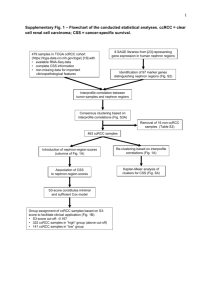
Supplementary Tables and Figures Table 1 Comparative
advertisement

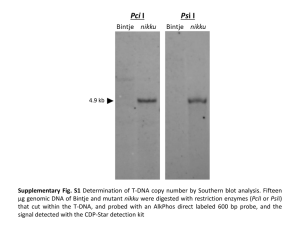
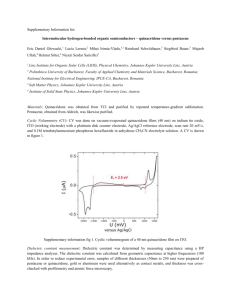
Supplementary Tables and Figures Table 1 Comparative biochemical properties of wild and recombinant TALip54 Properties Lip54 rTALip54 Protein type wild recombinant pH optima 9.0 8.0 Temperature optima 40 °C 50 °C Substrate specificity p-Nitrophenyl myristate p-Nitrophenyl laurate Enantioselectivity Solvent based enantio inversion Kumar et al. (2009) Solvent based enantio inversion Current research paper References Supplementary Figure Legends 1a: Schematic representation of overlapping PCR to amplify TAlipC 1b: Amplification of TALipC gene from genomic DNA of Trichosporon asahii MSR54 Lane 1:- molecular marker Lane 2:- Truncated gene amplified from cDNA Lane 3:- Full gene with introns amplified from gDNA Lane 4:- Full functional gene TAlipC amplified by overlapping PCR 1c: Native PAGE analysis of deglycosylate enzyme Deglycosylation was performed according to manufacturer’s instruction given in deglycosylation kit from New England Biolabs (Lot No. 0041403). Native ladders are shown in lane one, second and third lane corresponds to glycosylated and de-glycosylated TALipC, respectively. 2a: Arrhenius plot Log Vmax Vs 1/ Temperature (K-1) at pH8.0 2b: Florescence analysis to study the thermal behaviour of TALipC Florescence studies were performed by fluorospectrophotometer (Varian, Inc. Hansen Way, Palo Alto, CA, USA) where 292 nm was used for excitation and 300 to 550 nm for emission. 3: Kinetics parameter of TALipC studied on the hydrolysis of p-NP palmitate 4: GC chromatogram showing fatty acid selectivity during hydrolysis of an equimolar mixture of triacylglyceride mixture for a period of 10 min (a) and 30 min (b) Equimolar triacylglyceride mix (10 mM) [tricaprylin (8:0); tricaprin (10:0); trilaurin (12:0); trimyristin (14;0); tripalmitin (16:0)] was made in 2-propanol + 50mM pH 8.0 buffer and reaction was started with the addition of enzyme to make the final volume of 2.0 ml, where final concentration of substrate become 5 mM. The reaction mixture was incubated at 50 °C for various time intervals (10 min, 30 min). Reaction was terminated by adding 500 µl of 3M calcium chloride and centrifuged at 10,000 g for 5 min. The pellet was recovered and dissolved in hexane to be analysed by gas chromatography by using capillary column using conditions were: Temp – 250 ⁰C, pressure – 126.6 Kpa, total flow – 150.0 ml/min, column flow – 2.87 ml/min, linear flow – 50.9 cm/sec. Peak a and b corresponds to lauric acid and myristic acid having retention time 17.5 min and 20.8 min respectively, as per standards. 5: Solvent stability of TALipC 100% activity = 914 U/mg 6: Effect of various metal ions on the activity of lipase The enzyme was incubated in metal ions 20 mM for 1 h and assayed for lipase activity. Residual activity was calculated with respect to untreated enzyme as control (100 % = 915 U/mg) Supplementary Fig. 1a Supplementary Fig. 1b Supplementary Fig. 1c Supplementary Fig. 2a Supplementary Fig. 2b 400 Intensity at 380 nm 350 300 250 200 150 0 20 40 60 Temperature (°C) 80 100 Supplementary Fig. 3 11 10 3 1/V X10 umole/mg/min 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 -30 -25 -20 -15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 1/[S] X 10 -3(mM) Supplementary Fig. 4a a Supplementary Fig. 4b a b Supplementary Fig. 5 180 160 Relative activity (%) 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 l l l l r SO hano hano tone pano furan etate tano ethe form luene xane e t u t c o yl o c r e a r E B oro To He h l A d l t p M y y Ch Die Iso etrah Eth T DM Solvents Supplementary Fig. 6 180 160 Relative activity (%) 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Ba2+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Mn2+ Zn2+ 20 mM metal ions Cd2+ Hg2+