APES Semester 2 cumulative final exam study guide Unit 1 1. What
advertisement

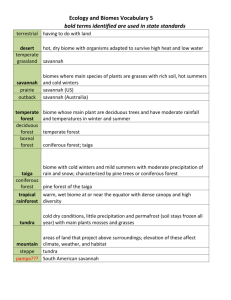
APES Semester 2 cumulative final exam study guide Unit 1 1. What are the macromolecules essential to life? 2. Laws of thermodynamics 3. Define geothermal energy, hypothesis 7 environmental science 4. Tragedy of the commons – examples of tragedies, examples of commons & how to stop 5. Gases found in the atmosphere 6. Math - rule of 70, how to calculate population density & population growth rate 7. Factors responsible for growth of human population over last 100 years 8. What would indicate a rapidly growing population ? What would indicate the quality of life of a population? Unit 2 1. Define biotic, abiotic factors, ENSO 2. Ehrlich’s prediction and why it didn’t come true 3. How is Earth’s atmosphere warmed? 4. % of US land in coastal areas 5. Example of positive and negative feedback loops. 6. Climate vs weather 7. Causes and effects of global climate change. 8. Why is biodiversity important? Unit 3 1. Steps of the nitrogen cycle 2. Nitrogen fixation 3. Define interspecific competition, intraspecific competition, geographic isolation, parasitism, competition, commensalism, mutualism 4. Why are so many species extinct? 5. Reservoirs in the carbon cycle. 6. Zebra muscles 7. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration equations Unit 4 1. Define: Euphotic zone, abyssal zone, bathyal zone, intertidal zone, limnetic zone, littoral zone, benthic zone, profundal zone 2. Types of lakes 3. What type of water would have the most dissolved oxygen? 4. Describe the following biomes: temperate deciduous forest, temperate rainforest, tropical dry forest, desert, boreal forest, temperate grassland, tropical rainforest, savanna, tundra, chaparral Unit 5 1. Define: umbrella species, ecotourism, land trust, monumentalism, paper parks, equiliobrium theory of island biogeography, umbrella species 2. First national park 3. % of earth forest 4. % of earth agriculture 5. How much forest do we lose per year? 6. National Park service, US forest service, & bureau of land management Unit 6 1. Soil horizons 2. Fundamental geological material for soil 3. How does a pest develop resistance? 4. Define a GM organism 5. Green revolution time period 6. Types of weathering 7. Size of soil particles 8. Define: intercropping, conservation tillage, contour farming, terracing, & shelterbelts 9. Problems caused by fertilizers. Unit 7 1. Consumptive vs nonconsumptive water use 2. Chemical property used to determine water quality 3. Major pollutants of groundwater 4. In what type of water would you find high dissolved oxygen content? 5. Indicates water is contaminated by human sewage 6. Greatest ecological crisis facing marine ecosystems 7. Define: by-catch, mangrove forest 8. Why is groundwater more easily depleted than surface water? 9. Why does groundwater retain contaminents for so long? 10. Damage from driftnetting and longline fishing. 11. What are the positive and negative effects of dams? Unit 8 & 9 1. Us primary fuel for energy 2. What happens when we burn fossil fuels? 3. What is the most widely used renewable energy source? 4. Define biomass energy, nuclear energy 5. World ranking of energy sources 6. Surface mining control & reclamation act of 1977 7. General mining law of 1872 8. Where does crude oil come from? 9. What happened at Chernobyl? 10. What are the new renewable? 11. Advantages and disadvantages of solar power 12. Disadvantages of wind 13. What is the most expensive method of generating electricity? Unit 10 1. Define Montreal protocol, Stockholm convention, allergens, teratogens, carcinogens, neurotoxins 2. What drives more people to move to the suburbs? 3. What is removed by scrubbers installed in smokestacks? 4. Consequences of acidic deposition 5. Layers of the atmosphere 6. Conversion of primary pollutants to secondary pollutants 7. Why do CFCs have such a long residence in the atmosphere? 8. Photochemical vs industrial smog 9. What causes acid rain? 10. Silent Spring 11. What are the effects of toxic pollutants on the environment, on plants & animals and on human health? 12. What are the benefits of stratospheric ozone and how are we destroying it? What are the negatives of tropospheric ozone and how is it formed? Unit 11 1. How much trash is generated per person per day? 2. How much of the waste stream is recycled? 3. What are some heavy metals? 4. Define: deep-well injection, surface impoundments, WTE facilities, E-wastes 5. How do we deal with solid waste? 6. Problems with landfills 7. Resource Conservation and Recovery Act 8. CERCLA