Set2
advertisement

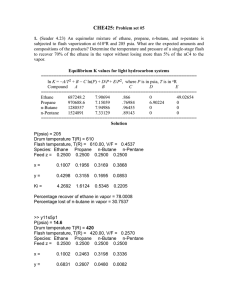
CHE425: Problem set #2 1. An experiment can be performed to determine the mass transfer coefficient by flowing pure water through a tube constructed of solid benzoic acid. The saturated concentration of benzoic acid is 2.0×10-2 g/cm3. The water velocity is 15 cm/s and the mass of the tube is reduced by 0.92 g after 3 hr. Determine the mass transfer coefficient for the dissolution of benzoic acid in water if the tube diameter is 1.0 cm and the tube length is 20 cm. 2. Liquid water at 25oC is to be aerated in a bubble column where finely air bubbles with diameter dB of 0.4 mm are injected cocurrently with the liquid. The interfacial contact area, a, between air and water can be calculated from the expression a = 6ε/dB, where ε is the volume fraction of the injected air. The bubble column is 2.5 m high with a superficial liquid velocity of 0.2 m/s. The oxygen concentration of the inlet water is 0.12×10-4 kmol/m3. The saturated oxygen concentration is 2.67×10-4 kmol/m3. Determine the oxygen concentration of the outlet water if the mass transfer coefficient for the transfer of oxygen from the liquid interface to the bulk water is 5.8×10-6 m/s. The diffusivity of oxygen in water is 2.42×10-9 m2/s. The volume fraction of the injected air is 0.2. Plot the ratio of the oxygen concentration in the outlet water to the saturated oxygen concentration as a function of bubble column height from 1 to 50 m. The plot must have a title “Plotted by your name” using Matlab. (3)1 What is the dew point temperature of a vapor mixture of 50 mol % of n-pentane and 50 mol % of n-butane at 200 psia? At what temperature is the vapor mixture completely condensed if the pressure is maintained constant at 200 psia? Table 3 Equilibrium K values for light hydrocarbon systems ============================================================= (1) ln K = A/T2 + B C ln(P) + D/P2 Compound A B C D Form ============================================================= n-Butane 1280557 7.94986 .96455 0 (1) n-Pentane 1524891 7.33129 .89143 0 (1) ============================================================= (4)1 A vessel initially containing propane at 30oC is connected to a nitrogen cylinder, and the pressure is increased to 300 psia. Assuming that the nitrogen is insoluble in liquid propane, what is the mol fraction of propane in the vapor phase? List all assumptions. The following data are available: the vapor pressure of propane at 30oC is 10.5 atm. (5)1 A vapor containing 50 mol % propane and 50 mol % n-butane is held at 100oF and the pressure is increased until the dew point is reached. What is the dew point pressure? Table 6 Equilibrium K values for light hydrocarbon systems ============================================================= (1) ln K = A/T2 + B C ln(P) + D/P2 (2) ln K = A/T2 + B C ln(P) + D/P , where P is in psia, T is in oR Compound A B C D Form ============================================================= Propane 970688.6 7.15059 .76984 6.90224 (2) n-Butane 1280557 7.94986 .96455 0 (1) ============================================================= (6)1 Find the pressure and the vapor liquid compositions when an equimolar mixture of propane and n-butane is 50% condensed at 100oF. (7)1 One mol of n-butane and 1 mol of n-pentane are charged into a container. The container is heated to 180oF where the pressure read 100 psia. Determine the quantities and compositions of the phases in the container. Use the K values from Table 1. Table 1 Equilibrium K values for light hydrocarbon systems ============================================================= (1) ln K = A/T2 + B C ln(P) + D/P2 (2) ln K = A/T2 + B C ln(P) + D/P Compound A B C D Form ============================================================= n-Butane 1280557 7.94986 .96455 0 (1) n-Pentane 1524891 7.33129 .89143 0 (1) ======================================================== (8)1 For the design of an absorption refrigeration system using propane as the working fluid, we require equilibrium data for mixtures of propane and a nonvolatile hydrocarbon solvent. Ideal liquid solutions are expected and we need propane partial pressure (total pressure, P) vs. mol fraction of propane in the liquid solution, xp. Using Matlab prepare a plot of P vs. xp for a temperature of 200oF. Cover the range 0.1 < xp 0.5. The plot must have a title “Plotted by your name”. 1 Kyle, B.G., Chemical and Process Thermodynamics, Prentice Hall, 1999