Chapter One Outline Cells: The Building Blocks of Life I. What is life
advertisement

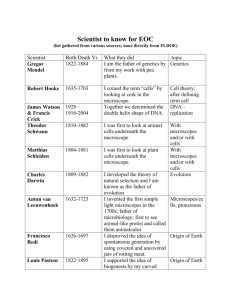
Chapter One Outline Cells: The Building Blocks of Life I. What is life? A. Characteristics of Living Things __________________________________ - living things *All living things have a cellular organization, contain similar chemicals, use energy, grow & develop, respond to their surroundings and ______________________________. 1. Cellular Organization a. _____________________ - basic unit of structure and function on an organism. b. _____________________ -single celled organisms (ex. ______________________) c. Multicellular -____________________________________________________________ 2. Chemicals of Life The most abundant chemical is ____________________________. Other chemicals include carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. 3. ____________________________ __________________ 4. Growth and Development _________________________ is a process of change during an organism’s life to produce a more complex organism. 5. Response to Surroundings __________________________ is a change in an organism’s surroundings that causes an organism to react. (Give me an example of a stimulus and then the response.) Stimulus: Response: 6. Reproduction ________________________ is to produce offspring that are similar to the parents. B. Life Comes From Life _______________________________ ________________________________ - the mistaken idea that living things arise from nonliving sources. _______________________________ ________________________________ - experiment in which a scientist conducts two tests that are identical in every aspect except for one factor _______________________________ ________________________________ - the once factor that a scientist changes in a controlled experiment. (The other name is the ___________________________ _______________________________.) C. Needs of Living Things Living things must satisfy their basic needs for _____________, water, _________________ ____________________, and ______________ _______________________ ____________________. 1. Energy a. ______________________- organisms that can make their own food ex: b. ______________________ - organisms that cannot make their own food (internally) ex: c. All living things need ________________ to survive. d. Living space e. Stable internal conditions _____________________________ us the maintenance of stable internal conditions despite changes in surroundings. II. Discovering Cells A. First Sightings of Cells *The invention of the ____________________ __________________ made it possible for people to discover and learn about cells. ___________________________ - instrument that makes small objects look larger _______________________ ______________________________ - light microscope that has more than one ___________________. 1. Robert Hooke English scientist and inventor who observed the structure of a thin slice of ________ using a _______________ microscope he built himself, 2. Anton von Leeuwenhoek Dutch business man who made his own _________________. He looked a __________ _______________________ and ___________________ ____________________. 3. Matthias Scheiden and Theodor Schwann Scheiden concluded that all ___________________________ are made of cells; Schwan concluded that all ___________________________ are made of cells B. Cell Theory The cell theory states: 1. All living things are composed of _______________________. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and __________________ in all ________________ ___________________________. 3. All __________________ are produced from __________________ _________________. C. How a Light Microscope Works 1. Magnification- the ability to make things look __________________ than they are. a. The lens (or lenses) in a light microscope magnify an object by bending ___________________ that passes through it (them) b. A convex lens is a lens with a _________________________ ______________________. 2. _____________________________ - the ability to clearly distinguish the individual parts of an object. D. Electron Microscopes Electron microscopes use a __________________________________________________ instead of light to examine a specimen. III. Looking Inside Cells *__________________________________ are tiny cell structures that carry our specific functions within the cell. A. __________________ ________________________ - Rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. B.____________________ ________________________- outside boundary of a cell that controls what substances come in and out of a cell. C.Nucleus1. ___________________ ________________________ -protects the nucleus 2. Chromatin- Contains genetic materials that directs the __________________ of a ____________________. 3. Nucleolus-_____________________________________________________________________ D. Organelles in the ______________________________________________ *Cytoplasm is the region between the cell membrane and the ____________________ (Clear, thick, gel-like fluid) * Organelles function to ____________________________ _____________________________, build and transport needed materials, and store and recycle wastes. 1. Mitochondria - _________________ _____________________ structures that produce most of the ___________________________ a cell needs to carry out it’s functions 2. Endoplasmic reticulum 3. Ribosomes 4. Golgi Bodies 5. Chloroplasts 6. ______________________________ 7. Lysosomes E. Bacterial _________________________ F. _____________________________ Cells IV. The Origin of Life A. Earth’s Early Atmosphere B. ________________________ Chemicals C. The First ________________________. Chapter 2 Preview I. Cell Transport A. Passive transport B. ___________________ transport 1. Transport of ________________________ 2. Transport by __________________________ II. Photosynthesis A. The process in which plants use _________________________ to make _______________________. B.