Transport Study Guide Key
advertisement

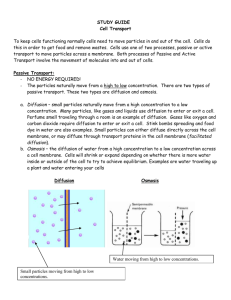
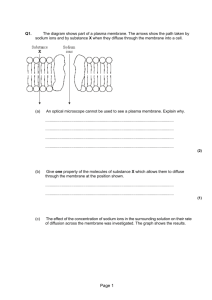
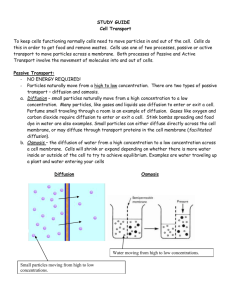
Cell Transport Test Study Guide KEY 1. What three things can affect the rate of diffusion? a. Temperature b. Pressure c. Concentration 2. What are the three types of proteins found in the cell membrane? a. Markers b. Receptors c. Channels 3. Name and define the 3 types of passive transport. a. Diffusion: when particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration b. Osmosis: when water moves from an area of high concentration of water to a low concentration of water c. Facilitated diffusion: when particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a protein channel in the membrane 4. Name and define the 3 types of active transport. a. Active transport: when particles move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration b. Endocytosis: when the membrane takes particles into the cell via vesicles (enter the cell) c. Exocytosis: when the membrane removes particles from the cell via vesicles (exit the cell) Fill in the blanks. 5. Passive transport is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. 6. Active transport needs energy (ATP) in order to function because molecules move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. 7. Give an example for the following terms: a. Diffusion: nutrients moving into the cell through the lipid bilayer b. Osmosis: water moving out of a cell in a salt water solution c. Active Transport (protein type): sodium potassium pump d. Facilitated diffusion: sugar molecules moving into the cell via a protein channel 8. Name and define the two types of endocytosis. a. Phagocytosis: the process of the cell ingesting particles into the cell via vesicles b. Pinocytosis: the process of the cell ingesting liquids into the cell via vesicles 9. Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Definition High concentration of solute in a solution Equal amount of solute in a solution Low amount of solute in a solution Example of solution Salt water Saline Distilled water What happens to cell Shrink Stays the same Swells and may burst 10. What are the 4 steps of the Sodium-Potassium pump and what is necessary for this process to happen? a. Three sodium ions enter the protein channel b. ATP binds to protein channel and it changes shape allowing the sodium ions OUT of the cell c. Two potassium ions enter the protein channel d. ATP binds to the protein channel and it changes shape allowing the potassium ions INTO the cell 11. Why do doctors inject saline solution into your veins instead of just water if you were dehydrated? Saline is an isotonic solution and has equal amount of water and other ions in it similar to your blood cells. If you were injected with pure water, this would put your blood cells into a hypotonic solution and your red blood cells would swell and potentially burst.