Chapter 10 - The Theory of Evolution
advertisement
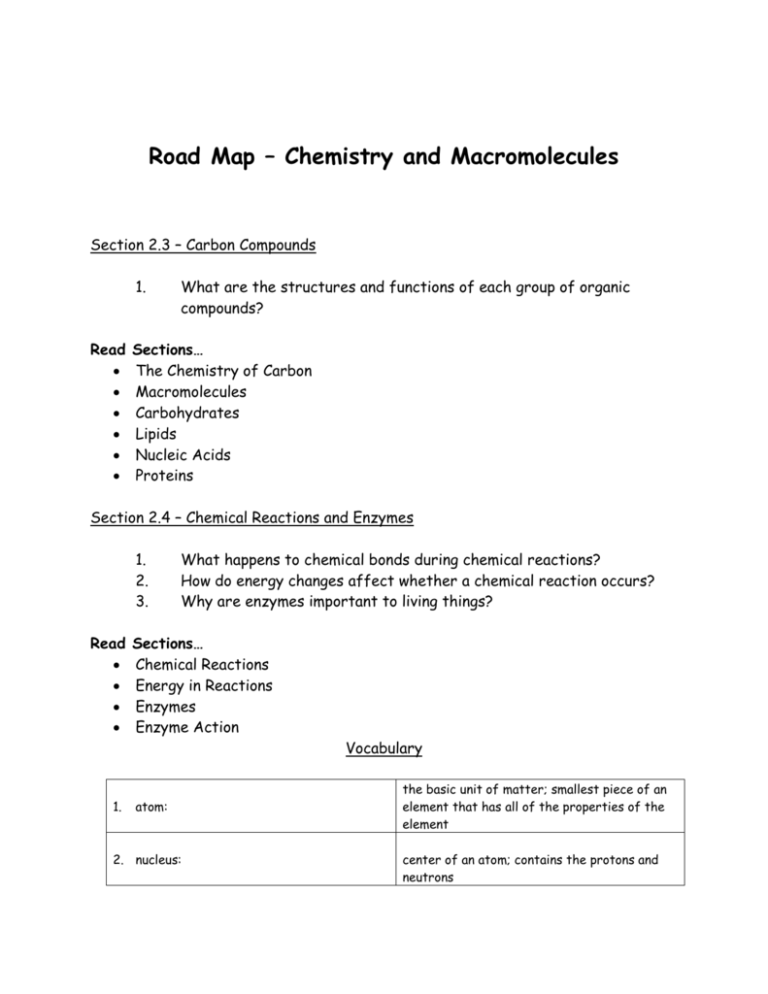
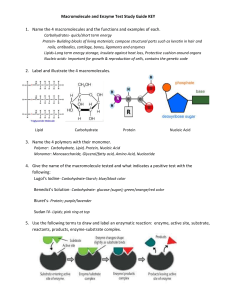
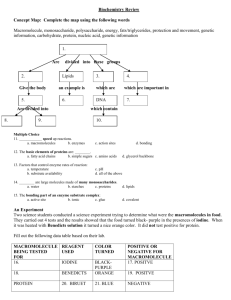
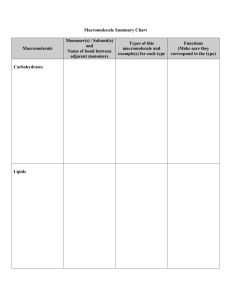
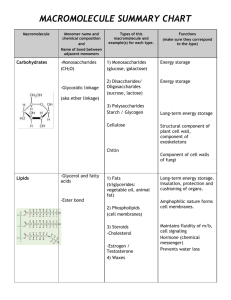
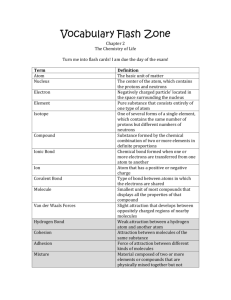
Road Map – Chemistry and Macromolecules Section 2.3 – Carbon Compounds 1. Read What are the structures and functions of each group of organic compounds? Sections… The Chemistry of Carbon Macromolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids Proteins Section 2.4 – Chemical Reactions and Enzymes 1. 2. 3. Read What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? How do energy changes affect whether a chemical reaction occurs? Why are enzymes important to living things? Sections… Chemical Reactions Energy in Reactions Enzymes Enzyme Action Vocabulary 1. atom: 2. nucleus: the basic unit of matter; smallest piece of an element that has all of the properties of the element center of an atom; contains the protons and neutrons 3. electron: negatively charged subatomic particle, orbits the nucleus in shells 4. element: substance consisting of entirely one type of atom 5. compound: substance formed by combining two or more elements 6. ionic bond: bond formed when a positive ion is attracted to a negative ion 7. ion: an atom that has an overall charge because it has gained or lost electrons 8. covalent bond: bond formed when 2 atoms share electrons 9. molecule: smallest unit of most compounds 10. monomer: small unit that can join to other units to form a polymer 11. polymer: large compound formed from the linking together of many monomers 12. carbohydrate: macromolecule made of C, H, and O in a 1:2:1 ratio; major source of energy for the human body 13. monosaccharide: single unit of sugar 14. lipid: macromolecule composed mainly of C, H, and O. Includes fats, oils, and waxes 15. nucleic acid: macromolecule that contains the genetic information of an organism 16. nucleotide: the smallest piece(monomer) of a nucleic acid 17. protein: macromolecule that contains C, H, O, and N. and that makes up most of your body, also needed by the body for growth and repair and to make enzymes 18. amino acid: monomer that can be linked together to form proteins 19. chemical reaction: process that changes one set of chemicals into another 20. reactant: element or compound that enters into a chemical reaction 21. product: element or compound that is produced by a chemical reaction 22. activation energy: energy required to get a chemical reaction started 23. catalyst: substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction protein that acts as a biological catalyst substrate reactant of an enzyme catalyzed reaction 24. enzyme: