Immunology Notes
advertisement

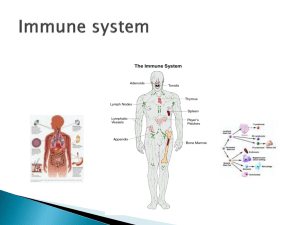
Immunology Notes 1. The Immune (Lymphatic) system: the body’s special defense response against foreign organisms: a. bacteria b. viruses c. transplants d. transfusions e. self 2. Comprised of two semi-independent parts Lymph bathes the tissues of the body and the lymphatic vessels collect and move it eventually back into the blood circulation A. lymphatic vessels which transport fluids the have escaped from the vascular system back to the blood special system of drainage vessels which weave between tissue cells and blood capillaries of nearly all tissues not found in bone, CNS, epidermis, skin, teeth, cartilage and bone marrow. Resolves problem of circulatory dynamics of lost fluids and proteins into interstitial fluid Takes in cell debris, pathogens and cancer cells Lymphangitis: inflammation of lymphatic vessels: red lines seen through skin that are tender Right lymphatic duct drains from the right upper arm, right side of the head and thorax Thoracic duct drains the lymph from the rest of the body a. Pumpless b. Very low pressure c. One way – only toward the heart Lymphedema: severe localized edema as a result of anything preventing normal return of lymph to blood i.e. tumors, mastectomy B. lymphoid tissues and organs: house phagocytic cells and lymphocytes lymph itself is comprised of water, plasma, ions and lymphoid cells Primary organs: a. Thymus gland: Found in the lower neck region and extends into thorax * Size increases through adolescence; decreases during adulthood and by old age it atrophies and is completely replaced by fatty tissues. * Produces mature T cells. Immature thymoctyes leave bone marrow and migrate into the thymus * The mature T-cells are then released into the bloodstream. The T-cells become immunocompetent by the secretion of thymosin and thymopoietin. b. Bone marrow: All the cells of the immune system are initially derived from the bone marrow. – bone marrow derived stem cells differentiate into either mature cells of the immune system or into precursors of cells that migrate out the bone marrow to continue their maturation elsewhere. c. The bone marrow produces B cells, natural killer cells, granulocytes and immature thymoctyes, in addition to red blood cells and platelets. Secondary Organs: d. Lymph nodes: found throughout the body kidney shaped and less the 2.5 cm in length composed of T and B cells, macrophages, found in inguinal, axillary, cervical regions, near gastrointestional tract filter antigens out of lymph Lymph nodes can become swollen from infection, inflammatory conditions, an abscess or cancer. Other causes of enlarged lymph nodes are rare. By far, the most common cause of swollen lymph nodes is infection. When swelling appears suddenly and is painful, it is usually caused by injury or an infection. Enlargement that comes on gradually and painlessly may, in some cases result from cancer of a tumor Which lymph nodes are swollen depends on the type of problem and the body parts involved. Identifying the location can help determine the possible cause Swollen lymph nodes may also be caused by some medications (like phenytoin for seizures) or certain vaccinations (namely typhoid). b. spleen i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. viii. located in left side of abdominal cavity largest lymphatic organ extract aged, defective blood cells, platelets removes debris, foreign matter, bacteria, viruses, toxins stores breakdown products of RBCs for reuse site of RBC production in fetus stores platelets splenectomy: surgical removal of spleen, macrophages in liver and bone marrow take over function of the spleen ix. B cells become activated and produce large amounts of antibody – lymphocyte proliferation, immune surveillance and response c. tonsils and adenoids i. ring of lymphatic tissue around the entrance to the pharynx ii. palatine, lingual, pharyngeal (adenoids) iii. have invaginations called crypts that trap bacteria and particulate matter iv. filters and prevents pathogens from entering respiratory and digestive systems d. Peyer’s Patches i. Lymph nodules found in distal potion of the ileum of the small intestine ii. Also concentrated in wall of appendix iii. Similar to tonsils iv. Destroy bacteria v. Generate “memory” lymphocytes for long term immunity e. Mucosa-Associated Lymphatic Tissue (MALT) i. Peyer’s Patches, appendix nodules, tonsils, nodules in bronchi Key Points ii. Major cells of the immune system (leukocytes/WBC’s) arise and develop in primary organs iii. Secondary organs are responsible for 1. filtering foreign substances 2. providing space for antigenic reactions