Cellular Transport Vocabulary
advertisement

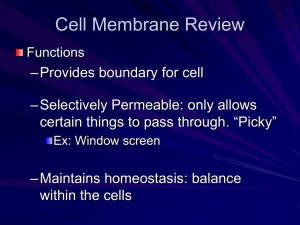
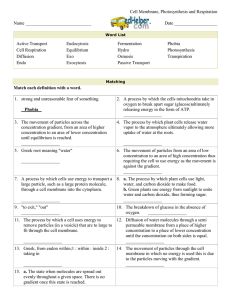
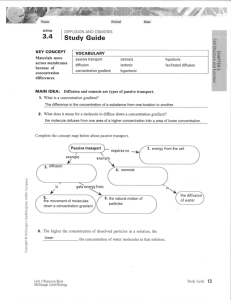
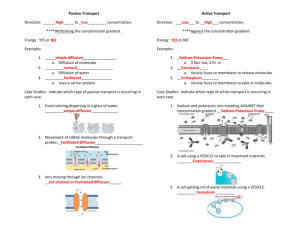
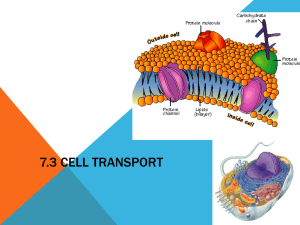
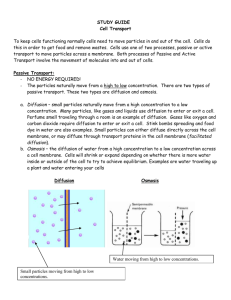
The following document is a running list of vocabulary terms for the Carbohydrate, Lipid and Protein unit for Biology. The unit is one of the larger units and contains a lot of vocabulary to keep straight. In order the help the students I have created this study option for home. Key terms will be added as we introduce them in class- I will put the new terms in a new chart to cut down on printing waste, but the same document will be sent home each time. A copy of this document will also be posted on my teacher website located at: http://www.greenwoodsd.org/Page/1009 To use as Flash Cards: 1. Cut only on solid lines. 2. Fold the card on the dotted line and put a small piece of tape on the open end to secure and make the flash card that should show the definition on one side and the vocabulary word on the other. To Use a Matching Activity: 1. Cut the chart apart completely by cutting on all lines. 2. Have your child mix up the cards and try to match the correct definition with the correct vocabulary term. (A second chart can be printed to act as a key) Fluid Mosaic Describes the cell membrane. Fluid due to movement of phospholipids and mosaic due to different molecules such as proteins embedded in the phospholipids Selective Permeability Allows some but not all particles/molecules to pass through Phospholipids Make up the cell membrane. Fluid. Hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails Protein Pore An open protein that allows certain particles to pass through the cell membrane based on size and shape Protein Pump A pump in the cell membrane which helps move particles during active transport from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration Protein Channel A protein that binds to a signal molecule and triggers a cellular response; based on size and shape Protein Receptor A protein that detects a signal and acts because of it. Ex: Insulin Diffusion The movement of molecules from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration (no energy required) Facilitated diffusion The movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to low concentration using transport proteins Osmosis The diffusion of water from hypotonic areas to hypertonic areas Hypertonic Higher concentrations of particles hypotonic Lower concentrations of particles Isotonic A cell has the same concentration of particles inside and out or moves at an equal rate Passive Transport The movement of molecules down the concentration gradient from high to low without using energy Active Transport The movement of molecules up their concentration gradient from low to high using energy Concentration Gradient The difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another Endocytosis The use of a vesicle to move larger particles across the cell membrane so they may ENter the cell Exocytosis The use of a vesicle to move larger particles across the cell membrane so that they may EXit the cell