Concentration Activity Part 2 | 213.3KB
advertisement

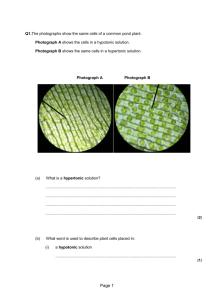
Concentration Activity Part 2 PSI Biology Name__________________________ Concentration Relationships Once we have determined the concentration of any two solutions, across a membrane, we are able to predict the diffusion of molecules. We utilize specific terminology to characterize the relationship of concentration between two solutions. Isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic solutions : The terms isotonic, hypertonic and hypotonic are usually used in reference to cells, but are also frequently used to compare the concentration of a solute in two solutions. Isotonic solutions (iso means equal) Isotonic solutions are two solutions that have the same concentration of a solute. Hypertonic solution (hyper means above or over) A hypertonic solution is one of two solutions that has a higher concentration of a solute. Hypotonic solution (hypo means under, beneath) A hypotonic solution is one of two solutions that has a lower concentration of a solute. Once we have determined, or been provided with, the concentration of two solutions, we can identify the concentration relationship between them. Examples: 1. A dialysis bag with a concentration of glucose = 10g/ml in placed into a beaker of solution with a concentration of 100g/ml. What is the concentration relationship between these two solutions? We can state this relationship in more than one way: The beaker solution is hypertonic to the bag solution. OR The bag solution is hypotonic to the beaker solution. In most cases, you will see the relationship stated as follows: The beaker solution is hypertonic OR the bag solution is hypotonic. Practice: 1. When comparing two solutions we determine that solution 1 is hypertonic. Explain what this means to the reader: www.njctl.org PSI Biology Membranes & Enzymes 2. Two solutions are isotonic to one another. What will be the net movement of glucose molecules contained in both solutions and why? Example: Adding concentration calculations to concentration relationships: 1. The illustration below represents a lab set-up. The contents of the bag and the beaker solutions can be found within the image labels. 20mg sucrose in 100ml water 20mg sucrose in 10ml water http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/story.php?title=practice-regents-2 Step one: Determine the concentration of each solution relative to sucrose. Beaker: Bag: 20mg sucrose 100 ml water = .20 g/ml sucrose 20mg sucrose 10 ml water = 2.0 g/ml sucrose Step two: Identify the concentration relationship between the beaker solution and the bag solution. The solution in the bag has a higher concentration of sucrose relative to the beaker solution. Therefore, we can identify the bag solution as hypertonic. OR The solution in the beaker has a lower concentration of sucrose relative to the bag solution. Therefore, we can identify the beaker solution as hypotonic. www.njctl.org PSI Biology Membranes & Enzymes Practice: 1. A dialysis bag has been placed into a beaker solution. The bag contains a solution of 35g NaCl in 50ml of water. The beaker solution contains 70g of NaCl in 100 ml of water. Complete step one: Complete step two: Application to osmosis and the effect on cells: The concentration of solutions inside and outside of cells becomes critical to the survival of cells. In addition, the permeability of the cell membrane plays a critical role in the effect of concentration upon cells. Utilizing the concepts of concentration relationships, we can predict how a solution may affect a cell in a given environment. Example: 1. A cell is placed into a hypotonic solution. Predict the effect of osmosis upon the cell. What we know: the solution outside of the cell has a lower concentration of solutes and therefore a higher concentration of water, than the environment inside the cell. Which way will the water diffuse? The net movement of water will be into the cell. Possible effect upon the cell: The cell will swell with incoming water, possibly even bursting, depending upon the concentration differential or gradient. www.njctl.org PSI Biology Membranes & Enzymes Practice: 1. A cell is placed into a hypertonic solution. Predict the effect of osmosis upon the cell. What we know: the solution outside of the cell has a ____________________concentration of solutes and therefore a ______________________ concentration of water, than the environment inside the cell. Which way will the water diffuse? The net movement of water will be _____________________ the cell. Possible effect upon the cell: The cell will _______________________water. 2. A cell is hypertonic to its environment. Predict the effect of osmosis upon the cell. What we know: the solution outside of the cell has a ___________________ concentration of solutes and therefore a ________________________concentration of water, than the environment inside the cell. Which way will the water diffuse? The net movement of water will be ________________________the cell. Possible effect upon the cell: The cell will ________________________ water. www.njctl.org PSI Biology Membranes & Enzymes 3. Consider the images seen below. Each represents a cell placed into an environment. There is a concentration relationship between the cell and its environment in each example. Complete the information found in the chart beneath the set of images. The cell has been The cell has been The cell has been placed into a placed into a placed into a _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ environment. environment. environment. The net movement The net movement The net movement of of water molecules of water molecules water molecules is is ___________________ is ___________________ ___________________ the cell. the cell. the cell. Possible affect of Possible affect of Possible affect of osmosis upon the osmosis upon the osmosis upon the cell: cell: cell: www.njctl.org PSI Biology Membranes & Enzymes