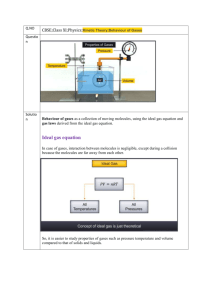
Gases Notes All gases share some physical properties: These
advertisement

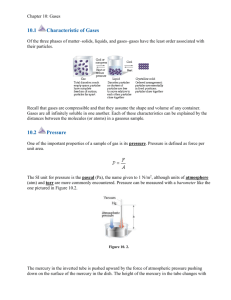
Gases Notes All gases share some physical properties: These properties combine to describe the behavior of gases using the “gas laws” Pressure Pressure is the amount of force per given amount of area (P=F/area) ________________ forces exert greater ________________________ When the area over which the pressure is exerted is __________________, the pressure is _________________ Why is there more pressure on you the deeper you move in a body of water? Why is it harder to breathe when you’re up in a mountain? Atmospheric pressure The pressure exerted by the _____________________ on the earth ______________________________ as you move up About _____________________+ (pounds per square inch) at sea level Standard pressure “normal” atmospheric pressure at sea level Standard Pressure: Barometer Manometer Kinetic Molecular Theory A set of ideas (__________________) used to describe and explain the ___________________ of gases Any gas that behaves exactly in this manner is called an “____________ ______________” There are not any “ideal gases” in real life. _____________ ______________ behave much like “ideal” gases unless they are under high ____________ and ________________. Point 1 Gases are composed of tiny particles called _______________ Molecules are so far apart that gases are mostly _________ _______________ Because of this, gases can be easily compressed and mixed Point 2 Gas molecules posses _______________ ________________ Gas molecules are in Pressure is… Point 3 Collisions between gas molecules and each other or the container are ___________________ No ______________ ______________ is changed into another form of energy (like heat) The pressure of an enclosed gas will _____________ change unless its temperature or volume _____________ Point 4 Molecules of a gas are not They move ____________________________ of each other Point 5 Individual molecules of a gas are moving at different speeds because they have different ___________ ________ The average kinetic energy (__________) is ____________ ____________________ to the temperature of a gas Boyles Law Pressure and volume are inversely related at a constant temperature and number of moles Conceptual: Relationship: Temperature Absolute temperature is measured in _________________ (K) 0 K is K = °C + 273 °C = K – 273 Standard temperature: 273 K Charles’ Law Volume and temperature are ______________ related when ___________ and number of moles is constant Conceptual: Relationship: Gay-Lussac’s Law Conceptual: Combined Gas Law A combination of Boyle’s, Charles’, and Gay-Lussac’s Laws, where P1V 1 P 2V 2 T1 T2 Avogadros Hypothesis Equal volumes of gases contain an equal ______________ of __________ (n) when compared at the same _____________ and ____________ Molar volume of any gas: If P, V, and T are the same, then n is the same (constant) R= R= R= PV nR or, PV nRT T What is the volume of 0.2 moles of a gas at STP? (measure pressure in kPa) Molar mass When the mass of an ________________ mass is given, you can solve for _____________ ___________ Number of moles (n) = mass (m)/Molar mass (Mm) Substituted into the ideal gas law: Density Since… n= Denisty The ideal gas law can be written so solve for density: Dalton’s Law of Partial pressure • The total ___________ of a mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressures of the ______________ gases • PT = Effusion • Effusion is the ___________ of gas molecules through an extremely tiny opening into a region of lower pressure • • Diffusion • Diffusion is the tendency of molecules to move toward areas of lower concentration until the concentration is uniform throughout the system • Graham’s Law • The rate of effusion (or diffusion) of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass (at constant T and P). • .