Glands

Independent work.
Human Body
The human body is the entire structure of a human being and comprises a head, neck, trunk (which includes the thorax and abdomen), arms and hands, legs and feet. Every part of the body is composed of various types of cell.
At maturity, the estimated average number of cells in the body is given as 37.2 trillion. This number is stated to be of partial data and to be used as a starting point for further calculations. The number given is arrived at by totalling the cell numbers of all the organs of the body and cell types. The composition of the human body is made up of a number of certain elements including carbon, calcium and phosphorus.
The study of the human body involves anatomy and physiology. The human body can show anatomical non-pathological anomalies known as variations which need to be able to be recognised. Physiology focuses on the systems and their organs of the human body and their functions. Many systems and mechanisms interact in order to maintain homeostasis.
Muscles
Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.
Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command.Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.
Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers.
These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.
The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning "little mouse" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.
Hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis, or skin.
Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair. Most common interest in hair is focused on hair growth, hair types and hair care, but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably keratin. Attitudes towards hair, such as hairstyles and hair removal, vary widely across different cultures and historical periods, but it is often used to indicate a person's personal beliefs or social position, such as their age, gender, or religion.
Teeth
A tooth (plural teeth) is a small, calcified, whitish structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores, also use teeth for hunting or for defensive purposes. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness. The cellular tissues that ultimately become teeth originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm.
The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, such as sharks, the teeth are attached by tough ligaments to the hoops of cartilage that form the jaw.
Some animals develop only one set of teeth (monophyodont) while others develop many sets (polyphyodont). Sharks, for example, grow a new set of teeth every two weeks to replace worn teeth. Rodent incisors grow and wear away continually through gnawing, which helps maintain relatively constant length.
The industry of the beaver is due in part to this qualification. Many rodents such as voles (but not mice) and guinea pigs, as well as leporidae like rabbits, have continuously growing molars in addition to incisors.
Teeth are not always attached to the jaw, as they are in mammals. In many reptiles and fish, teeth are attached to the palate or to the floor of the mouth, forming additional rows inside those on the jaws proper. Some teleosts even have teeth in the pharynx. While not true teeth in the usual sense, the denticles of sharks are almost identical in structure, and are likely to have the same evolutionary origin. Indeed, teeth appear to have first evolved in sharks, and are not found in the more primitive jawless fish - while lampreys do have tooth-like structures on the tongue, these are in fact, composed of keratin, not of dentine or enamel, and bear no relationship to true teeth.Though "modern" teeth-like structures with dentine and enamel have been found in late conodonts, they are now supposed to have evolved independently of later vertebrates' teeth.
Living amphibians typically have small teeth, or none at all, since they commonly feed only on soft foods. In reptiles, teeth are generally simple and conical in shape, although there is some variation between species, most notably the venom-injecting fangs of snakes. The pattern of incisors, canines, premolars and molars is found only in mammals, and to varying extents, in their evolutionary ancestors. The numbers of these types of teeth varies greatly between species; zoologists use a standardised dental formula to describe the precise pattern in any given group.
Eyes
Eyes are the organs of vision. They detect light and convert it into electrochemical impulses in neurons. The simplest photoreceptor cells in conscious vision connect light to movement. In higher organisms the eye is a complex optical system which collects light from the surrounding environment, regulates its intensity through a diaphragm, focuses it through an adjustable assembly of lenses to form an image, converts this image into a set of electrical signals, and transmits these signals to the brain through complex neural pathways that connect the eye via the optic nerve to the visual cortex and other areas of the brain. Eyes with resolving power have come in ten fundamentally different forms, and 96% of animal species possess a complex optical system. Image-resolving eyes are present in molluscs, chordates and arthropods.
The simplest "eyes", such as those in microorganisms, do nothing but detect whether the surroundings are light or dark, which is sufficient for the entrainment of circadian rhythms.From more complex eyes, retinal photosensitive ganglion
cells send signals along the retinohypothalamic tract to the suprachiasmatic nuclei to effect circadian adjustment.
Glands
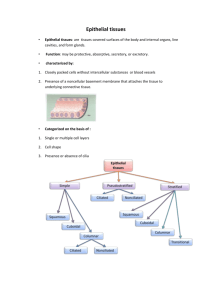
A gland is an organ in an animal's body that synthesizes a substance such as hormones for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland).
Glands are divided based on their function into two groups:
Endocrine glands
Endocrine glands secrete substances that circulate through the blood stream.
These glands that secrete their products through the basal lamina into the blood stream and lack a duct system. These glands often secrete hormones, and play an important role in maintaining homeostasis. The pineal gland, thymus gland, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, and the two adrenal glands are all endocrine glands.
Exocrine glands
Exocrine glands secrete their products through a duct onto an outer surface of the body, such as the skin or the human gastrointestinal tract. Secretion is directly onto the apical surface. The glands in this group can be divided into three groups:
Apocrine glands a portion of the secreting cell's body is lost during secretion.
Apocrine gland is often used to refer to the apocrine sweat glands, however it is thought that apocrine sweat glands may not be true apocrine glands as they may not use the apocrine method of secretion.
Holocrine glands the entire cell disintegrates to secrete its substances (e.g., sebaceous glands)
Merocrine glands cells secrete their substances by exocytosis (e.g., mucous and serous glands). Also called "eccrine".
The type of secretory product of exocrine glands may also be one of three categories:
Serous glands secrete a watery, often protein-rich product.
Mucous glands secrete a viscous product, rich in carbohydrates (e.g., glycoproteins).
Sebaceous glands secrete a lipid product.These glands are also known as oil glands.