3.1 Worksheet
advertisement

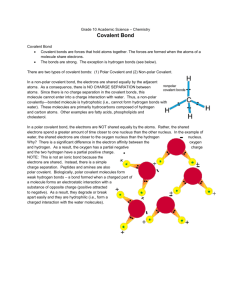
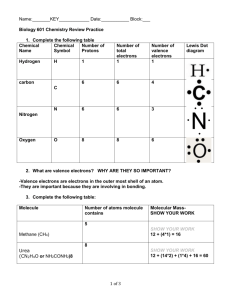
What 6 elements make up over 90% of all biological material? NCHOPS Ionic bond (transfer of electrons) vs. covalent bond (sharing of electrons) List the 5 characteristics of living things Metabolize, reproduce, evolve, organized, and respond to environment List the biological organization in order of complexity starting with the least complex Atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystem, biosphere Electronegativity: Attraction of an atom for its valence electrons Polar covalent bond: Two atoms share electrons unequally Water: partial charges due to water’s higher electronegativity Describe the properties of water that contribute to the upward movement of water in a tree? Adhesion- Clinging of one substance to another (water to cellulose) Cohesion- Hydrogen bonds used to hold water molecules to others How can the freezing of water crack boulders? Water expands when it freezes due to hydrogen bonds becoming more stable and creating more space between molecules. It liquid water were to run into a crack in the boulder and froze, it would expand inside the rock. Many mammals control their body temperature by sweating. Which property of water is most directly responsible for the ability to sweat to lower body temperature? a) Water’s change in density due to temperature b) Water’s high surface tension c) The release of heat by the formation of hydrogen bonds d) The absorption of heat by the breaking of hydrogen bonds (hydrogen bonds must be broken to vaporize) The bonds that are broken when water vaporizes are a) Ionic b) Hydrogen c) Covalent d) Polar covalent e) Nonpolar covalent Measurements show that the pH of a particular lake is 4.0. What is the hydrogen ion concentration of the lake? a) 4.0 M b) 104 M c) 10-7 M d) 10-4 M What is the hydroxide concentration of the lake described in the previous question? a) 10.0 M b) 10-10 M c) 10-7 M d) 10-12 M Which of the following would contain a polar covalent bond? a) Cl2 b) NaCl c) H2O d) CH4 e) C6H12O6 The partial negative charge at one end of a water molecule is attracted to a partial positive charge of another water molecule. What is this type of attraction called? Hydrogen bond If the pH of a solution is decreased from 7 to 6, it means the conc. of H+ has increased 10 times what it was at pH 7 Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids? Carboxyl and amine Organic compounds contain Carbon Structural isomers: differ in arrangement of atoms and location of double bonds Geometric isomers: same covalent partnership, but differ in spatial arrangement about a double bond Enantiomers: differ in spatial arrangement around a middle carbon (mirror images) Most amino acids