Geologic Time Study Guide Name: Sedimentary rocks record past
Geologic Time Study Guide Name:____________________
1.
Sedimentary rocks record past geological events and what other important information?
2.
Give me an example of a geologic event that could be recorded in rocks.
3.
What scientist proposed the principle of uniformitatrianism? What does this principle state?
4.
The statement “the present is key to the past” rephrases what principle?
5.
What types of rocks would geologists most likely find evidence of past life forms?
6.
What is the principle of cross-cutting relationships?
7.
What is the law of superposition?
8.
What dating process places geologic events in proper sequence?
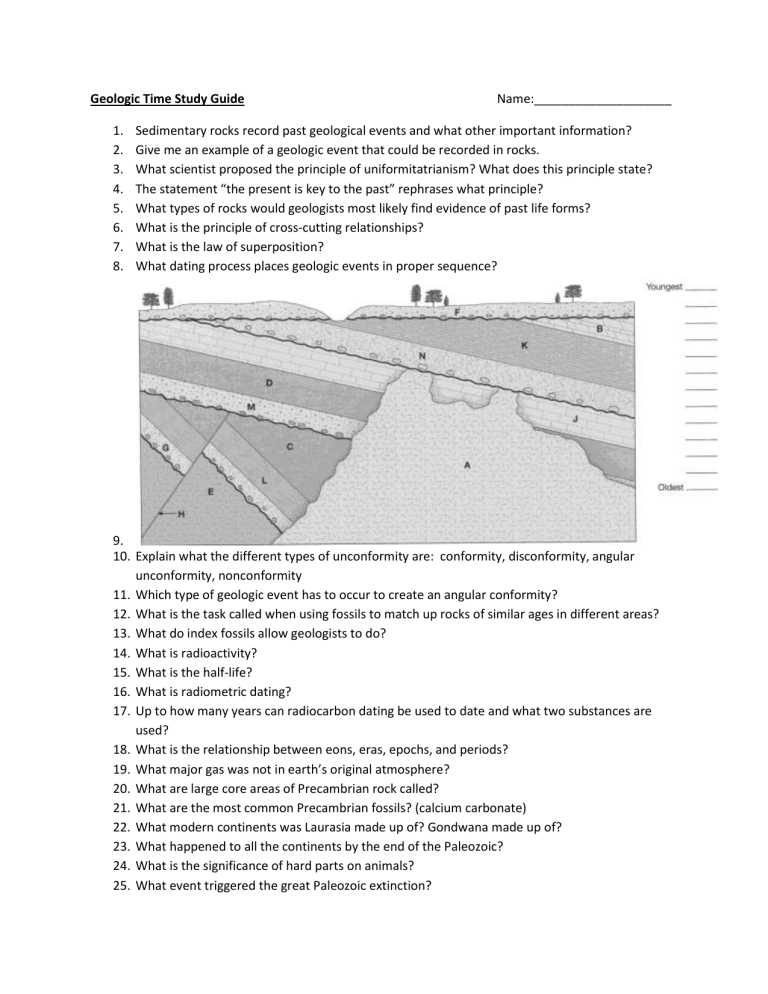
9.
10.
Explain what the different types of unconformity are: conformity, disconformity, angular unconformity, nonconformity
11.
Which type of geologic event has to occur to create an angular conformity?
12.
What is the task called when using fossils to match up rocks of similar ages in different areas?
13.
What do index fossils allow geologists to do?
14.
What is radioactivity?
15.
What is the half-life?
16.
What is radiometric dating?
17.
Up to how many years can radiocarbon dating be used to date and what two substances are used?
18.
What is the relationship between eons, eras, epochs, and periods?
19.
What major gas was not in earth’s original atmosphere?
20.
What are large core areas of Precambrian rock called?
21.
What are the most common Precambrian fossils? (calcium carbonate)
22.
What modern continents was Laurasia made up of? Gondwana made up of?
23.
What happened to all the continents by the end of the Paleozoic?
24.
What is the significance of hard parts on animals?
25.
What event triggered the great Paleozoic extinction?
26.
Which period is known as the “age of fishes”?
27.
Why did amphibians diversify so rapidly in the late Paleozoic?
28.
During which era did the supercontinent Pangaea begin to break up?
29.
How did the Rocky Mountains form? (it’s in your notes)
30.
Life was restricted to what environment during the early Paleozoic?
31.
What dominated the Mesozoic era?
32.
What is the significance of Archaeopteryx?
33.
What most likely killed the dinosaurs?
34.
What are the 2 main periods of the Cenozoic and how many years do each encompass?
35.
How are mammals different than reptiles? (List 3)
36.
Where was most of North America during the Cenozoic?
37.
Draw a mini timeline of the Phanerozoic Eon and include the years.