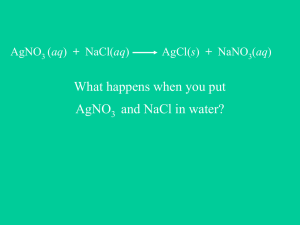CH 115 Fall 2014Worksheet 21 What is a double
advertisement

CH 115 Fall 2014 Worksheet 21 1. What is a double-replacement reaction? What is a precipitation reaction? A double replacement reaction is one in which the cations in two compounds swap places. It can be generally visualized as: AX + BY BX + AY. A precipitation reaction is a special type of double-replacement reaction in which one of the products formed is a solid, insoluble ionic compound. 2. Write and balance the following chemical reactions that will take place. a). Lead (II) nitrate mixed with sodium chloride Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 NaCl (aq) PbCl2 (s) + 2 NaNO3 (aq) b). Iron (II) sulfate mixed with magnesium nitrate FeSO4 (aq) + Mg(NO3)2 (aq) Fe(NO3)2 (aq) + MgSO4 (aq) c). Potassium hydroxide mixed with magnesium sulfate 2 KOH (aq) + MgSO4 (aq) Mg(OH)2 (s) + K2SO4 (aq) d). Calcium chloride mixed with potassium carbonate CaCl2 (aq) + K2CO3 (aq) CaCO3 (s) + 2 KCl (aq) e). Silver nitrate mixed with barium chloride 2 AgNO3 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) 2 AgCl (s) + Ba(NO3)2 (aq) f). Copper (II) nitrate mixed with sodium hydroxide Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 NaOH (aq) Cu(OH)2 (s) + 2 NaNO3 (aq) 3. What is a total ionic equation? What is a net ionic equation? What is the process for writing both of these equations? To write a total ionic equation, break up all of the compounds that are aqueous into their ionic components. To write a net ionic equation, cross out all the spectator ions (ions that are present on both the reactants and products side of the equation). A net ionic equation shows you which ions actually react. NEVER break apart solids, liquids, gases, or weak acids when writing a total or net ionic equation. 4. Can you write a total and net ionic equations for each of the chemical reactions given in question #2? a). Total – Pb2+ (aq) + 2 NO3- (aq) + 2 Na+ (aq) + 2 Cl- (aq) PbCl2 (s) + 2 Na+ (aq) + 2 NO3- (aq) Net – Pb2+ (aq) + 2 Cl- (aq) PbCl2 (s) b). Total – Fe2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq) + Mg2+ (aq) + 2 NO3- (aq) Fe2+ (aq) + 2 NO3(aq) + Mg2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq) Net – none (all ions cross out) c). Total – 2 K+ (aq) + 2 OH- (aq) + Mg2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq) Mg(OH)2 (s) + 2 K+ (aq) + SO42- (aq) Net – 2 OH- (aq) + Mg2+ (aq) Mg(OH)2 (s) d). Total – Ca2+ (aq) + 2 Cl- (aq) + 2 K+ (aq) + CO32- (aq) CaCO3 (s) + 2 K+ (aq) + 2 Cl- (aq) CH 115 Fall 2014 Worksheet 21 Net – Ca2+ (aq) + CO32- (aq) CaCO3 (s) e). Total – 2 Ag+ (aq) + 2 NO3- (aq) + Ba2+ (aq) + 2 Cl- (aq) 2 AgCl (s) + Ba2+ (aq) + 2 NO3- (aq) Net – 2 Ag+ (aq) + 2 Cl- (aq) 2 AgCl (s) f). Total – Cu2+ (aq) + 2 NO3- (aq) + 2 Na+ (aq) + 2 OH- (aq) Cu(OH)2 (s) + 2 Na+ (aq) + 2 NO3- (aq) Net – Cu2+ (aq) + 2 OH- (aq) Cu(OH)2 (s)