Guided Notes- Chapter 6 - Periodic Table
6.1 Organizing the Table
Chemists used the properties of elements to sort them into __________________.
Chlorine, bromine, and iodine have very similar ___________________________________.
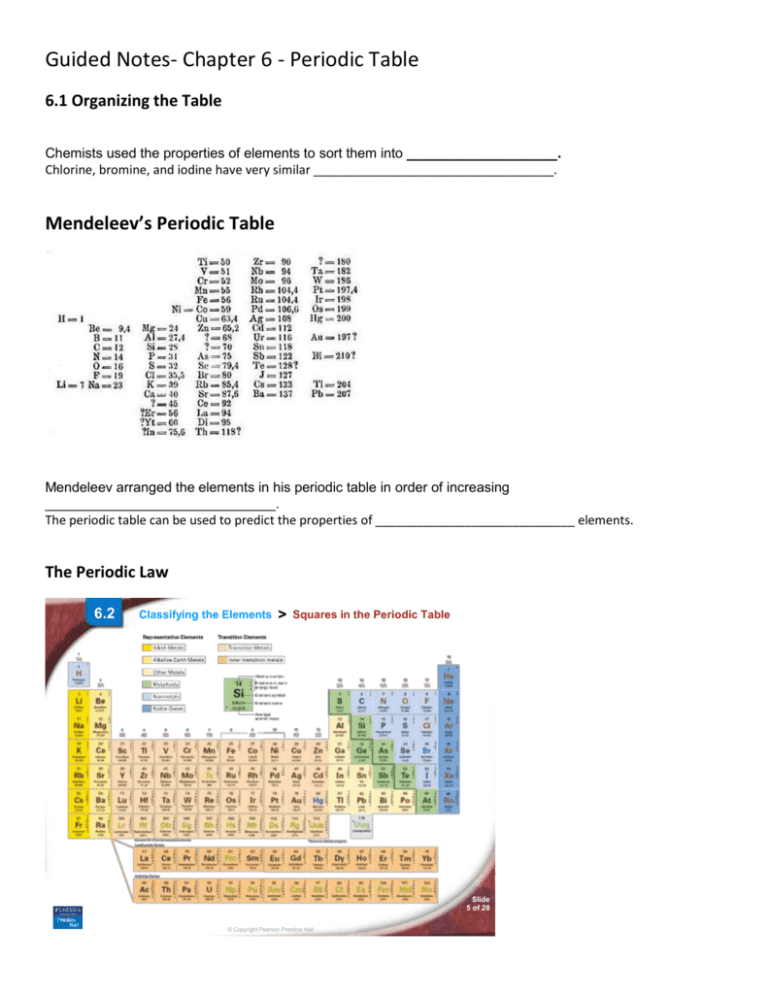
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
Mendeleev arranged the elements in his periodic table in order of increasing
______________________________.
The periodic table can be used to predict the properties of _____________________________ elements.
The Periodic Law
6.2
Classifying the Elements
>
Squares in the Periodic Table
Slide
5 of 28
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged in order of increasing _____________________________.
The ____________________________________ states: When elements are arranged in order of increasing
atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties.
•The properties of the elements within a period ____________________ as you move across a period from left
to right.
Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids
Across a period, the properties of elements become ___________ metallic and more ___________________.
__________________________are good conductors of heat and electric current.
•80% of elements are __________________________.
•Metals have a high __________________________, are ___________________, and are
_____________________.
In general, _______________________________ are poor conductors of ________________ and electric
current.
•Most nonmetals are _______________ at room temperature.
•A few nonmetals are ______________, such as sulfur and phosphorus.
•One nonmetal, bromine, is a __________________________
A _____________________________ generally has properties that are similar to those of metals and
nonmetals.
The behavior of a metalloid can be controlled by __________________________________
Questions:
1.The modern periodic table has elements arranged in order of
a. colors.
b. melting and boiling points.
c. increasing atomic mass.
d. increasing atomic number.
2.Mendeleev arranged the elements in his periodic table in order of increasing
a. atomic number.
b. number of protons.
c. number of electrons.
d. atomic mass
3. Which one of the following is NOT a general property of metals?
A .ductility
b. malleability
c. having a high luster
d. poor conductor of heat and electricity
6.2 Classifying the Elements
The periodic table displays:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Elements can be sorted into __________________, representative elements, transition metals, or
____________________________ based on their electron configurations.
The _____________________ are the elements in Group 18 of the periodic table.
Elements in groups 1,2 ,and 13- 17 are often referred to as ___________________________________________because
they display a wide range of physical and chemical properties.
The s and p sublevels of the highest occupied energy level are ____________ filled.
In atoms of the Group 1 , there is only ________________ electron in the highest occupied energy level.
In atoms of the Group 14 elements below, there are ______________ electrons in the highest occupied energy level.
Groups 3-12
There are two types of transition elements _______________________________________________________. They are
classified based on their electron configurations. In atoms of a transition metal, the highest occupied s sublevel and a
nearby __________sublevel contain electrons.In atoms of an inner transition metal, the highest occupied s sublevel and
6.2
Classifying the Elements
> Transition Elements
Blocks of Elements
Slide
19 of 28
a nearby ____________ sublevel generally contain electrons.
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Questions
1. An alkali metal would have in the highest occupied energy level
a.
an s2 electron.
b.
an s1 electron.
c.
p2 electrons.
d.
p6 electrons.
2. Which of the following information about elements is usually NOT included in a periodic
table?
a.
color
b.
symbol
c.
atomic number
d.
atomic mass
3. Which one of the following is incorrectly labeled?
a. Ne, noble gas
b. Cu, transition metal
c. Ga, transition metal
d. Cl, halogen
4. Transition metals are characterized as being different than representative elements because
they have electrons in which suborbitals?
a. p
b. d
c. s
d. F
6.3 Periodic trends
The __________________________________ is one half of the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same
element when the atoms are joined.
In general, atomic size ________________________________________ from top to bottom within a group and
_____________________________________ from left to right across a period.
Ions
Positive and negative ions form when electrons are __________________________________ between atoms.
Some compounds are composed of particles called ions.
_______________________ is an atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge.
________________________ is an ion with a positive charge.
_______________________ is an ion with a negative charge.
Trends in Ionization Energy
The energy required to remove an electron from an atom is called ____________________________________
The energy required to remove the first electron from an atom is called the __________________ ionization energy.
The energy required to remove an electron from an ion with a 1+ charge is called the_______________________
ionization energy.
First ionization energy tends to ______________________________ from top to bottom within a group and
________________________________ from left to right across a period.
Trends in Ionic Size
During reactions between metals and nonmetals, metal atoms tend to _________________ electrons, and nonmetal
atoms tend to _____________________________ electrons. The transfer has a predictable effect on the size of the ions
that form. __________________are always smaller than the atoms from which they form. _______________________
6.3
Periodic Trends
>
Trends in Ionic Size
Relative Sizes of Some Atoms and Ions
Slide
20 of 31
are always larger than the atoms from which they form.
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
_________________________________________ is the ability of an atom of an element to attract electrons when the
atom is in a compound.
In general, electronegativity values ______________________________ from top to bottom within a group. For
representative elements, the values tend to _________________________ from left to right across a period.
The trends that exist among these properties can be explained by variations in atomic structure
Questions
1.
Which of the following sequences is correct for atomic size?
a. Mg > Al > S
b. Li > Na > K
c. F > N > B
d. F > Cl > Br
2. Metals tend to
a.
b.
c.
d.
gain electrons to form cations.
gain electrons to form anions.
lose electrons to form anions.
lose electrons to form cations.
3.Which of the following is the most electronegative?
a. Cl
b. Se
c. Na
d. I