Thermal Decomposition of Group 2 Carbonates
advertisement
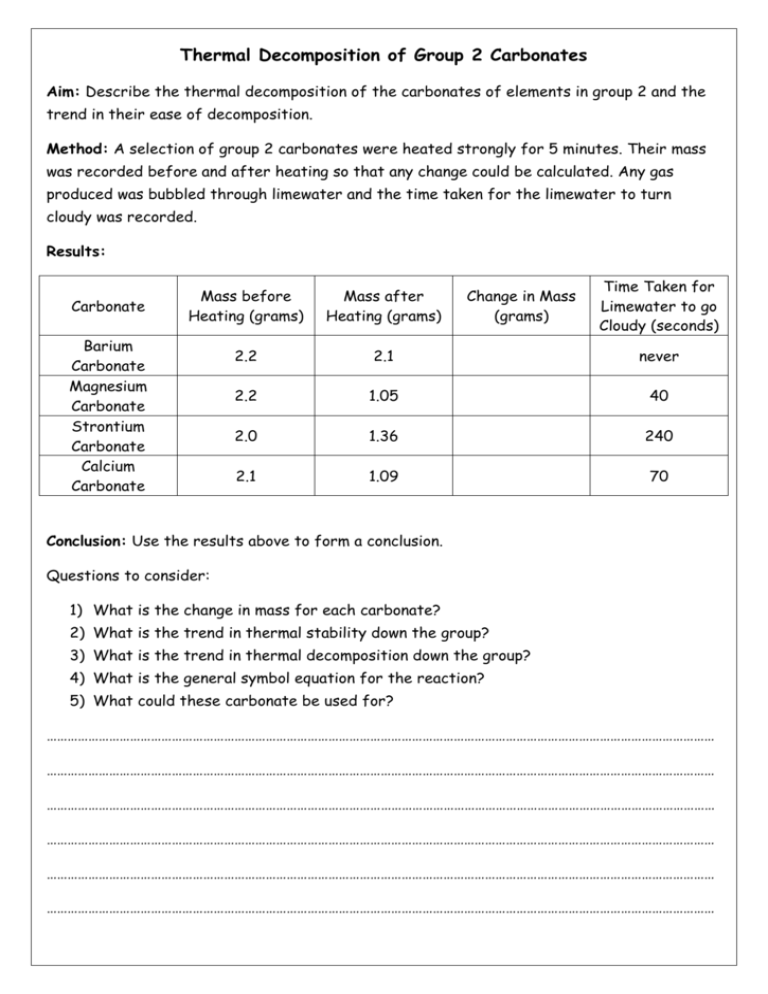
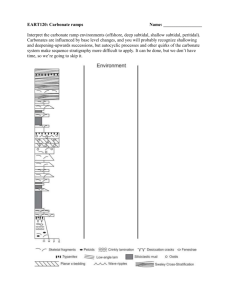
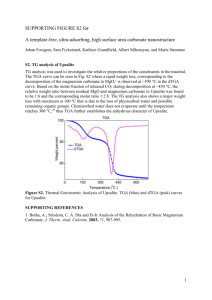
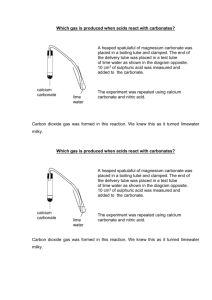
Thermal Decomposition of Group 2 Carbonates Aim: Describe the thermal decomposition of the carbonates of elements in group 2 and the trend in their ease of decomposition. Method: A selection of group 2 carbonates were heated strongly for 5 minutes. Their mass was recorded before and after heating so that any change could be calculated. Any gas produced was bubbled through limewater and the time taken for the limewater to turn cloudy was recorded. Results: Carbonate Mass after Heating (grams) 2.2 2.1 never 2.2 1.05 40 2.0 1.36 240 2.1 1.09 70 Barium Carbonate Magnesium Carbonate Strontium Carbonate Calcium Carbonate Change in Mass (grams) Time Taken for Limewater to go Cloudy (seconds) Mass before Heating (grams) Conclusion: Use the results above to form a conclusion. Questions to consider: 1) What is the change in mass for each carbonate? 2) What is the trend in thermal stability down the group? 3) What is the trend in thermal decomposition down the group? 4) What is the general symbol equation for the reaction? 5) What could these carbonate be used for? ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Reactions of Group 2 Elements Aim: Describe the redox reactions of the Group 2 elements Magnesium Barium with oxygen and with water. Explain the trend in reactivity of Group 2 elements down the group in terms of atomic size, shielding and nuclear attraction. Group 2 Element Observations of the Reaction with Oxygen Observation of the Reaction with Water Magnesium Calcium Strontium Barium Use your observations to state the trend in reactivity as you go down group 2. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………. Explain this trend in terms of atomic size, shielding and nuclear attraction. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………. Write a general symbol equation for the reaction of a group 2 metal with oxygen …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………. Write a general symbol equation for the reaction of a group 2 metal with oxygen …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..………….