Teacher notes for ZSL Whipsnade Zoo quizzes
advertisement

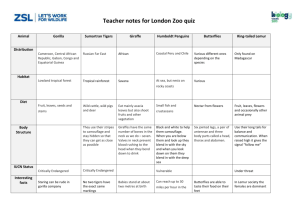
Teacher notes for Whipsnade Zoo quiz Animal Distribution Habitat Elephants India, Sri Lanka, Amur Tigers Russian Far East Giraffe African African Lions Extinct in North Africa. Malaysia, Indonesia Now found in Africa, and Southern China south of the Sahara Mountains and Forests Savanna forest Varied, from grasslands of East Africa to sands of the Kalahari Desert Diet Vegetation, fruit, twigs, small branches, bark and roots Body Structure IUCN Status Endangered Small animals like fish and frogs - but mostly they like to eat wild pigs and deer Eat mainly acacia leaves but also shoot fruits and other vegetation Carnivorous, mainly Has the lightest colour coat out of all Tiger species Giraffes have the same number of bones in the neck as we do – seven. Valves in neck prevent blood rushing to the head when they bend down to drink Camouflage with the open Savanna to help them hunt Endangered mammals from giraffes to buffalo, deer and Cheetah Greater OneHorned Rhino Ring-tailed Lemur Africa Nepal Only found on Madagascar Adapted to Savanna or open grassland but also dense woodlands Tropical and Subtropical Grasslands, Savanna, and Shrublands Carnivorous, mostly feed on smaller antelope Leaves, twigs and tall grass Fruit, leaves, flowers and occasionally other animal prey The ‘tear marks’ on a Cheetah’s face helps them reflect the glare from the sun when they are hunting during the day. They have a folding upper lip that can grasp leaves and twigs but can fold it away to graze on the tall grass of the terrain. Use their long tails for balance and communication. When raised high it gives the signal “follow me” Vulnerable There are 2500 left in the wild Under threat carrion Range constantly being reduced but not endangered yet. Teacher notes for Whipsnade Zoo quiz Interesting facts Also called Siberian Tiger Babies stand at about two metres at birth Lions are social and territorial animals who live in family groups called prides The Cheetah doesn’t roar like other big cats, lions and tigers. Instead it gently purrs and even makes sounds similar to chirping to communicate to others Their horn could be between 8 to 25 inches long In Lemur society the females are dominant National Curriculum links Key Stage 1- Using their observations and ideas to suggest answers to questions Key Stage 2 Working scientifically: Asking relevant questions and using different types of scientific enquires to answer them Living things and their habitats: Recognise that living things can be grouped in a variety of ways Physical Geography: describe and understand key aspects including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains Geographical skills and fieldwork: use maps, atlases, globes Animals: Identify producers, predators and prey Key Stage 3 Geographical skills and fieldwork: Build on their knowledge of globes, maps and atlases and apply and develop this knowledge routinely in the classroom and in the field Genetics and evolution: differences between species Motion and forces: Speed