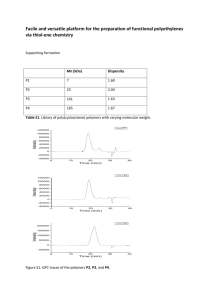
pubdoc_2_24205_775
advertisement

Synthetic Biodegradable Polymers: Biodegradable polymers offer the advantage of being able to be eliminated from the body after fulfilling their intended use. Therefore, avoid the usual costly and complicated procedures to remove the implants or scaffolds. It is not surprising that biodegradable biomaterials are becoming more and more important in biomaterials and tissue engineering field. In this chapter, some of the important synthetic polymers will be reviewed. Several biodegradable polymers such as polylactide (PLA), polyglycolide (PGA), poly(glycolide-co-lactide) (PLGA), poly(dioxanone), poly(trimethylene carbonate), poly(carbonate), and so on have been used extensively or tested on a wide range of medical applications due to their good biocompatibility, controllable biodegradability, and relatively good processability. PLA, PGA, and PLGA are bioresorbable aliphatic polyesters belonging to the group of poly α-hydroxy acids. These polymers degrade by nonspecific hydrolytic scission of their ester bonds. 1- Poly(glycolide): Poly( glycolide) (PGA) is synthesized through the ring opening polymerization of glycolide to yield high-molecular-weight materials. The monomer glycolide is synthesized from the dimerization of glycolic acid. PGA is the simplest linear aliphatic polyester. It is highly crystalline (45% 55%) with a high melting point (220°C -225°C) and a glass transition temperature of 35°C -40°C. Because of its high degree of crystallization, it is not soluble in most organic solvents except for highly fluorinated organic solvents such as hexafluoroisopropanol. PGA Fibers exhibit high strength and modulus because of its high degree of crystallinity. But it is too stiff to be used as sutures except as braided material. PGA was used to develop the first totally synthetic absorbable suture that has been marketed as Dexon since the 1960s by Davis and Geek. Sutures of PGA lose about 50% of their strength after two weeks and 100% after four weeks and are completely absorbed in 4 - 6 months. PGA biodegrades by a combination of hydrolytic scission and enzymatic (esterase) action producing glycolic acid which either can enter the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle to be finally excreted by the body as carbon dioxide and water or is excreted in urine . Glycolide can be copolymerized with other monomers, such as lactide and trimethylene carbonate, to yield copolymer with various mechanical and biodegradation properties for different applications.