Objectives - Goodsamim.com
advertisement

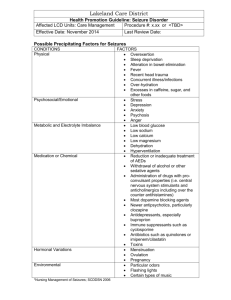
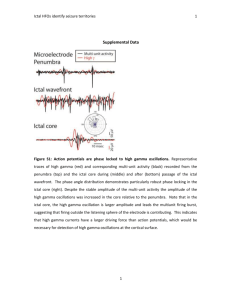
September 18, 2012 Academic Half Day Objectives: 1. Acute Headache in Adults: a. Distinguish between primary and secondary headaches, and list several diagnoses in each category. b. Describe the red flags associated with acute headache and the differential diagnosis and diagnostic modalities required to evaluate them. c. Know the diagnostic criteria for migraine headache. d. Know the illness scripts (stereotypical presentation) for the following conditions that cause headache: subarachnoid hemorrhage, migraine with and without aura, intracranial hypertension headache, temporal arteritis, meningitis, and post-lumbar headache. 2. Evaluation of the First Seizure: a. Define a generalized seizure, partial seizure, and a simple partial seizure versus a complex partial seizure. b. List at least 10 causes of seizures (table 1) c. Describe some important historical features that are important to tease out in the history to determine whether a seizure occurred and its precipitating cause. d. What other diagnoses are in the differential of a seizure? e. When is neuroimaging required in the evaluation of a new onset seizure? When is a lumbar puncture indicated? f. What other diagnostic tests are often ordered in the evaluation of a first seizure? g. When is antiepileptic therapy recommended in the treatment of a first seizure? 3. Neutropenic Fever a. What are three factors in a neutropenic patient related to developing severe infections? b. What is the definition of neutropenic fever? c. When should empiric antibiotics be started in neutropenic fever? d. What are the qualitative defects that can occur with neutrophils when patients have hematological malignancies? e. What should the initial evaluation of a neutropenic patient involve? f. What type of coverage should be started in a neutropenic patient that remains febrile despite broad spectrum antibiotic coverage for after 4-7 days?