BIOS 1300 SI WORKSHEET 1 (Chapter 1) SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries
advertisement

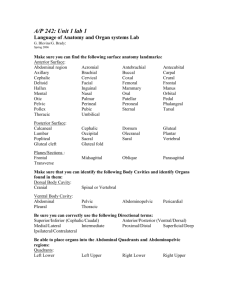
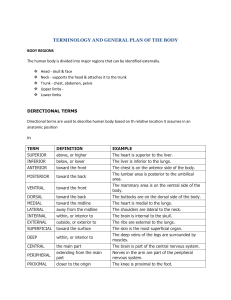
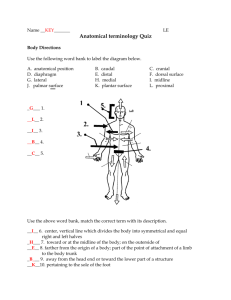
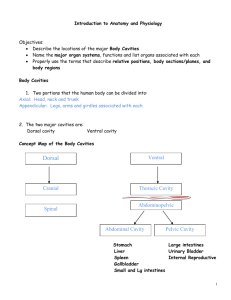
BIOS 1300 SI WORKSHEET 1 (Chapter 1) SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries September 2, 2014 REMEMBER: *Anatomy is the study of internal and external body structures *Physiology is the study of how living organisms perform functions *ALL SPECIFIC FUNCTIONS ARE PERFORMED BY SPECIFIC STRUCTURES!!! 1.What is the difference between gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy? 2. The study of the structure of tissues is called: (circle one) a. Gross Anatomy b. Cytology c. Histology d. Organology 3.Identify major levels of organization from the simplest to the most complex. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 4.Define homeostasis and explain why homeostatic regulation is important to an organism. 5.When homeostasis fails, organ systems function less efficiently or even malfunction. The result is the state we call disease. If the situation is not corrected, death can be a result. T/F 6.Explain the function of negative feedback systems and also briefly explain how a positive feedback system works and differs from a negative feedback system. 7.Increased pressure in the aorta triggers mechanisms to lower blood pressure. This is an example of _______________ feedback. 8.The increasingly forceful labor contractions during childbirth are an example of __________________ feedback. 9.Increased blood sugar stimulates the release of a hormone from the pancreas that stimulates the liver to store blood sugar. This is an example of ______________ feedback 10.A rise in blood calcium levels triggers the release of a hormone that lowers blood calcium levels. This is an example of ________________ feedback. 11.A homeostatic regulatory mechanism consists of three parts. List and briefly explain each of these parts. 1. 2. 3. 12.When the body continuously adapts by utilizing homeostatic systems, it is said to be in a state of __________________ equilibrium. 13.Define the term “gradient”. 14.If matter or energy moves from the point where a certain variable has a _________________value to the point with a ________________value, we say it flows DOWN the concentration gradient. 15.Movement of matter or energy from a LOWER value to a HIGHER value explains movement ___________ a concentration gradient (Hint: This process requires an input of energy) 16.List the 4 types of gradients we encounter in biological systems and state the direction in which matter and energy universally flow. 1. 2. 3. 4. - Universally, matter and energy flow ________________ gradients 17.What is the purpose of anatomical terms? 18.The Ventral Body Cavity is subdivided into the Thoracic Cavity and the ______________________ Cavity. These two cavities are separated by, the respiratory muscle, known as the __________________. 19.The Thoracic cavity is subdivided into the left and right pleural cavities, separated by the __________________. 20.In the Thoracic cavity the Pericardial membrane (serous membrane) surrounds the _______________, whereas, the pleura surrounds the ____________. 21.Between the visceral and parietal pericardium lies the _______________ _____________and between the parietal and visceral pleura lies the _______________ ________________. 22.Between the visceral and parietal peritoneum, of the Abdominopelvic cavity, lies the _____________ _____________. 23.In which body cavity would you find each of the following organs? 1. Heart 2. Small intestine and Large intestine 3. Lungs 4. Kidneys 24.Which of the planes passes through the body at a slant or an angle