Biology: - WordPress.com
advertisement
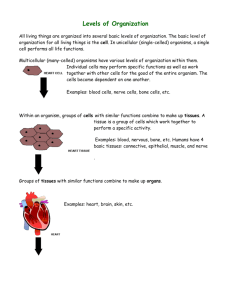
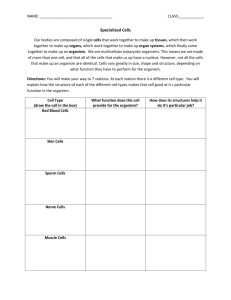
THE SCOPE OF BIOLOGY bi·ol·o·gy [bahy-ol-uh-jee] –noun 1.the science of life or living matter in all its forms and phenomena, esp. with reference to origin, growth, reproduction, structure, and behavior. source: http://dictionary.reference.com/ Biology: The study of life MR STRANGER (life processes/functions/activities) Characteristics of all Living Things 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Highly organized Made of 1 or more cells Use energy Definite form, limited size & life span Grow Responds to changes in environment Ability to reproduce Change over time Biosphere Down To DNA: It’s ALL Biology!! Earth: A collection of varied ecosystems Community: All living organisms of An ecosystem Population: Pelicans: group of A single species Organism: One Brown pelican Brain Organ system: Nervous system Organ: Brain Spinal Cord Tissue: Nervous tissue Cell: Nerve cell Organelle: Nucleus Molecule: DNA Atom: Nitrogen Synthesis • the chemical combining of simple substances to form more complex substances Transport • the process by which substances move into or out of cells or are distributed within cells Respiration (cellular) • the process of releasing energy (ATP) in a complex series of chemical reactions Nutrition Regulation • the process by which • the control and organism takes in food coordination of all and breaks it down so the life activities it can be used for metabolism • involves ingestion, digestion, and egestion Growth • the process by which living organisms increase in size Excretion • the removal of metabolic wastes from an organism Reproduction • the process by which living things produce new organisms of their own kind • not needed for the survival of an individual organism Metabolism: • the sum of all the life functions Homeostasis: • the condition of maintaining a constant internal environment in an organism Give examples when an organism is not at homeostasis? Movement • Locomotion: ability to get from one place to another • Sessile (inability to move)