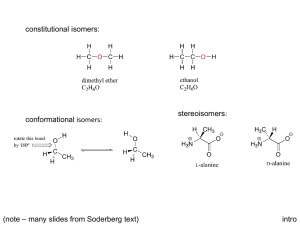
word
advertisement

CHEM 122: Introduction to Organic Chemistry Chapter 6: Chirality: The Handedness of Molecules. 1. Which of the following objects are chiral (assume that there is no label or other identifying mark)? a) b) c) d) e) Pair of scissors Tennis ball Paper clip Beaker The swirl created in water as it drains out of a sink or bathtub. 2. 2-Pentanol is chiral, but 3-pentanol is not. Explain. 3. 2-Butene exists as a pair of cis-trans isomers. Is cis-2-butene chiral? Is trans-2butene chiral? Explain. 4. Which of the following compounds contain stereocenters? a) b) c) d) 2-Chloropentane 3-Chloropentane 3-Chloro-1-butene 1,2-Dichloropropane 5. Which of the following compounds contain stereocenters? a) b) c) d) Cyclopentanol 1-Chloro-2-propanol 2-Methylcyclopentanol 1-Phenyl-1-propanol 6. Draw the mirror image for each molecule: COOH H H2 N C H CH3 a) OH b) CH 2 OH H H OH O OH H HO c) H3 C H H OH d) NH 2 7. Mark each stereocenter in these molecules with an asterisk. Note that not all contain stereocenters. OH CH3 O N CH3 a) OH b) O O OH NH 2 c) d) 8. Label all stereocenters in each molecule with an asterisk. How many stereoisomers are possible for each molecule? OH CH2COOH a) CH3CHCHCOOH b) CHCOOH OH c) HO—CHCOOH OH d) 9. For centuries, Chinese herbal medicine has used extracts of Ephedra sinica to treat asthma. The asthma-relieving component of this plant is ephedrine, a very potent dilator of the air passages of the lungs. The naturally occurring stereoisomer is levorotatory and has the following structure. HO H C H NHCH 3 C CH3 Ephedrine a) Mark each stereocenter in ephedrine with an asterisk. b) How many stereoisomers are possible for this compound? c) The specific rotation of naturally occurring ephedrine is -41o. What is the specific rotation of its enantiomer? 10. What is a racemic misture? Is a racemic mixture optically active? That is, will it rotate the plane of polarized light? 11. Which of the eight alcohols with a molecular formula of C5H12O are chiral? 12. Write the structural formula of an alcohol with the molecular formula C6H14O that contains two stereocenters. 13. Consider a cyclohexane ring substituted with one hydroxyl group and one methyl group. Draw a structural formula for a compound of this composition that: a) Does not show cis-trans isomerism and has no stereocenters. b) Shows cis-trans isomerism but has no stereocenters. c) Shows cis-trans isomerism and has two stereocenters. 14. Compound A (C5H8) is not optically active and cannot be separated into enantiomers. It reacts with bromine in carbon tetrachloride to discharge the orange color of bromine and form Compound B (C5H8Br2). When Compound A is treated with H2 in the presence of a transition metal catalyst, it is converted to compound C (C5H10). When treated with HCl, compound A is converted to compound D (C5H9Cl). Given this information, propose structural formulas for compounds A, B, C, D. Hint: There are at least three possibilities for Compound A and, in turn, three possibilities for Compounds B, C, and D. 15. Following is a chair conformation of glucose, the most prevalent carbohydrate in the biological world (Chapter 12). HO HO CH2OH O OH OH a) Identify the five stereocenters in this molecule. b) How many stereoisomers are possible c) How many pair of enantiomers are possible?