Genetics and Inheritance Test Review
advertisement

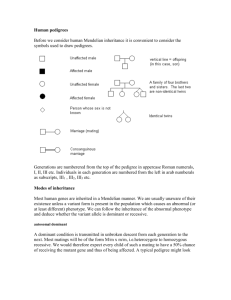
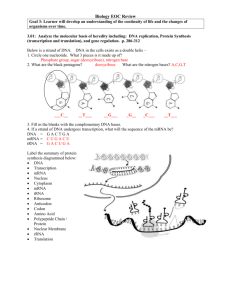
Genetics and Inheritance Test Review Name___________________________________________ Test Info: 35 multiple choice Questions, 3 Short answers Honors: Different test with 35 multiple choice and 5 short answers Period_______________________ 1. 2. Mitosis: a. What are the phases and what occurs during the phases? b. What types of cells are produced and why? c. Where does it occur? d. Type of reproduction: Meiosis: a. What are the phases and what occurs during the phases? i. Meiosis I ii. Meisosis II b. What types of cells are produced and why? c. Where does it occur? d. Type of reproduction: 3. Which type of reproduction results in increased genetic variation? 4. Describe the process occurring in the picture to the left 5. Explain how crossing over increases genetic variation? 6. What happens to sister chromatids in anaphase of meiosis II? 7. What types of cells are Haploid? Where are they found? 8. What types of cells are Diploid? Where are they found? 9. Two similar chromosomes that you inherit from your parents (one from your mother, one from your father) are called? 10. How many chromosomes does a human inherit from their mother? How many autosomes and how many sex chromosomes? 11. Describe what happens before, during and after DNA replication has taken place 12. At what point in the cell cycle does DNA replication occur and why? 13. Four different segments of a DNA molecule are represented below. There is an error in the DNA in which molecule? 14. What could cause a mutation in DNA? 15. Identify the process shown at point Z? 16. What type of RNA molecule carries amino acids to the site of protein synthesis 17. Describe the structure and function of DNA. 18. Describe the structure and function of RNA. 19. Describe the direction of transfer of genetic information in most living things using the terms, Protein, DNA, mRNA, tRNA. 20. The process of synthesizing mRNA along a DNA template is called… 21. Brown eye color is dominant; blue is recessive. If a brown-eyed man marries a blue-eyed woman and they have a browneyed boy and a blue-eyed girl, we can safely conclude… A. the man is not the true father. B. the man is heterozygous. C. eye color is sex-linked. D. both parents are homozygous. 22. John has genotype NN. His genotype would best be described as: 23. When crossing a homozygous recessive with a heterozygote, what is the chance of getting an offspring with the homozygous recessive phenotype? 24. Black fur in mice (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). Short tails (T) are dominant to long tails (t). What fraction of the progeny of the cross BbTt X BBtt will have black fur and long tails? 25. In snapdragons, heterozygotes have pink flowers, whereas homozygotes have red or white flowers. When plants with red flowers are crossed with plants with white flowers, what proportion of the offspring will have pink flowers? 26. Homozygous dominant guinea pigs are white. Homozygous recessive guinea pigs are black. Heterozygous guinea pigs are spotted with both black and white. This is an example of… 27. In 1944 Charlie Chaplin was involved in a legal battle over the paternity of a child born to Joan Berry, a young starlet. The baby was blood type B, the mother A, and Chaplin O. From what you know about the inheritance of blood types, could Chaplin have been the father of the child? (At the time of the trial, blood group evidence was not admissible in California courts. Charlie Chaplin was declared responsible for the child's support.) 28. Huntington's disease is caused by a dominant allele. If one of your parents has the disease, what is the probability that you, too, will have the disease? 29. What term describes the physical traits of a person? 30. Why are there so many phenotypes in polygenic inheritance? 31. A man with type A blood mates with a female with type B blood. Without any other info, what are all possible blood types of the offspring? 32. The idea that for any particular trait, the pair of alleles of each parent separate and only one allele from each parent passes to an offspring is Mendel's principle of: 33. Consider the following pedigree. The most likely mode of inheritance is: Autosomal recessive, Autosomal dominant, X-linked recessive, or X-linked dominant 34. This diagram shows a pedigree for a recessive genetic disorder. What is the genotype of individual 6? 35. Widow’s peak is an autosomal dominant condition. The pedigree given shows a family in which shaded individuals have the condition. Explain the pedigree.