Gregor Mendel
advertisement

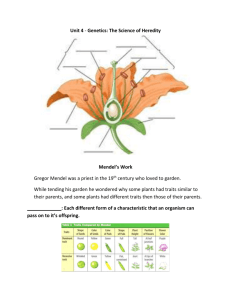
__________________ ____________________ was an Austrian monk. While living at his monastery, he became interested in the study of _______________ (botany). He used the abbey _____________________ to perform his experiments. Father of Genetics: The basic laws of ____________________ were first formed during the mid ________________ by Mendel. His work laid the ________________________ to the further study of heredity. He is often referred to as “The __________________ of Genetics”. Mendel based his studies on garden _____________ __________________. They are easy to grow, and have many ______________________ traits. In a relatively short time, Mendel was able to see ___________________ in these traits over many ____________________ of plants. Pea plants have many visible traits such as: plant height, ______________ or ______________, seed color: ______________ or __________________, pod shape: ______________ or ___________________, pod color: ____________________ or _________________, seed shape: _________________ or _____________________. Mendel’s Experiments: Mendel noticed that some plants always produced _________________ that had a form of a trait exactly like the parent plant. He called these plants __________________ plants. For instance, purebred short plants ___________________ produced short offspring, and ____________________ tall plants always produce _______________ offspring. First experiment: Mendel crossed purebred plant with __________________ forms of a trait. He called these plants the _______________________ ______________________________, or P generation. For example, purebred tall plants were ________________ with purebred short plants. Mendel observed that all of the offspring grew to be _______________ plants. None resembled the short parent. He called this generation of offspring the _________________ ________________, or F1 generation. Second experiment: Mendel then crossed two of the offspring ______________ plants produced from his first experiment. Mendel called this second generation of plants the ________________________________________. To his surprise, Mendel observed that this generation had a mix of ________________ and ____________________ plants. This occurred even though none of the F1 generation plants were short. Law of Segregation. Mendel’s First law, the _______________ _____ _____________________ has three parts. Mendel concluded that: 1. Plant traits are handed down through ____________________ _______________________. 2. Because offspring obtain hereditary factors from both parents, each plant must contain ______________ ________________ for every trait. 3. The factors in a pair _________________ during the formation of sex cells. Dominant and Recessive Genes. Mendel went on to reason that one ____________ (gene) in a pair may mask, or hide, the other factor. For instance, in his first experiment, when he crossed a ___________________________ tall plant with a _______________________ short plant all of the offspring were _______________. Although all of the offspring had both tall and short factors, they only displayed the _____________ factor. He concluded that the tallness factor masked the shortness factor. Today, scientists refer to these ‘factors’ as _______________. The different forms of a gene are called __________________. Alleles that mask or hide other alleles such as the tall allele are said to be ___________________. A ________________ allele, such as the short allele, is masked or covered up whenever the dominant allele is present. Homozygous genes. What Mendel referred to as a “purebred” plant, we now know this to mean that the plant has ____________ identical genes for a particular trait. For example, a purebred tall plant has two genes for ____________, and a purebred short plant has two genes for _______________. The modern scientific term for purebred is _______________________. According to Mendel’s Law of Segregation, each parent donates ___________ height gene to the offspring. Since each parent had only short genes to donate, all of the offspring will also have ____________ short genes (homozygous), and will therefore be short. Heterozygous genes. In Mendel’s first experiment, F1 offspring received one __________ gene and one ______________ gene from the parent plants. Therefore, all offspring contained both _______________, a short and a tall allele. When both alleles are present, the plant is said to be a hybrid for that trait. The modern scientific term for hybrid is ________________________. Although the offspring have both a ___________ and a ____________ allele, only the tall allele is expressed and is therefore ______________________ over short.





![Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide Heredity [12/10/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006638861_1-0d9e410b8030ad1b7ef4ddd4e479e8f1-300x300.png)