Tuesday
advertisement
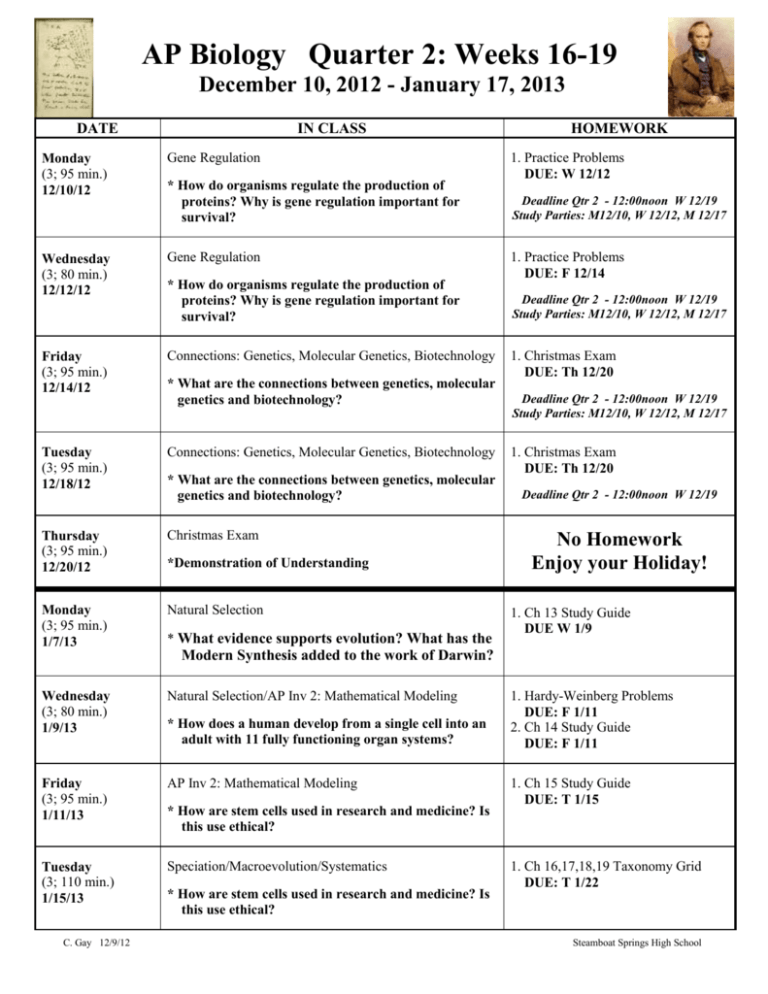
AP Biology Quarter 2: Weeks 16-19 December 10, 2012 - January 17, 2013 DATE IN CLASS Monday (3; 95 min.) 12/10/12 Gene Regulation Wednesday (3; 80 min.) 12/12/12 Gene Regulation Friday (3; 95 min.) 12/14/12 Connections: Genetics, Molecular Genetics, Biotechnology Tuesday (3; 95 min.) 12/18/12 Connections: Genetics, Molecular Genetics, Biotechnology Thursday (3; 95 min.) 12/20/12 Christmas Exam Monday (3; 95 min.) 1/7/13 Natural Selection * How do organisms regulate the production of proteins? Why is gene regulation important for survival? * How do organisms regulate the production of proteins? Why is gene regulation important for survival? * What are the connections between genetics, molecular genetics and biotechnology? * What are the connections between genetics, molecular genetics and biotechnology? *Demonstration of Understanding * What evidence supports evolution? What has the HOMEWORK 1. Practice Problems DUE: W 12/12 Deadline Qtr 2 - 12:00noon W 12/19 Study Parties: M12/10, W 12/12, M 12/17 1. Practice Problems DUE: F 12/14 Deadline Qtr 2 - 12:00noon W 12/19 Study Parties: M12/10, W 12/12, M 12/17 1. Christmas Exam DUE: Th 12/20 Deadline Qtr 2 - 12:00noon W 12/19 Study Parties: M12/10, W 12/12, M 12/17 1. Christmas Exam DUE: Th 12/20 Deadline Qtr 2 - 12:00noon W 12/19 No Homework Enjoy your Holiday! 1. Ch 13 Study Guide DUE W 1/9 Modern Synthesis added to the work of Darwin? Wednesday (3; 80 min.) 1/9/13 Natural Selection/AP Inv 2: Mathematical Modeling Friday (3; 95 min.) 1/11/13 AP Inv 2: Mathematical Modeling Tuesday (3; 110 min.) 1/15/13 Speciation/Macroevolution/Systematics C. Gay 12/9/12 * How does a human develop from a single cell into an adult with 11 fully functioning organ systems? * How are stem cells used in research and medicine? Is this use ethical? * How are stem cells used in research and medicine? Is this use ethical? 1. Hardy-Weinberg Problems DUE: F 1/11 2. Ch 14 Study Guide DUE: F 1/11 1. Ch 15 Study Guide DUE: T 1/15 1. Ch 16,17,18,19 Taxonomy Grid DUE: T 1/22 Steamboat Springs High School TuesdayThursday 1/15-17/13 8:20-10:10 10:10-10;25 10:25-12:15 12:15-1:00 1:00-2:50 SEMESTER EXAM SCHEDULE Tuesday 1 3 4 Wednesday 2 Break 6 Lunch 7 Thursday 0 5 8 Knowledge Viruses o Lytic vs lysogenic cycles, Prophage o Viral structure o Plant and animal viruses, retroviruses, reverse transcriptase Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes o Operon: regulatory genes, promoter, operator, functional genes, repressor o Types of operons: repressor (lac and tryp), activators Cellular Differentiation and Cloning in Eukaryotes o Cellular differentiation o Cloning and regeneration o Nuclear transplantation o Embryonic stem cells vs. adult stem cells Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes o DNA Packaging: histones, nucleosomes, supercoils, centromere, kinetocore, telomeres o X chromosome inactivation, Barr bodies o Control of transcription: transcription factors, enhancers, silencers, alternative RNA splicing o Control of translation: breakdown of mRNA, initiation of translation, protein activation, protein breakdown Genetic Control of Embryonic Development o Cascade of gene expression, cell-to-cell signaling, homeotic genes, regulatory protein gradients o Signal-transduction pathway o Homeobox sequences Genetic Basis of Cancer o Oncogenes, proto-oncogene, tumor suppressor genes, multiple hit hypothesis o Environmental factors: carcinogens, mutagens, lifestyle choices Evidence of Evolution o Darwin’s voyage and descent with modification o Evidence of evolution: fossil record, biogeography, comparative anatomy (homologous and analogous structures), comparative embryology, molecular biology Darwin’s Theory and the Modern Synthesis o Natural selection and artificial selection o Modern synthesis and population genetics o Microevolution o Hardy-Weinberg Principle (population size, isolation, mutations, random mating, natural selection o Genetic drift: bottleneck effect, founder effect o Gene flow o mutation Variation and Natural Selection o Polymorphic populations, clines, heterozygote advantage, neutral variation o Darwinian fitness o Types of natural selection: stabilizing selection, directional selection, diversifying selection o Sexual dimorphism o Limits of natural selection Concept of Species o Biological species concept, ring species o Other species concept: morphological species, genealogical species, ecological species o Reproductive barriers: prezygotic barriers (temporal, habitat, behavioral, mechanical, gametic), postzygotic barriers (hybrid inviability, hybrid sterility, hybrid breakdown) C. Gay 12/9/12 Mechanisms of Speciation o Geographic isolation and allopatric speciation o Adaptive radiation o Sympatric speciation and polyploidy o Gradualism vs. punctuated equillibrium Earth History and Macroevolution o Macroevolution and the geologic time scale o Radiometric dating o Continental drift: Pangea, Laurasia, Gondwana, plate tectonics o Mass extinctions o Exaptation o Evo-Devo and paedomorphosis o Phylogenetic trees and cladistics Systematics and Phylogenetic Biology o Systematic classification o Convergent evolution: homology vs. analogy o Molecular comparisons: protein comparisons, DNA and RNA comparisons, molecular clocks o Cladistic analysis The Domains of Life o Three domain system Early Earth and the Origin of Life o Early Earth environment o Origins of life, Miller-Urey o Ribozymes and RNA world o Molecular cooperatives Animal Evolution and Diversity o Characteristics of animals o Origins of the animal kingdom Invertebrates o Porifera: radial symmetry, body plan, nutrition and digestion o Cnidaria: radial symmetry, body plan, life cycle, nutrition and digestion, development o Platyhelminthes: bilateral symmetry, nutrition and digestion, flukes, tapeworms, body cavities, disease o Nematoda: body plan, nutrition and digestion, C. elegans, diseases o Mollusca: body plan, gastropods, bivalves, cephalopods o Annelida: segmentation, earthworms, polychetes, leeches o Arthropoda: body plan, horseshoe crab, arachnids, crustaceans, centipedes and millipedes, insects (types of metamorphosis) o Echinodermata: radial symmetry, body plan, water vascular system Vertebrates o Features of Chordates: nerve chord, notochord, pharengeal gill slits, post-anal tail o Tunicates and Lancelets o Vertebrates characteristics: skull and backbone, hinged jaws o Chondricthyes and Osteichthyes o Amphibians o Reptiles and amniotic eggs o Birds o Mammals: monotremes, marsupials, eutherials Phylogeny of the Animal Kingdom o Evolutionary trends: tissues, symmetry, body cavity, coelom Steamboat Springs High School C. Gay 12/9/12 Steamboat Springs High School