lyons chem test term2
advertisement

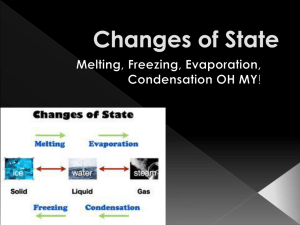
TERM 2: SCIENCE TEST PREPARATION CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL CHANGES Go and do these quiz question http://dimdima.com/science/Quiz/show_quiz.asp?q_aid=13&q_title=States%20of%20Matter http://www.chem4kids.com/extras/quiz_matterstates/index.html Quiz 1) Use this Venn Diagram to compare & contrast the three states of matter 1. Why is melting sugar a physical change but burning sugar is chemical change? 2. What is required for matter to change from one state to another? 3. What happens to most solids when they freeze? SOLUBILITY IN WATER 1. Circle items that are soluble in water Oil, sugar, salt Red means answer 2. Colloids are solutions with very small particles suspended in a liquid. True False. 3. The concentration of solutions is directly related to... Solubility Temperature Pressure All of the Above. 4. Name two situations were chemical changes cause damage to items. 5. Name two situations when chemical changes are useful for creating substances. FREEZING, MELTING AND PRESSURE Identify chemical and physical change in daily activities. 1. Making a cake 2. Rotting fruit or food spoiling 3. Water evaporating into the atmosphere 4. Soil erosion 5. Boiling an egg 6. Butter melting in a pan 7. Soda freezing in the freezer 8. Making bread 9. Plants decaying 10. Silver tarnishing 11. Chocolate bar melting in the sun 12. Chopping a block of wood in two pieces 13. Burning wood 14. Driving a nail in a board 15. Digesting food 16. Blowing up a balloon 17. Popping popcorn 1. How does pressure affect freezing point? 2. Can you suggest why water expands when it is frozen? REVERSIBLE CHANGES BOILING, EVAPORATING AND CONDENSING? 1. Identify the following situations as reversible or irreversible changes. 1. When peas are frozen they go hard. 2. When whisked egg is heated it scrambles. 3. When bicarbonate is added to water it fizzes. 4. When an ice cream is left in the sun it melts. 5. When custard powder is mixed with water it thickens. 6. When iron is exposed to water it goes rusty. 7. When bath salts are added to water they dissolve. 8. Write about two irreversible changes which cause damage. 9. Write about one irreversible change that is considered as useful. Identify the following situations in terms of Condensation or Evaporation 1. If you spill a little petrol on the ground at the petrol station, it rapidly disappears. 2. Paint dries on walls after a few hours. 3. When you spray perfume on your body, it feels cold. 4. When you breathe on the inside of the window when it is cold outside, a mist appears. 5. Sometimes it rains for a short time in the morning, but by the afternoon the puddles have disappeared. 6. On a rainy day the car windscreen mists up. 7. When you boil potatoes in the kitchen, water droplets run down the windows or walls. 8. Clouds form on a hot day over the sea. 9. Water keeps flowing into the Dead Sea, but the level is slowly dropping. Changing state 1. What happens during evaporation? A gas changes to a liquid A solid changes to a liquid A liquid changes to a gas 2. Butter going soft and runny on a hot day is an example of freezing melting condensing 3. What is the missing word? When water is...., it starts to change from a liquid to a solid. cooled heated boiled 4. Clouds are formed by rain falling hot air rising water vapour condensing 9. The movement of water around and around our world is called... condensation the water cycle evaporation 5. We use the same water today that dinosaurs used when they lived on the Earth. Is this true or false? True False Neither 6. A gas condenses into a liquid when it is... cooled warmed boiled 7. Which process is the opposite of condensation? Melting Freezing Evaporation 8. Which of these statements is FALSE? Evaporation is a change that can be reversed Evaporation only happens at 100°C Evaporation is helped by heat and by wind 10. Which of these is NOT a part of the water cycle? The Sun evaporates water on the Earth's surface into water vapour The water vapour rises, and cools and condenses into clouds When it rains, the clouds melt Gases, liquids and solids 1. Which of the following is NOT a gas? Air Car exhaust fumes The sea 2. You blow up a balloon. Is it heavier or lighter than the uninflated balloon? Heavier Lighter They weigh the same 3. When you squeeze a sponge under water, what are the bubbles that escape? Pieces of sponge 6. To change a solid metal to a liquid, you would heat it cool it bend it 7. Which of these is NOT an example of a solid? Dust Runny honey Gravel 8. Which one of these best describes a solid? My particles are packed tightly together. I keep my shape. My particles are loosely packed. I take the shape of my container. Air coming from the spaces in the sponge My particles have lots of room. I try to spread out in every direction. Water 9. Which one of these best describes a liquid? 4. Which material is a liquid? Sponge Shampoo Salt 5. Which material is a solid? Syrup Cooking oil My particles are packed tightly together. I keep my shape. My particles are loosely packed. I take the shape of my container. My particles have lots of room. I try to spread out in every direction. 10. Which one of these best describes a gas? My particles are packed tightly together. I keep my shape. My particles are loosely packed. I take the shape of my container. Cotton wool My particles have lots of room. I try to spread out in every direction.