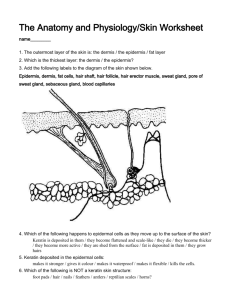
Basic Skin Functions Integumentary: “covering” Functions: Protect deeper tissues from: Mechanical damage Chemical damage Bacterial damage UV radiation Thermal damage Dessication damage(drying out): contains waterproofing keratin Aids in excretion of urea and uric acid (through sweat) Synthesizes Vitamine D: Modified cholesterol molecules in skin covered to vitamin D by sunlight Insulate and cushions the deeper body organs Regulating heat loss from the body surface Structure of the skin Dermis: Thicker than epidermis Two main layers: 1. Papillary layer: The upper dermal region. It is uneven and has finger like projections from its superior surface= Form fingerprints, contains sensory nerve endings 2. Reticular layer: The deepest skin layer. It contains blood vessels, sweat, oil glands and hair follicles Sebaceous Gland: Oil gland. Are found allover the skin, except on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. Subcutaneous tissue: It does not considered part of the skin, but it does anchor the skin to underlying organs. Epidermis: Superficial layer Divided into 5 layers including Stratum corneum: 20 to 30 cell layers thin. The shinglelike dead cell remnants, completely filled with keratin (water repellent, exceptionally tough protein) No blood vessels Made of living and nonliving cells Function: Gets nutrients, water, essential minerals from diffusion Contain pigments for skin color: 1. Melanin: a pigment which ranges in color from yellow to brown to black, is produced by specialized cells called melanocytes 2. Carotene: an orange-yellow pigment, can be found in carrots 3. Hemoglobin: pigment in red blood cells Appendages of the skin Cutaneous glands Exocrine glands that release their secretions to the skin surfca via ducts 1. Sebaceous glands = oil glands, produce sebum (a mixture of oily substances and fragmented cells, contains chemicals that kill bacteria) 2. Sweat glands: also called sudoriferous glands a. Eccrine glands: far mumerous and are found all over the body. Produce sweat (acidic) Heat regulation – nerve ending that causes sweat secreation b. Apocrine glands: confied to axillary and genital areas of the body Ducts empty into hair follicles Fatty acids and proteins that can be a food source for bacteria Hair and hair follicles Hair shaft: the part projecting from the surface of the scalp or skin Hair follicles: a. Epidermal sheath: Epithelia tissue that forms the hair b. Dermal sheath: dermal connective tissue, supplies blood vessels to the epidermal portion c. Arrector pili: small bands of smooth muscle cells, connect each side of the hair follicle to the dermal tissue. When contracted, these cause hair to stand up on end Nails Scale-like modifications of the epidermis Heavily kerationized Lack of pigment makes them colorless