Unit Organizer Industrial Revolution 2016
advertisement
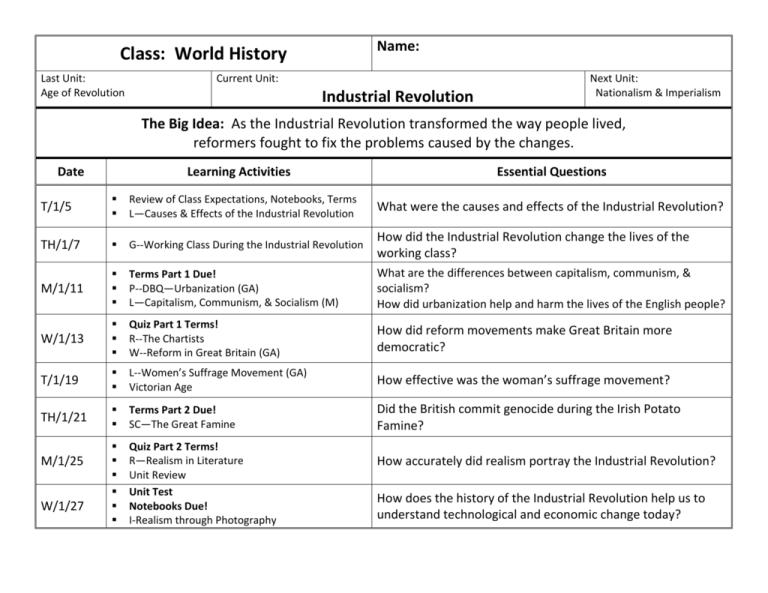
Name: Class: World History Last Unit: Age of Revolution Current Unit: Industrial Revolution Next Unit: Nationalism & Imperialism The Big Idea: As the Industrial Revolution transformed the way people lived, reformers fought to fix the problems caused by the changes. Date Learning Activities Essential Questions T/1/5 Review of Class Expectations, Notebooks, Terms L—Causes & Effects of the Industrial Revolution What were the causes and effects of the Industrial Revolution? TH/1/7 G--Working Class During the Industrial Revolution How did the Industrial Revolution change the lives of the working class? M/1/11 Terms Part 1 Due! P--DBQ—Urbanization (GA) L—Capitalism, Communism, & Socialism (M) What are the differences between capitalism, communism, & socialism? How did urbanization help and harm the lives of the English people? W/1/13 Quiz Part 1 Terms! R--The Chartists W--Reform in Great Britain (GA) How did reform movements make Great Britain more democratic? T/1/19 L--Women’s Suffrage Movement (GA) Victorian Age How effective was the woman’s suffrage movement? TH/1/21 Terms Part 2 Due! SC—The Great Famine Did the British commit genocide during the Irish Potato Famine? Quiz Part 2 Terms! R—Realism in Literature Unit Review Unit Test Notebooks Due! I-Realism through Photography M/1/25 W/1/27 How accurately did realism portray the Industrial Revolution? How does the history of the Industrial Revolution help us to understand technological and economic change today? Terms: Define in Notebook and Know for Quiz Read Ch. 9 & 10, pp. 280-335 Part 1 Terms Edmund Cartwright 286 James Watt 287 Entrepreneur 287 George Stephenson 288 John Stuart Mill 301 Adam Smith 300 Karl Marx 302 Part 2 Terms People Louis Pasteur 330 Charles Darwin 331 Charles Dickens 267 Victor Hugo * Victoria I 314 Prime Minister * Emmeline Pankhurst 315 Marie Curie 331 Places Liverpool 288 Manchester 290 Galapagos Islands * Ireland 320 Events Industrial Revolution G Enclosure Movement 283 The Communist Manifesto 302 Cholera Epidemic * Great Reform Act of 1832 313 Chartist Movement 314 Great Famine 320 Ideas Urbanization 289 Corporation 297 Capitalism 300 Laissez-faire 300 Socialism 302 Communism 302 Suffrage 313 Social Darwinism 332 Realism 266 State Standards: Industrial Revolution (1750—1880) In this unit, students will analyze the costs and benefits of the Industrial Revolution as the world shifted from an agrarian economy to one based on manufacturing. Students will examine the influence of the Industrial Revolution on the growth of cities, reform movements, and changing social structures around the world. Compelling Questions How did new choices created by the Industrial Revolution change the way people lived? (Standard 1) How did the Industrial Revolution affect the rise of labor? (Standard 2) How did the Industrial Revolution lay the foundation for competing economic systems? (Standard 3) What ideas of this period have the greatest impact on the 20th century? (Standard 4) In what ways did the Industrial Revolution lead to new economic, political, and social relationships? (Standard 5) *Definition provided by Ms. Garvey; L=Lecture, G=Group, I=Internet, P= Pair, R=Reading, SC=Socratic Circle; W=Writing, GA=Garvey, M=Meek








