Concept map - Sworn Junior College
advertisement

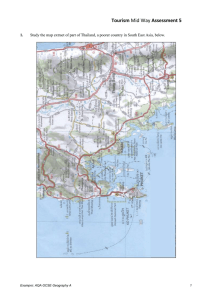
Sworn Junior College GEOGRAPHY 2nd A/ B Teachers: Lorraine Gultris Liliana Buratto 2015 1 Concept map 2 Goals The syllabus aims are to encourage students to develop: Knowledge: Students should be able to: Give definitions and explanations of relevant geographical terms and concepts Show working knowledge of relevant principles, theories and models Recall accurately the location and character of chosen places and environments Show knowledge of the physical and human processes at work Understanding and application Students should be able to: Understand the complex and interactive nature of physical and human environments Understand how processes bring changes in systems, distributions and environments Recognize the distinctiveness and the generality of places and environments Recognize the significance of spatial scale and of time scale Apply this geographical understanding to new contexts Skills and enquiry Students should be able to: Collect, record and interpret a variety of information from primary (fieldwork) sources and secondary sources (e.g. statistical data) Interpret a range of map and diagram techniques displaying geographical information Demonstrate skills of analysis and synthesis Use geographical understanding to develop their own explanations and hypotheses Evaluation and decision-making Students should be able to: Assess the effects of geographical processes and change on physical and human environments Consider the relative success or failure of initiatives and demonstrate a sense of judgment Analyze the viewpoints of different groups of people and identify conflicts of interest Assess the decision-making process in physical and human contexts Recognize a number of possible outcomes from a given situation. 3 Contents: Unit1: Economic Activities. Classification of economic activities: Primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary activities. Energy resources: Definition of resources. Types of resources: natural, human, renewable, non-renewable. Non-renewable: oil, natural gas, nuclear, fuelwood. Renewable: wind, solar energy, waves. Case study: Oil in Alaska. Farming: Farming system. Types of farming and its classification. Factors affecting farming. Farming in MEDCs and LEDCs Farming and the environment.. Industry as a system. Location of industries: industrial location factors. Growth and changing. location: high-tech industries, business and science parks. The Pacific Rim. Transnational corporations. Industry in less economically develop countries. Case study: industries in a developed city and industries in a developing city. Tourism: Recent trends and changing patterns. National Parks. Coastal and mountain resorts. Tourism in developing countries. Tourism and the environment. World development: Classification of industries. Employment structures. Differences in world development: economic wealth and social factors. Trade and interdependence. Aid. Case study: Japan – Kenya. Unit2: Weather and Climate. The atmosphere. Weather and climate. The weather elements. Their relationship. The atmospheric circulation and world climates: equatorial and tropical continental climates; the monsoon, Mediterranean and cold climates. Tropical cyclones. Global warming. Effects of global warming. Acid rain Unit 3: Land and water based hazards. Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The Earth: Internal structure. Special study of the mantle Plate tectonics. Types of plate movement. Tectonic hazards: Causes and effects of volcanic eruption in MEDCs and LEDCs. Causes and effects of earthquakes in MEDCs and LEDCs. Flooding. Drainage basins. River discharge and flood hydrographs. River processes. River landforms. Flooding. . Drainage basins management Soil erosion. Desertification 4