Science and Life Issues: Our Genes, Our Selves
advertisement
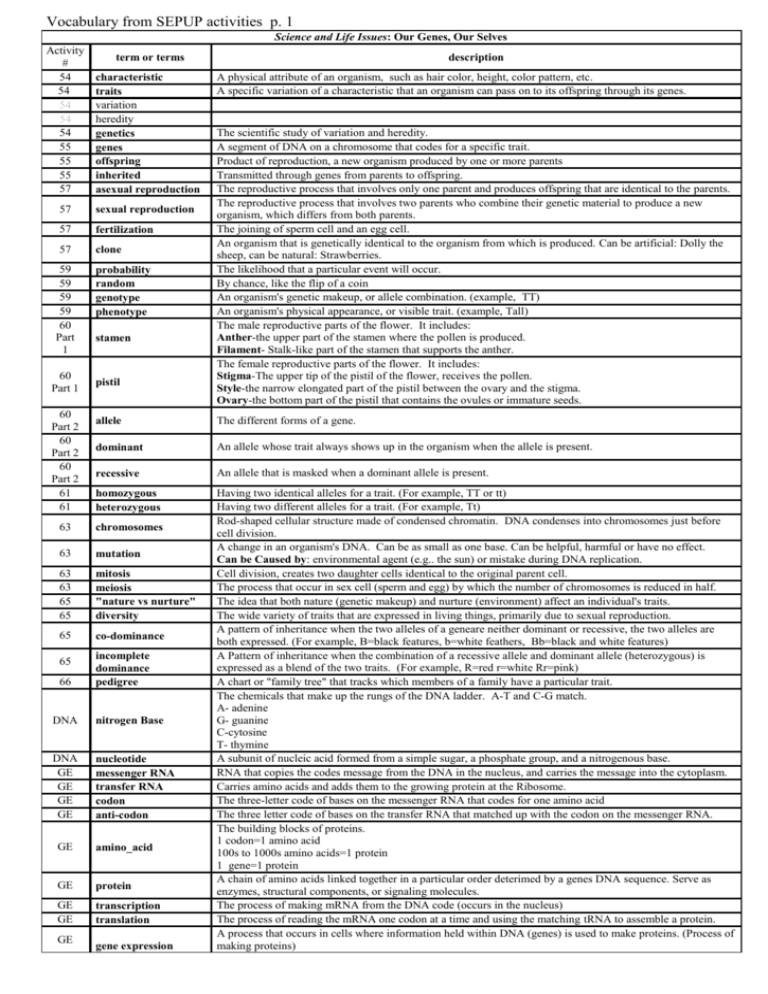
Vocabulary from SEPUP activities p. 1 Science and Life Issues: Our Genes, Our Selves Activity # 54 54 54 54 54 55 55 55 57 characteristic traits variation heredity genetics genes offspring inherited asexual reproduction 57 sexual reproduction 57 fertilization 57 clone 59 59 59 59 60 Part 1 60 Part 1 60 Part 2 60 Part 2 60 Part 2 61 61 term or terms probability random genotype phenotype stamen pistil dominant An allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present. recessive An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present. homozygous heterozygous Having two identical alleles for a trait. (For example, TT or tt) Having two different alleles for a trait. (For example, Tt) Rod-shaped cellular structure made of condensed chromatin. DNA condenses into chromosomes just before cell division. A change in an organism's DNA. Can be as small as one base. Can be helpful, harmful or have no effect. Can be Caused by: environmental agent (e.g.. the sun) or mistake during DNA replication. Cell division, creates two daughter cells identical to the original parent cell. The process that occur in sex cell (sperm and egg) by which the number of chromosomes is reduced in half. The idea that both nature (genetic makeup) and nurture (environment) affect an individual's traits. The wide variety of traits that are expressed in living things, primarily due to sexual reproduction. A pattern of inheritance when the two alleles of a geneare neither dominant or recessive, the two alleles are both expressed. (For example, B=black features, b=white feathers, Bb=black and white features) A Pattern of inheritance when the combination of a recessive allele and dominant allele (heterozygous) is expressed as a blend of the two traits. (For example, R=red r=white Rr=pink) A chart or "family tree" that tracks which members of a family have a particular trait. The chemicals that make up the rungs of the DNA ladder. A-T and C-G match. A- adenine G- guanine C-cytosine T- thymine A subunit of nucleic acid formed from a simple sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. RNA that copies the codes message from the DNA in the nucleus, and carries the message into the cytoplasm. Carries amino acids and adds them to the growing protein at the Ribosome. The three-letter code of bases on the messenger RNA that codes for one amino acid The three letter code of bases on the transfer RNA that matched up with the codon on the messenger RNA. The building blocks of proteins. 1 codon=1 amino acid 100s to 1000s amino acids=1 protein 1 gene=1 protein A chain of amino acids linked together in a particular order deterimed by a genes DNA sequence. Serve as enzymes, structural components, or signaling molecules. The process of making mRNA from the DNA code (occurs in the nucleus) The process of reading the mRNA one codon at a time and using the matching tRNA to assemble a protein. A process that occurs in cells where information held within DNA (genes) is used to make proteins. (Process of making proteins) 63 mutation 63 63 65 65 mitosis meiosis "nature vs nurture" diversity 65 co-dominance incomplete dominance pedigree DNA nitrogen Base DNA GE GE GE GE nucleotide messenger RNA transfer RNA codon anti-codon GE amino_acid GE protein GE GE transcription translation GE The scientific study of variation and heredity. A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait. Product of reproduction, a new organism produced by one or more parents Transmitted through genes from parents to offspring. The reproductive process that involves only one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parents. The reproductive process that involves two parents who combine their genetic material to produce a new organism, which differs from both parents. The joining of sperm cell and an egg cell. An organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which is produced. Can be artificial: Dolly the sheep, can be natural: Strawberries. The likelihood that a particular event will occur. By chance, like the flip of a coin An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combination. (example, TT) An organism's physical appearance, or visible trait. (example, Tall) The male reproductive parts of the flower. It includes: Anther-the upper part of the stamen where the pollen is produced. Filament- Stalk-like part of the stamen that supports the anther. The female reproductive parts of the flower. It includes: Stigma-The upper tip of the pistil of the flower, receives the pollen. Style-the narrow elongated part of the pistil between the ovary and the stigma. Ovary-the bottom part of the pistil that contains the ovules or immature seeds. The different forms of a gene. chromosomes 66 A physical attribute of an organism, such as hair color, height, color pattern, etc. A specific variation of a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes. allele 63 65 description gene expression